Market Overview
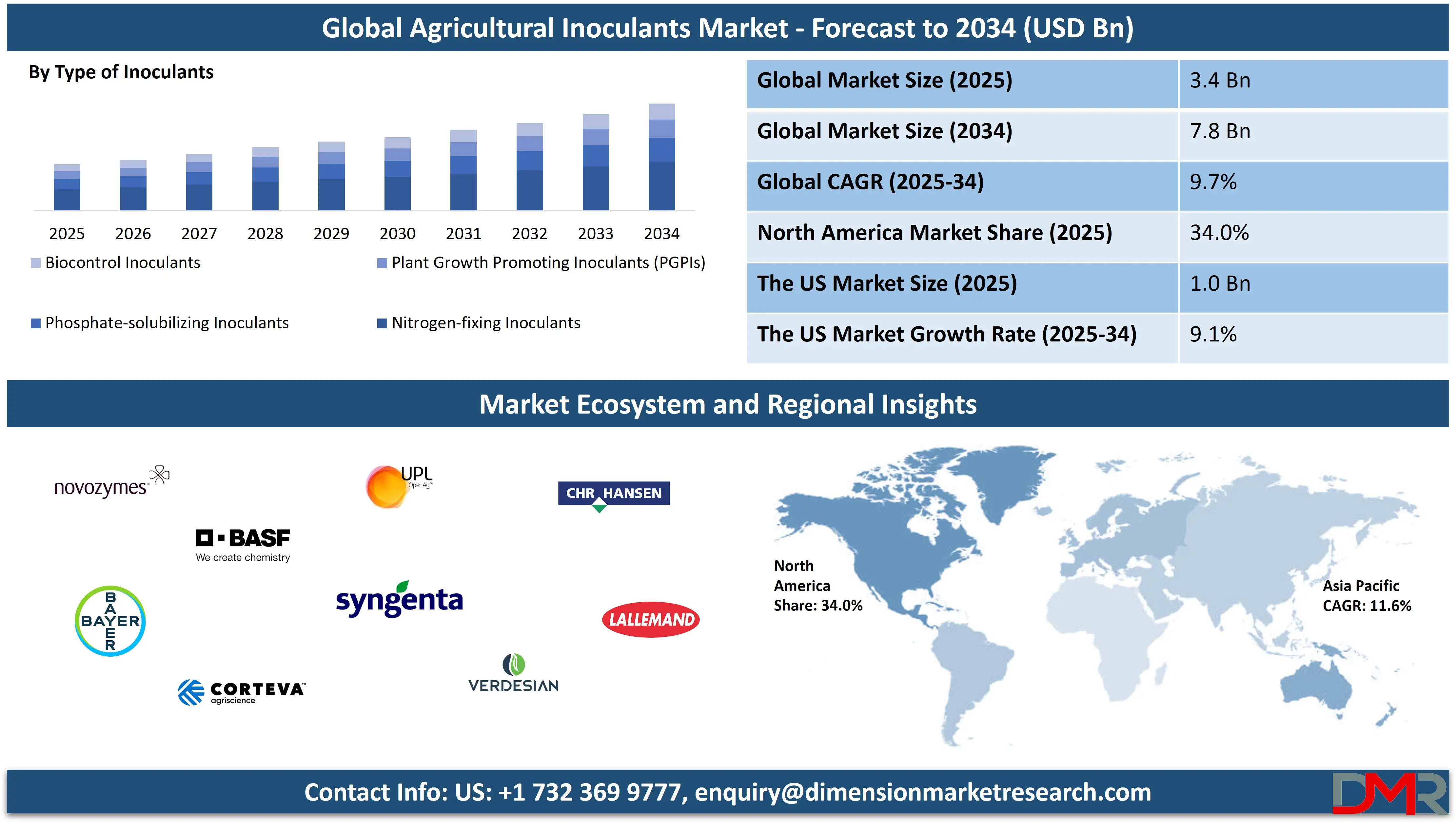
The global agricultural inoculants market is projected to reach USD 3.4 billion in 2025 and grow to USD 7.8 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 9.7%. This growth is driven by the rising adoption of biofertilizers, microbial inoculants, and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria across sustainable and precision farming practices.
Agricultural inoculants are bio-based formulations containing beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, or algae that are applied to soil, seeds, or plant surfaces to improve plant health and productivity. These microorganisms work symbiotically with plants, enhancing nutrient uptake, nitrogen fixation, and disease resistance. Unlike chemical fertilizers or pesticides, inoculants function as natural growth promoters and soil health enhancers, fostering sustainable Agriculture practices.
They play a crucial role in restoring soil biodiversity, improving crop yields, and reducing the dependency on synthetic agrochemicals. Depending on their function, inoculants can be classified as nitrogen-fixing agents, phosphate-solubilizing microbes, or plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Their application methods vary from seed coating to foliar sprays and soil amendments, tailored to different crop types and farming systems. With growing awareness around regenerative agriculture and eco-friendly farming, the adoption of microbial inoculants is becoming more widespread among both large-scale and smallholder farmers.
The global agricultural inoculants market is witnessing robust growth, driven by the rising demand for sustainable farming inputs and the need to enhance crop resilience under climate stress. This market encompasses a diverse range of biofertilizers, microbial consortia, and biostimulants that are tailored for use across various agro-climatic zones and crop categories. North America and Europe lead in terms of adoption, supported by favorable regulatory frameworks and widespread acceptance of organic farming methods, while Asia-Pacific and Latin America represent high-growth potential regions due to expanding agrarian economies and government initiatives promoting bio-inputs.
Technological advancements in microbial formulation, such as encapsulation and precision delivery systems, are further accelerating market development. Moreover, the integration of inoculants with precision farming tools, machine learning, and digital farming platforms is creating new value propositions for growers. As global food security and soil regeneration become critical priorities, agricultural inoculants are emerging as a key component of climate-smart farming and long-term productivity strategies.
Together, the concept and global outlook of agricultural inoculants reflect a transformative shift in how food systems are being reimagined through microbiological innovation and ecological farming methods. These biologically active inputs bridge the gap between traditional organic practices and modern agricultural science, offering a viable solution to issues such as soil degradation, nutrient imbalance, and declining crop productivity. As farmers globally look for resilient and cost-effective solutions that align with sustainable development goals, the synergistic role of microbial inoculants in enhancing soil fertility and crop health becomes relevant.
Their integration into holistic crop management strategies supports eco-friendly food production. It contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving biodiversity, reinforcing their critical role in the future of global Agriculture. Interestingly, sustainability trends across industries—from biodegradable materials to Eco-Friendly Straws—mirror the same environmental consciousness that is driving inoculant adoption in farming.
The US Agricultural Inoculants Market
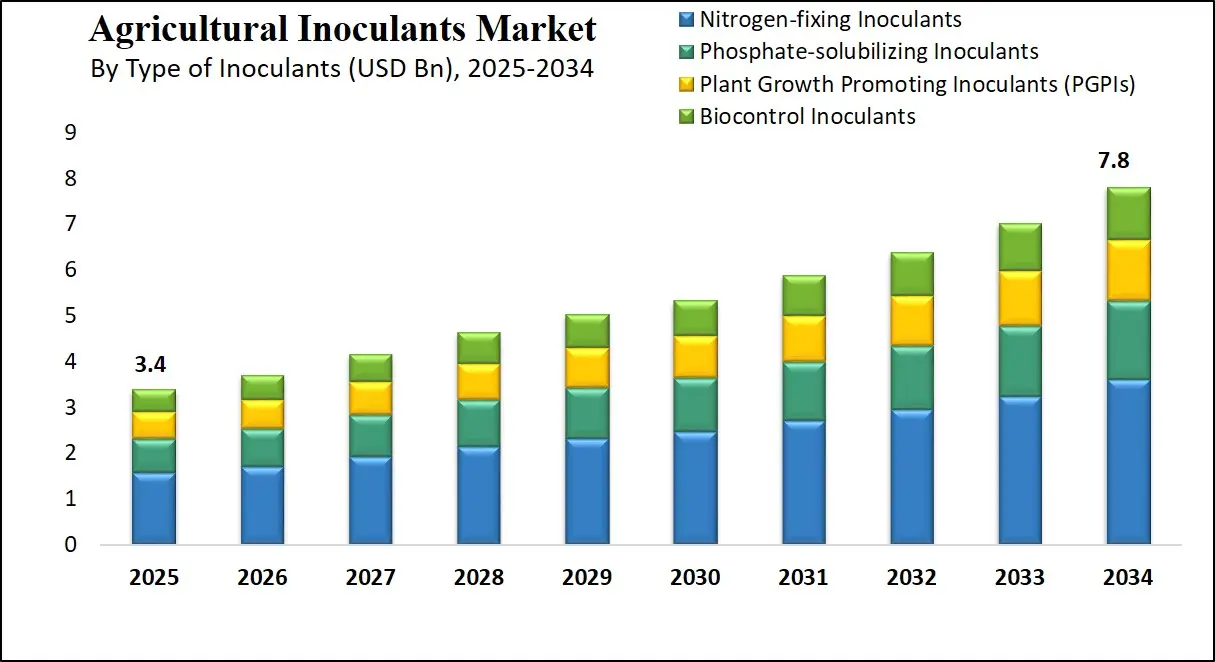
The U.S. Agricultural Inoculants Market size is projected to be valued at USD 1.0 billion in 2025. It is further expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period, holding USD 2.1 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 9.1%.
The U.S. agricultural inoculants market is undergoing significant transformation as farmers and agribusinesses shift toward more sustainable and regenerative farming practices. With growing concerns around soil degradation, nutrient loss, and chemical overuse, microbial inoculants are being adopted for their ability to enhance plant nutrition naturally.
These biological inputs, particularly nitrogen-fixing bacteria and phosphate-solubilizing microbes, are gaining popularity in the large-scale production of crops like soybeans, corn, and wheat. The Midwest and Pacific regions have emerged as key hubs for adoption, where conservation tillage and cover cropping are widely practiced. The use of microbial seed treatments and rhizobial inoculants is expanding due to their role in improving nutrient efficiency and root development, especially under climate stress conditions such as drought or soil salinity.
Policy support and educational outreach programs are further strengthening the inoculant ecosystem across the United States. Government initiatives promoting soil health and sustainable agriculture, combined with university-led extension services, have improved awareness and accessibility of biological & agricultural biologicals inputs.
Technological innovation in liquid and encapsulated formulations has made microbial inoculants more adaptable to various application methods, including seed coating and in-furrow treatment. Additionally, the growing emphasis on organic certification and carbon farming is encouraging the use of eco-friendly crop inputs. As the U.S. farming community continues to focus on long-term soil productivity and reduced agrochemical dependency, agricultural inoculants are positioned as a key solution within integrated crop management systems.
Europe Agricultural Inoculants Market
The Europe agricultural inoculants market is estimated to reach approximately USD 800 million in 2025. This substantial share is driven by the region's strong emphasis on environmental sustainability, organic agriculture, and regulatory restrictions on chemical fertilizer usage. Countries like France, Germany, Italy, and Spain are at the forefront of adopting microbial-based solutions such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphate-solubilizing inoculants, and biocontrol agents.
The EU’s Farm to Fork strategy, which aims to reduce the use of synthetic agrochemicals and promote biodiversity, has significantly boosted the demand for natural crop inputs, including biofertilizers and plant growth-promoting microorganisms. Moreover, Europe has a robust network of agronomic research institutions and bio-based input manufacturers that are actively involved in developing advanced, multi-functional inoculant formulations tailored to specific climatic and soil conditions.
The projected CAGR of 8.9% from 2025 to 2034 further underscores the region’s momentum in transitioning to regenerative and eco-friendly farming systems. Increased consumer demand for organic produce, integrated with subsidies and financial incentives for sustainable farming practices, is expected to drive consistent growth across the inoculants sector. Additionally, Europe’s high adoption of precision farming technologies allows for better integration of microbial inputs through targeted application techniques such as seed treatment and drip irrigation.
Collaborations between agricultural cooperatives, technology providers, and biotech firms are also facilitating the large-scale dissemination of knowledge and access to inoculant products, particularly among mid-sized and large farms. As climate resilience and soil restoration become top priorities, agricultural inoculants are set to play a central role in Europe’s evolving agri-food value chain.
Japan Agricultural Inoculants Market
Japan’s agricultural inoculants market is projected to reach around USD 140 million in 2025. While smaller in absolute size compared to regions like North America and Europe, Japan’s market is characterized by its high-tech, quality-focused approach to agriculture. The country places a strong emphasis on residue-free produce, soil regeneration, and eco-conscious farming, which aligns well with the use of microbial inoculants such as mycorrhizal fungi, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and biocontrol agents.
Japan’s farmers, particularly in fruit, vegetable, and rice cultivation, are integrating these inputs to enhance nutrient uptake, suppress soil pathogens, and improve crop resilience, without growing the chemical load on their fields. Local R&D initiatives supported by academic institutions and agri-tech companies also play a key role in advancing region-specific microbial solutions that cater to Japan’s diverse soil types and controlled-environment farming systems.
With a forecasted CAGR of 7.6% from 2025 to 2034, Japan’s inoculants market is set for steady growth, fueled by rising interest in organic farming and the government’s support for sustainable agricultural development under programs like the Green Food System Strategy. As arable land becomes limited, Japanese farmers are focusing on maximizing productivity through soil healthcare quality management and biological inputs.
In addition, the adoption of smart farming technologies, such as automated fertigation and sensor-based crop monitoring, is enabling more precise application of microbial products, making inoculants more efficient and easier to integrate. While scale may be smaller, the country’s commitment to high-quality production, innovation in microbial formulation, and environmental stewardship is positioning Japan as a niche yet influential player in the global agricultural inoculants landscape.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Key Takeaways
- Market Value: The global agricultural inoculants market size is expected to reach a value of USD 7.8 billion by 2034 from a base value of USD 3.4 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of 9.7%.
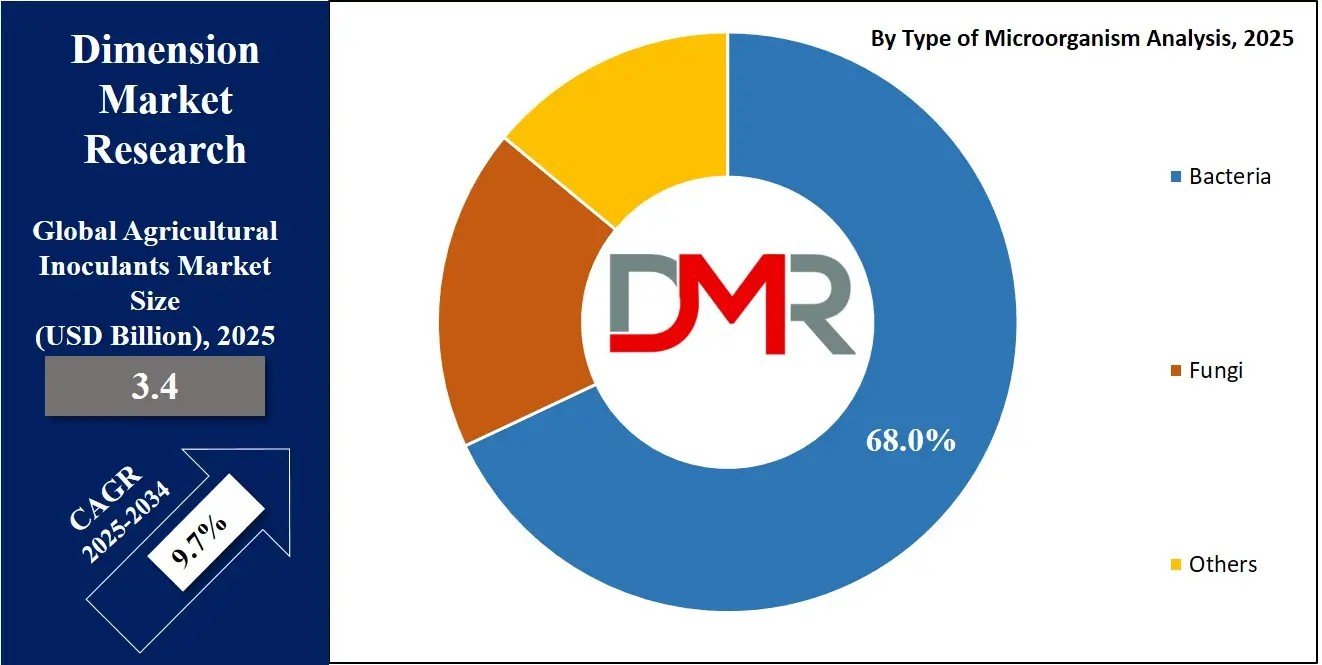
- By Type of Microorganism Segment Analysis: Bacteria are anticipated to dominate the type of microorganism segment, capturing 68.0% of the total market share in 2025.
- By Type of Inoculant Segment Analysis: Nitrogen-fixing Inoculants are poised to consolidate their dominance in the type of inoculant segment, capturing 46.0% of the total market share in 2025.
- By Crop Type Segment Analysis: Cereals & Grains are expected to maintain their dominance in the crop type segment, capturing 40.0% of the total market share in 2025.
- By Formulation Segment Analysis: Solid formulations will lead in the formulation segment, capturing 58.0% of the market share in 2025.
- By Function Segment Analysis: Soil Fertility Enhancement will dominate the function segment, capturing 52.0% of the market share in 2025.
- By Mode of Application Segment Analysis: Seed Inoculation will lead the mode of application segment, capturing 55.0% of the market share in 2025.
- Regional Analysis: North America is anticipated to lead the global agricultural inoculants market landscape with 34.0% of total global market revenue in 2025.
- Key Players: Some key players in the global agricultural inoculants market are Novozymes, BASF SE, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, UPL Limited, Syngenta AG, Verdesian Life Sciences, and Chr. Hansen Holding A/S, Lallemand Inc., Rizobacter Argentina S.A., T. Stanes & Company Limited, AgriLife, BioWorks Inc., KALO Inc., and Other Key Players.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Use Cases
- Enhancing Legume Productivity through Rhizobial Inoculants: In countries with extensive legume cultivation, such as Brazil, India, and the U.S., rhizobial inoculants are widely used to boost biological nitrogen fixation. These microbial inputs colonize legume roots and form nodules that convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants. This natural process significantly reduces the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, lowers input costs, and improves overall soil fertility. For example, soybean farmers across Brazil have reported yield increases and improved plant vigor by using specific strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum, a species tailored to the regional soil and climate. The use of these plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria contributes to long-term soil health while supporting sustainable agriculture practices.
- Improving Phosphorus Availability in Cereal Crops: Phosphate-solubilizing inoculants are applied in maize and wheat production to address phosphorus fixation issues, especially in calcareous and acidic soils. These biofertilizers work by secreting organic acids that mobilize bound phosphates in the soil, making them more available for root absorption. In India and sub-Saharan Africa, where phosphate rock application is limited or expensive, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) such as Bacillus megaterium and Pseudomonas fluorescens have been adopted to enhance early plant growth and root development. This leads to improved nutrient uptake and better crop yield optimization, especially in smallholder and low-input farming systems. The integration of PSBs with traditional fertilization methods is helping build resilient cropping systems in nutrient-poor regions.
- Biocontrol Applications in Vegetable and Fruit Production: In horticulture, particularly in Europe and North America, agricultural inoculants with biocontrol properties are being deployed to manage soil-borne pathogens and improve plant immunity. Fungal inoculants like Trichoderma harzianum and bacterial agents such as Bacillus subtilis are used in tomato, pepper, and strawberry cultivation to suppress diseases like Fusarium wilt, root rot, and powdery mildew. These microbial formulations act by competing with harmful pathogens, producing antibiotics, or inducing systemic resistance in host plants. As a part of integrated pest management (IPM), such biological inoculants not only reduce the need for synthetic fungicides but also support compliance with organic farming standards and consumer demand for chemical-free produce.
- Drought Tolerance and Soil Resilience in Arid Farming Regions: In arid and semi-arid zones such as Australia, the Middle East, and parts of the western United States, microbial inoculants are used to combat abiotic stress factors like drought and salinity. Certain strains of mycorrhizal fungi and Azospirillum species are introduced into soil to improve root architecture, enhance water retention, and increase tolerance to osmotic stress. These microbes establish symbiotic relationships with plant roots, allowing crops to access deeper soil moisture and nutrients during prolonged dry periods. Farmers growing sorghum, millet, and cotton have reported significant resilience improvements using such inoculants. These applications are central to climate-smart agriculture, as they promote efficient water use and long-term soil structure restoration in degraded landscapes.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Agricultural Inoculants Market
- Accelerated Microbial Strain Discovery: AI-driven bioinformatics and machine learning are streamlining the identification of new beneficial microbial strains, such as rhizobia, mycorrhizae, and nitrogen-fixing bacteria, for use as inoculants. By analyzing large genomic and environmental datasets, AI helps pinpoint the most effective microbial species for crop-specific conditions, significantly speeding up discovery and reducing lab-based trial-and-error.
- Precision Optimization of Formulation and Fermentation: Advanced AI tools enable dynamic adjustment of fermentation parameters, like pH, temperature, nutrient supply, and oxygen levels, during production. This leads to consistently high yields, improved viability of microbial cultures, and better shelf stability. Real-time monitoring and AI feedback loops result in robust inoculants that perform reliably under diverse agricultural conditions.
- Site-Specific Application and Field Performance: AI-powered predictive models leverage soil quality data, weather forecasts, and crop health indicators to recommend optimal inoculant types, dosages, and timing. Deployment via precision equipment, guided by AI, is tailored to field zones, maximizing microbial establishment and effectiveness. As a result, farmers see enhanced crop yields and better resource utilization.
- Quality Control and Shelf-life Assurance: Inoculant manufacturers are deploying AI-operated sensor arrays and computer vision systems to monitor live microbial count, moisture, and contamination during production and storage. Machine learning algorithms predict shelf-life trends and alert when formulation integrity is compromised. This reduces waste, ensures product consistency, and strengthens regulatory compliance.
- Feedback-Driven Product Innovation: AI systems integrate field data, such as yield response curves, plant health measurements, and environmental variables, to optimize future inoculant blends. Manufacturers can track performance across seasons and geographies, enabling data-backed R&D for next-generation products tailored to regional challenges and climate conditions.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Stats & Facts
-
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO / FAOSTAT)
- FAOSTAT is the world’s largest agrifood systems database, covering production, trade, land use, inputs, and sustainability for over 245 countries since 1961.
- It receives approximately 2.4 million visits annually from policymakers, researchers, and industry stakeholders.
-
EU Organic Farming (European Commission Directorate‑General for Agriculture & Rural Development)
- Between 2012 and 2020, EU organic farmland increased by over 50%, with an average annual growth rate of 5.7%.
- In 2020, 9.1% of EU agricultural land was managed organically.
- France, Spain, Italy, and Germany accounted for 59% of EU organic land in 2020.
- In 2020, organic arable farms spent 45–90% less on fertilizers and 75–100% less on plant protection products than conventional farms.
-
EU Farm to Fork Strategy (European Commission)
- Target to reduce nutrient losses by at least 50% and reduce fertilizer use by 20% by 2030.
- Target to achieve 25% of EU agricultural land under organic farming by 2030.
- Target to cut pesticide use and risk by 50%, including hazardous pesticides, by 2030.
- From 2018 to 2022, the use and risk of chemical pesticides in the EU dropped by 46%, and “more hazardous” pesticides dropped by 25%.
- From 2021 to 2022, EU chemical pesticide use dropped by 12% and hazardous pesticide use by 4%.
- In 2018 and 2019, the EU achieved pesticide use/risk reductions of 8% and 5%, respectively, compared to the 2015–2017 baseline.
- In 2019, hazardous pesticide use was reduced by 12% compared to the same baseline.
-
EU Agricultural and Environmental Overview (OECD / Eurostat)
- The EU has approximately 10 million farms cultivating 156.7 million hectares, about 38% of the total land area.
- 64% of EU farms are smaller than 5 hectares.
- In 2019, EU agriculture generated EUR 181.5 billion in value added, accounting for roughly 1.3% of GDP.
- That same year, EU output included 299.3 million tonnes of cereals, 158.2 million tonnes of milk, and 43.5 million tonnes of meat.
- In 2018, mineral fertilizer use in the EU totaled 11.3 million tonnes of nitrogen and phosphorus.
- The EU nitrogen balance improved from 51 kg N/ha/year (2004–06) to 47 kg N/ha/year (2013–15).
-
Regional Fertilizer Use (FAO Statistical Yearbook)
- In 2022, Asia accounted for 55% of global inorganic fertilizer use; the Americas 28%; Europe 11%; Africa 4%; Oceania 2%.
- Between 2000 and 2022, fertilizer usage increased in Asia (+54%), the Americas (+55%), Africa (+74%), and Oceania (+37%), while it decreased in Europe by 10%.
- In Europe, fertilizer composition was roughly 66% nitrogen, 16–25% phosphorus, and 19% potassium.
- Between 2000 and 2022, potassium use in Europe declined by 22% and nitrogen use by 1%.
-
India’s Soil Health Card Scheme (Government of India)
- Launched in February 2015 to provide crop-specific fertilizer guidance to around 14 crore farmers.
- By February 2016, over 1.12 crore soil health cards had been distributed and 81 lakh samples tested.
- By mid-May 2017, 7.25 crore soil health cards had been issued to farmers.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Market Dynamics
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Driving Factors
Rising Demand for Sustainable Farming Practices
As global agriculture pivots toward sustainability, there is a growing emphasis on reducing chemical fertilizer dependency. Farmers and agribusinesses are adopting microbial inoculants as eco-friendly alternatives that support organic farming, restore the soil microbiome, and promote regenerative cultivation. These biological inputs enhance nutrient efficiency, improve root development, and contribute to carbon-neutral farming, making them integral to long-term soil and crop health strategies.
Government Incentives and Regulatory Support
Many countries are offering financial and policy-based incentives to promote the use of biofertilizers and biological crop enhancers. Agencies like the USDA and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) are fast-tracking regulatory approvals for microbial-based products. Subsidies, extension services, and awareness programs under schemes such as India’s Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana or Brazil’s Low Carbon Agriculture Plan (ABC) are making agricultural inoculants more accessible and trusted among farmers.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Restraints
Lack of Awareness and Technical Knowledge among Farmers
Despite growing adoption, a significant portion of the farming population, especially in developing regions, lacks awareness of how to effectively use microbial inoculants. Knowledge gaps regarding dosage, timing, compatibility with conventional inputs, and storage conditions limit the full potential of these bio-based products. This barrier also affects adoption in traditional farming systems where chemical reliance remains high.
Variable Performance under Field Conditions
The effectiveness of agricultural inoculants often depends on environmental variables such as soil pH, temperature, and moisture. Inconsistent field performance due to poor soil-rhizosphere compatibility or microbial survival rates can deter long-term use. The lack of standardized field trials and variable results across geographies has made some farmers skeptical of the return on investment, particularly in monoculture or industrial farming settings.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Opportunities
Integration with Precision Agriculture Technologies
The convergence of biological crop inputs with precision farming and data-driven agriculture presents a huge opportunity. By combining soil sensors, drone-based spraying, and AI-driven nutrient mapping with microbial seed treatments, farmers can target inoculant application with greater accuracy and efficiency. This approach enhances the performance of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) while reducing waste and improving environmental outcomes.
Expansion in Emerging Economies with Large Agrarian Bases
Countries like India, Indonesia, Nigeria, and Vietnam offer untapped potential for bioinoculant deployment, given their large farming populations and growing awareness of sustainable practices. Local production of low-cost, region-specific microbial formulations and partnerships with agricultural cooperatives or NGOs can accelerate penetration in these high-potential markets. Support from international climate finance initiatives further boosts market accessibility in these regions.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Trends
Rise of Multi-Strain and Consortia-Based Inoculants
There’s a growing trend toward using multi-strain microbial consortia that combine bacteria, fungi, and other beneficial microbes to deliver broader agronomic benefits. These formulations target multiple functions simultaneously, such as nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, and disease suppression, enhancing plant resilience and productivity. This evolution is helping move the market beyond single-function inoculants to more robust and adaptable products.
Commercialization of Shelf-Stable and Liquid Formulations
Innovations in microbial encapsulation, fermentation, and liquid formulation technologies are making bioinoculants more stable and easier to apply. Long shelf-life and compatibility with modern delivery systems like drip irrigation or foliar sprays are making these products attractive for both smallholders and commercial farms. These advancements are also solving traditional logistical challenges associated with the storage and transportation of live microbes.
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Type of Microorganism Analysis
In the type of microorganism segment of the agricultural inoculants market, bacteria are expected to maintain a dominant position, accounting for approximately 68.0% of the total market share in 2025. This dominance is largely due to their proven effectiveness, versatility, and widespread use across diverse crop types and soil conditions. Bacterial inoculants, such as Rhizobium, Azospirillum, and Bacillus species, play a critical role in enhancing soil fertility by promoting biological nitrogen fixation, solubilizing essential nutrients like phosphorus, and stimulating root growth through the secretion of plant hormones.
Their adaptability to various environmental conditions and compatibility with modern farming practices, including seed treatment and fertigation systems, have led to increased adoption globally. Moreover, ongoing research and advancements in microbial biotechnology have enabled the development of region-specific and crop-specific bacterial strains, further boosting their efficiency and reliability in both conventional and organic farming systems.
In comparison, fungi represent a smaller but steadily growing share within the microorganism segment. Fungal inoculants, especially mycorrhizal fungi and Trichoderma species, contribute significantly to plant health by establishing symbiotic relationships with plant roots, improving water absorption, and enhancing resistance to soil-borne diseases. Mycorrhizal fungi, in particular, extend the root surface area through their hyphal networks, enabling better uptake of immobile nutrients such as phosphorus, zinc, and copper.
Trichoderma fungi offer biocontrol properties by outcompeting harmful pathogens and triggering plant defense mechanisms. While fungi currently hold a lower market share compared to bacteria, their unique benefits in stress tolerance and soil rehabilitation are gaining attention, particularly in regions facing challenges like drought, salinity, and degraded soils. As awareness of integrated biological farming solutions increases, the use of fungal inoculants is expected to grow steadily alongside bacterial products.
By Type of Inoculant Analysis
Within the type of inoculant segment, nitrogen-fixing inoculants are expected to consolidate their lead, accounting for around 46.0% of the total market share in 2025. This segment’s dominance is rooted in the essential role that nitrogen plays in plant metabolism and growth, and the widespread use of nitrogen-dependent crops such as soybeans, pulses, and legumes. Nitrogen-fixing inoculants contain beneficial microbes like Rhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, and Azospirillum, which establish symbiotic relationships with plant roots and convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for the plant.
These inoculants significantly reduce the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, cutting both input costs and environmental impact. Their effectiveness across diverse geographies and soil types has made them a staple in sustainable and organic farming practices. Furthermore, government programs promoting eco-friendly crop inputs are further accelerating their adoption, especially in regions where nitrogen deficiency is prevalent.
Phosphate-solubilizing inoculants represent another vital component of this segment, though with a comparatively smaller share. These inoculants are particularly important in addressing phosphorus availability, a common nutrient limitation in many agricultural soils. Microorganisms such as Bacillus megaterium and Pseudomonas fluorescens are used in these formulations to break down insoluble phosphate compounds in the soil and convert them into forms that plants can absorb.
This function becomes especially valuable in acidic or alkaline soils where phosphorus tends to become fixed and unavailable. By improving phosphorus uptake efficiency, these inoculants not only enhance root development and flowering but also contribute to overall yield improvement. Their growing adoption is seen in cereal crops, vegetables, and horticultural applications, particularly in regions where phosphorus fertilizers are expensive or overused. As sustainable nutrient management becomes a priority, phosphate-solubilizing inoculants are gaining traction as a practical solution for improving soil fertility and reducing chemical inputs.
By Crop Type Analysis
In the crop type segment of the agricultural inoculants market, cereals and grains are projected to retain their dominant position, capturing 40.0% of the total market share in 2025. This stronghold is largely driven by the vast global cultivation area and high demand for staple crops such as wheat, rice, maize, and barley. These crops form the backbone of global food security, prompting widespread adoption of productivity-enhancing solutions like microbial inoculants. Inoculants used in cereal and grain cultivation, particularly nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing formulations, help improve nutrient uptake, stimulate root growth, and increase resistance to environmental stress.
Their effectiveness in boosting yield and reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers has made them a preferred choice for both large-scale commercial farmers and those practicing regenerative agriculture. Additionally, the compatibility of these crops with seed inoculation methods contributes to the segment’s sustained dominance, making it a central focus for manufacturers and agricultural extension programs.
Oilseeds and pulses form the second-largest crop type segment and are expected to continue contributing significantly to the market. Crops such as soybeans, groundnuts, chickpeas, and lentils are not only vital for food and oil production but also for enriching soil fertility through their symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. This unique attribute makes inoculants, especially rhizobial strains, an integral part of their cultivation process.
In oilseed and pulse production, microbial inoculants help improve nodulation, nitrogen assimilation, and pod development, resulting in better yield and crop quality. With growing demand for plant-based proteins and edible oils, particularly in developing regions, the adoption of biofertilizers in these crop categories is expected to rise steadily. Moreover, governments and agricultural cooperatives are actively promoting the use of inoculants in pulse production to boost soil health and reduce the input cost burden for farmers.
By Formulation Analysis
In the formulation segment of the agricultural inoculants market, solid formulations are expected to maintain their leadership, accounting for approximately 58.0% of the total market share in 2025. These formulations, which include powders, granules, and peat-based carriers, have long been favored for their stability, ease of storage, and compatibility with traditional seed treatment practices. Solid inoculants are particularly popular in large-scale crop cultivation like cereals, pulses, and oilseeds, where mechanical seed coating is widely practiced.
Their extended shelf life and minimal need for refrigeration make them practical for distribution in regions with limited infrastructure. Additionally, solid formulations are often more cost-effective, appealing to smallholder farmers and cooperatives seeking affordable biofertilizer options. Their success in delivering viable microbial populations to the rhizosphere, even under varied climatic and soil conditions, reinforces their continued dominance in the market.
Liquid formulations, while currently holding a smaller share, are gaining traction due to their ease of application and growing suitability for modern precision agriculture systems. These inoculants are typically applied through foliar sprays, drip irrigation, or in-furrow treatments, making them ideal for high-value horticultural crops and controlled-environment agriculture.
Liquid formulations offer better microbial dispersion and can be blended with other inputs, allowing for customized nutrient and microbial delivery. Their fast action and reduced clogging risk in irrigation systems are particularly advantageous in intensive farming setups. Although they require more careful storage and shorter shelf life management, advancements in encapsulation and carrier technology are gradually improving their stability and viability. As farming practices evolve toward automation and targeted application, liquid inoculants are expected to see increased adoption, particularly among progressive growers and commercial farms.
By Function Analysis
In the function-based segmentation of the agricultural inoculants market, soil fertility enhancement is projected to dominate, accounting for around 52.0% of the total market share in 2025. This leadership stems from the essential role of inoculants in improving nutrient availability and promoting efficient nutrient cycling within the soil ecosystem. Microbial inoculants that fix atmospheric nitrogen, solubilize phosphorus, and mobilize micronutrients like zinc and potassium are widely applied to enrich the soil and support sustainable plant growth.
These biofertilizers not only reduce the dependency on synthetic inputs but also contribute to long-term soil health by maintaining microbial diversity and improving soil structure. In both organic and conventional farming systems, enhancing soil fertility remains a foundational goal, making these inoculants a preferred choice across major crop types, including cereals, legumes, and vegetables. Their use is especially prominent in degraded or nutrient-deficient soils where restoring biological activity is key to growing productivity.
Plant disease resistance represents another important functional segment, gaining recognition for its ability to reduce chemical pesticide usage and support integrated crop protection strategies. Inoculants used for this purpose include strains of beneficial fungi like Trichoderma and bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis, which suppress harmful pathogens through competitive exclusion, production of antifungal compounds, and induction of systemic resistance in host plants.
These biological agents help manage soil-borne diseases such as root rot, wilt, and damping-off, commonly seen in vegetable, fruit, and ornamental crops. The growing awareness of chemical residue risks and the demand for organic produce are driving the adoption of disease-resistant microbial products. While this segment currently holds a smaller share compared to soil fertility enhancement, it is experiencing strong growth potential, particularly in high-value crop markets and protected cultivation environments where disease pressure and quality standards are both high.
By Mode of Application Analysis
In the mode of application segment of the agricultural inoculants market, seed inoculation is expected to lead with an estimated 55.0% market share in 2025. This method involves directly coating seeds with beneficial microorganisms before planting, ensuring early and efficient colonization of the rhizosphere. Seed inoculation is favored for its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and precision in delivering microbial strains like Rhizobium, Azospirillum, or phosphate-solubilizing bacteria to the exact point of root development. It enhances seed germination, promotes uniform growth, and improves nutrient uptake from the early stages of crop establishment.
This mode is especially popular in the cultivation of legumes, cereals, and oilseeds, where compatibility between crop type and microbial strain is well established. Its adaptability to both mechanized and manual farming systems further boosts its appeal in developed and developing regions alike. Additionally, seed inoculation supports sustainable farming by reducing the need for excessive chemical inputs while improving soil biology over time.
Soil inoculation, while holding a smaller share, plays a crucial role in enhancing overall soil health and nutrient dynamics. This method involves introducing microbial inoculants directly into the soil either before sowing or during crop growth stages through broadcasting, furrow application, or drip irrigation. It is particularly effective in restoring degraded soils, improving microbial biodiversity, and addressing nutrient deficiencies across larger root zones. Soil inoculation is commonly used in horticultural crops, tree plantations, and regions where seed treatment is impractical or ineffective due to seed coating limitations or environmental factors. It is also suitable for crops with longer growth cycles or those grown in mixed or intercropping systems.
Although it may require higher volumes of inoculant and more precise handling, its ability to influence soil structure, moisture retention, and disease suppression makes it a valuable method in both organic and regenerative farming approaches. With growing interest in holistic soil management, soil inoculation is gradually gaining momentum as a complementary or standalone application strategy.
The Agricultural Inoculants Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Type of Microorganism
By Type of Inoculant
- Nitrogen-fixing Inoculants
- Phosphate-solubilizing Inoculants
- Plant Growth Promoting Inoculants (PGPIs)
- Biocontrol Inoculants
By Crop Type
- Cereals & Grains
- Oilseeds & Pulses
- Fruits & Vegetables
- Others
By Formulation
By Function
- Soil Fertility Enhancement
- Plant Disease Resistance
- Stress Tolerance
- Other Growth Promotion
By Mode of Application
- Seed Inoculation
- Soil Inoculation
- Foliar Application
- Others
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Regional Analysis
Region with the Largest Revenue Share
North America is projected to lead the global agricultural inoculants market in 2025, capturing approximately 34.0% of the total market revenue, driven by advanced farming practices, widespread adoption of sustainable agriculture, and strong institutional support. The region benefits from a high level of awareness among farmers regarding the benefits of microbial inoculants, particularly in improving soil fertility and reducing dependency on synthetic agrochemicals.
Countries like the United States and Canada have been early adopters of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing inoculants, especially in the large-scale cultivation of soybeans, corn, and wheat. Government programs promoting environmentally friendly inputs, integrated with robust research and development activities led by universities and private agritech firms, have further accelerated innovation and market penetration. The integration of inoculants with precision farming technologies and digital agriculture platforms also enhances their application efficiency and appeal in North America’s technologically advanced agricultural landscape.
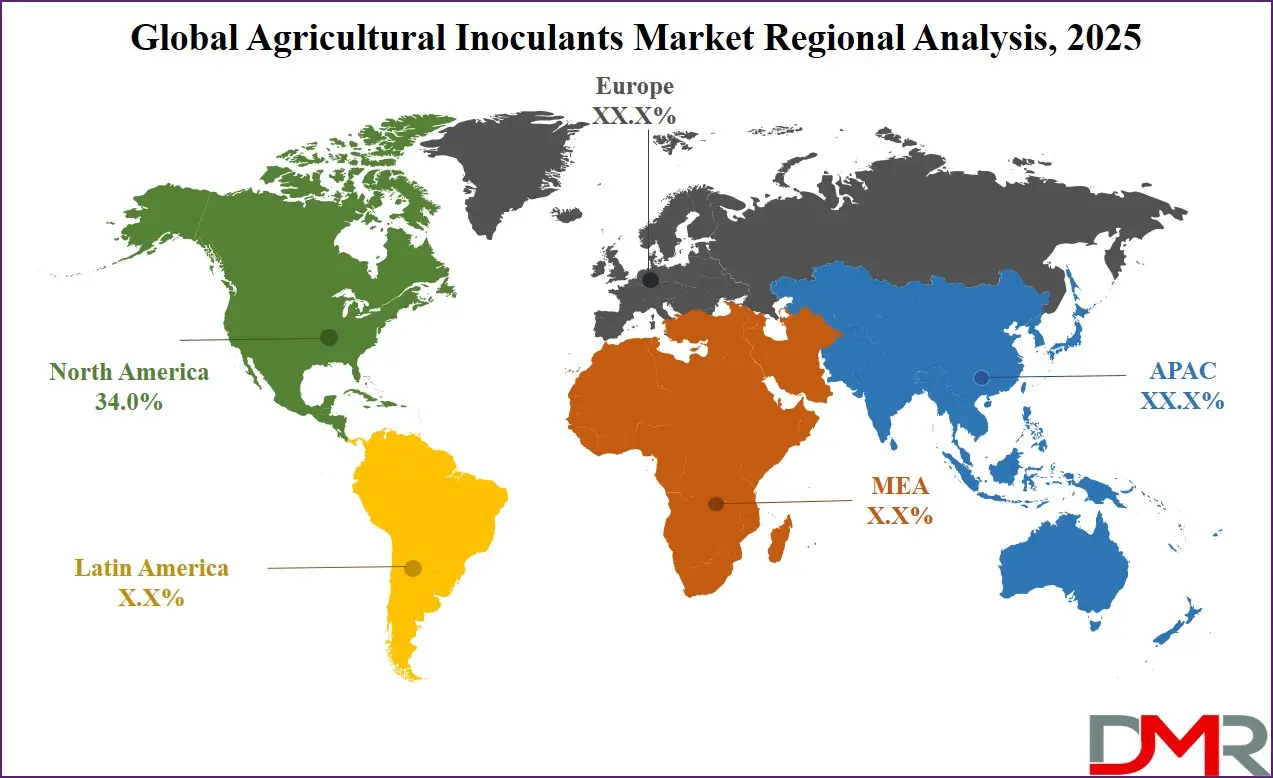
Region with significant growth
Asia-Pacific is expected to register the highest CAGR in the global agricultural inoculants market over the forecast period, driven by expanding agricultural activities, growing demand for sustainable farming inputs, and growing awareness of biofertilizers among smallholder farmers. Countries like India, China, and Vietnam are investing heavily in organic farming initiatives and soil health restoration programs, which are fueling the adoption of microbial inoculants such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi.
Government-backed schemes promoting eco-friendly agriculture, combined with rising food security concerns and pressure to improve crop productivity on limited arable land, are accelerating market growth in the region. Additionally, improvements in rural infrastructure, greater accessibility to microbial products, and a growing agritech ecosystem are expected to further boost inoculant uptake across Asia-Pacific, making it the fastest-growing regional market.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Competitive Landscape
The global competitive landscape of the agricultural inoculants market is characterized by the presence of both multinational agrochemical giants and specialized biotech firms, each vying for market share through innovation, strategic partnerships, and regional expansion. Leading companies such as Novozymes, BASF SE, Bayer AG, and Corteva Agriscience dominate the market through extensive R&D capabilities, robust distribution networks, and a broad portfolio of microbial products tailored to different crops and soil conditions.
Meanwhile, emerging players like Rizobacter, Verdesian Life Sciences, and Plant Health Care plc are gaining ground by focusing on region-specific formulations and offering integrated biological solutions for soil health and crop resilience. Mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations with research institutions are common strategies aimed at strengthening microbial strains, improving formulation technologies, and expanding access to emerging markets. With growing demand for sustainable and regenerative agriculture, competition is intensifying, pushing companies to invest in product efficacy, shelf stability, and compatibility with precision agriculture tools to secure a competitive edge.
Some of the prominent players in the global agricultural inoculants market are
- Novozymes
- BASF SE
- Bayer AG
- Corteva Agriscience
- UPL Limited
- Syngenta AG
- Verdesian Life Sciences
- Chr. Hansen Holding A/S
- Lallemand Inc.
- Rizobacter Argentina S.A.
- T. Stanes & Company Limited
- AgriLife
- BioWorks Inc.
- KALO Inc.
- Premier Tech Ltd.
- Valent BioSciences LLC
- Plant Health Care plc
- SOM Phytopharma (India) Ltd.
- Kiwa Bio-Tech Products Group Corporation
- Italpollina S.p.A.
- Other Key Players
Global Agricultural Inoculants Market: Recent Developments
- June 2025: NexusBioAg introduced three new inoculant blends, BioniQ, TagTeam BioniQ, and Optimize LV, formulated to enhance pulse crop growth and nutrient uptake across Canadian farmlands. The launch supports the growing demand for microbial seed treatments tailored to local agronomic conditions.
- May 2025: BASF’s Agricultural Solutions division announced its intent to spin off and pursue an IPO by 2027. The move is aimed at enhancing its strategic focus on biological crop inputs, including agricultural inoculants, while expanding market share in Asia and Latin America.
- April 2025: BASF provided CAD 160,000 in grants to 12 rural Canadian agricultural organizations as part of its “Growing Home with BASF” initiative, reinforcing its long-term commitment to supporting sustainable farming communities and bio-based innovation.
- February 2025: A market study projected the global microbial agricultural inoculants sector to grow by USD 303.2 million between 2025 and 2029, citing increased farmer awareness and regulatory pressure to reduce chemical fertilizer dependence.
- March 2023: UPL and Novozymes launched Jumpstart Liquid in Argentina, a seed-applied inoculant based on Penicillium bilaiae. The product is designed to mobilize soil-bound phosphorus, improve root development, and boost nutrient use efficiency in soybean cultivation.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 3.4 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 7.8 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
9.7% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 1.0 Bn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Type of Microorganism (Bacteria, Fungi, and Others), By Type of Inoculant (Nitrogen-fixing Inoculants, Phosphate-solubilizing Inoculants, Plant Growth Promoting Inoculants (PGPIs), and Biocontrol Inoculants), By Crop Type (Cereals & Grains, Oilseeds & Pulses, Fruits & Vegetables, and Others), By Formulation (Solid, Liquid, and Others), By Function (Soil Fertility Enhancement, Plant Disease Resistance, Stress Tolerance, and Other Growth Promotion), and By Mode of Application (Seed Inoculation, Soil Inoculation, Foliar Application, and Others) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, Rest of Europe; Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
Novozymes, BASF SE, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, UPL Limited, Syngenta AG, Verdesian Life Sciences, and Chr. Hansen Holding A/S, Lallemand Inc., Rizobacter Argentina S.A., T. Stanes & Company Limited, AgriLife, BioWorks Inc., KALO Inc., and Other Key Players. |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The global agricultural inoculants market size is estimated to have a value of USD 3.4 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 7.8 billion by the end of 2034.
The US agricultural inoculants market is projected to be valued at USD 1.0 billion in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 2.1 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 9.1%.
North America is expected to have the largest market share in the global agricultural inoculants market, with a share of about 34.0% in 2025.
Some of the major key players in the global agricultural inoculants market are Novozymes, BASF SE, Bayer AG, Corteva Agriscience, UPL Limited, Syngenta AG, Verdesian Life Sciences, and Chr. Hansen Holding A/S, Lallemand Inc., Rizobacter Argentina S.A., T. Stanes & Company Limited, AgriLife, BioWorks Inc., KALO Inc., and Other Key Players.
The market is growing at a CAGR of 9.7 percent over the forecasted period.