Market Overview
The global carbon emissions market is projected to grow from USD 988.2 billion in 2025 to USD 6,276.0 billion by 2034, registering a robust CAGR of 22.8%. Driven by growing industrialization, regulatory frameworks, carbon trading initiatives, and investments in low-carbon technologies, the market is witnessing significant expansion in emission reduction strategies, carbon credits, and renewable energy adoption globally.
Carbon emissions refer to the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere primarily from human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, industrial processes, deforestation, and agricultural practices. These emissions contribute significantly to climate change by enhancing the greenhouse effect, which traps heat in the Earth's atmosphere and leads to rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and environmental degradation.

ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Carbon emissions are measured in metric tons and are closely monitored by governments, environmental organizations, and industries to evaluate their impact on air quality, carbon footprint, and sustainability targets. Effective management and reduction of carbon emissions are essential to achieving climate goals, promoting renewable energy adoption, and ensuring a balanced and resilient ecosystem.
The global carbon emissions market encompasses the economic, regulatory, and technological systems established to monitor, trade, and mitigate greenhouse gas releases globally. This market integrates various mechanisms such as carbon credits, emission trading schemes, carbon offset programs, and carbon taxation frameworks to incentivize industries and organizations to reduce their overall carbon footprint.
Participants include energy producers, manufacturing industries, transportation sectors, agriculture, and governments, all of which interact to establish market-driven strategies aimed at controlling emissions levels. The market also reflects growing investments in low-carbon technologies, carbon capture and storage solutions, and renewable energy projects that facilitate measurable reductions in greenhouse gases.
The market is influenced by evolving international climate policies, regulatory standards, and growing societal awareness regarding environmental sustainability. Financial institutions and corporations are adopting carbon accounting practices and reporting frameworks to comply with emission reduction targets and support sustainable business operations.

ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Technological innovations in energy efficiency, clean fuels, and monitoring systems are driving market expansion and creating new opportunities for carbon credit trading. The global carbon emissions market thus serves as a dynamic ecosystem connecting environmental objectives with economic incentives, enabling coordinated efforts to combat climate change while fostering sustainable industrial growth.
The US Carbon Emissions Market
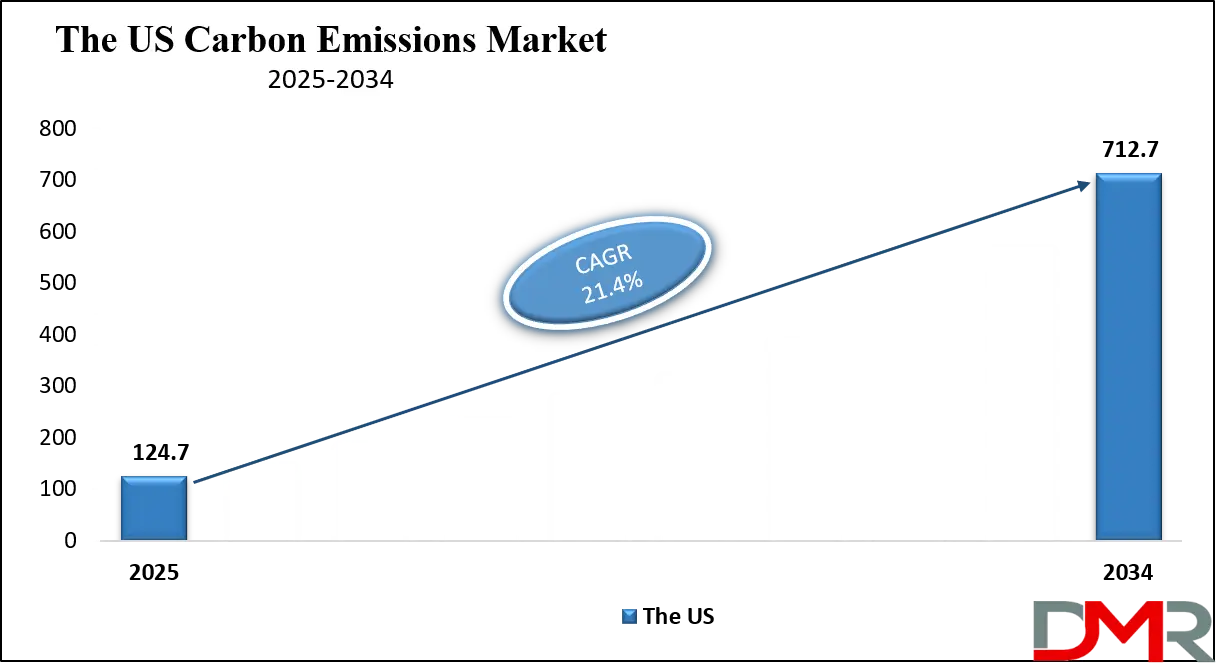
The U.S. Carbon Emissions market size is projected to be valued at USD 124.7 billion by 2025. It is further expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period, holding USD 712.7 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 21.4%.
The US carbon emissions market represents one of the largest and most structured markets globally, driven by stringent federal and state-level climate regulations, emission reporting standards, and carbon pricing mechanisms. The market encompasses diverse sectors, including power generation, transportation, manufacturing, and industrial processes, all of which are responsible for significant greenhouse gas emissions. With growing adoption of emission trading schemes, carbon offset programs, and renewable energy initiatives, companies are actively implementing decarbonization strategies and carbon management solutions to reduce their overall carbon footprint.
The market is further supported by technological innovations such as carbon capture, utilization, and storage, energy-efficient processes, and sustainable fuels, which collectively help mitigate environmental impact while aligning with national and international climate goals.
Investment in clean energy infrastructure, low-carbon technologies, and corporate sustainability initiatives is driving market growth across the United States. Public and private sector collaborations are accelerating the adoption of carbon accounting practices, emission reduction targets, and carbon credit trading.
Regulatory frameworks such as the Clean Air Act, state-specific cap-and-trade programs, and voluntary carbon markets are creating measurable incentives for emission reductions. As awareness of climate change intensifies, stakeholders are increasingly prioritizing sustainable operations, climate risk management, and reporting transparency. The US carbon emissions market is thus evolving as a dynamic ecosystem that integrates economic, environmental, and technological strategies to support a low-carbon future.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Europe Carbon Emissions Market
The European carbon emissions market is projected to reach approximately USD 69.1 billion in 2025, driven by the region’s ambitious decarbonization goals and strong regulatory frameworks. Policies such as the European Union Emissions Trading System, carbon taxation, and mandatory emission reporting are compelling industries to adopt low-carbon technologies and enhance energy efficiency.
The energy, transportation, and manufacturing sectors remain major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, prompting widespread deployment of renewable energy, carbon capture and storage, and emission monitoring systems. Investments in sustainable industrial practices and climate-focused innovations are further supporting Europe’s position as a leading market in the global carbon emissions landscape.
The European market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 16.5%, reflecting the region’s robust sustainability initiatives, technological advancements, and active participation in carbon trading and offset programs. Companies are increasingly integrating electrification of industrial processes, green fuels, and smart energy management systems to reduce their carbon footprint. Rising environmental awareness among consumers and investors is also driving demand for transparent carbon accounting and ESG reporting. These factors collectively ensure that Europe maintains strong growth while aligning with global decarbonization trends.
Japan Carbon Emissions Market
The Japanese carbon emissions market is anticipated to reach around USD 39.5 billion in 2025, supported by government policies and corporate initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Japan’s industrial and energy sectors, including manufacturing, power generation, and transportation, contribute significantly to carbon output, creating a strong demand for low-carbon solutions. Government initiatives, such as the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures and carbon trading programs, encourage companies to implement decarbonization strategies, invest in renewable energy, and adopt carbon capture technologies to meet national climate objectives.
The Japanese market is projected to grow at an adjusted compound annual growth rate of approximately 13.5%, reflecting steady industrial decarbonization, technological adoption, and policy-driven initiatives. Japanese companies are focusing on energy-efficient operations, electrification of industrial processes, and sustainable fuel alternatives to minimize emissions.
Additionally, participation in carbon credit trading and adherence to ESG reporting frameworks are enhancing transparency and accountability. These strategies position Japan as a steadily expanding market within the broader global carbon emissions sector, contributing to international sustainability efforts.
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Key Takeaways
- Market Value: The global Carbon Emissions market size is expected to reach a value of USD 6,276.0 billion by 2034 from a base value of USD 988.2 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of 22.8%.
- By Source Segment Analysis: Energy Sector will dominate the source segment, capturing 73.0% of the market share in 2025.
- By Gas Type Segment Analysis: Carbon Dioxide will account for the maximum share in the gas type segment, capturing 74.0% of the total market value.
- By End-Use Industry Segment Analysis: The Power Generation Industry is expected to consolidate its dominance in the end-use industry segment, capturing 31.0% of the market share in 2025.
- Regional Analysis: Asia Pacific is anticipated to lead the global Carbon Emissions market landscape with 52.0% of total global market revenue in 2025.
- Key Players: Some key players in the global Carbon Emissions market are Saudi Aramco, Chevron, Gazprom, ExxonMobil, National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC), BP, Royal Dutch Shell, Coal India, Pemex, Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA), PetroChina, Peabody Energy, ConocoPhillips, Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC), Kuwait Petroleum Corporation, and Others.
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Use Cases
- Carbon Trading and Emission Reduction Programs: Carbon trading schemes and emission reduction programs are key mechanisms in the global carbon emissions market, enabling companies and governments to buy and sell carbon credits to offset their greenhouse gas emissions. These programs incentivize industrial sectors, energy producers, and transportation companies to adopt low-carbon technologies and implement energy efficiency measures. By creating a market-driven approach, carbon trading helps in controlling industrial carbon footprints, meeting regulatory compliance, and encouraging investments in renewable energy projects, carbon capture initiatives, and sustainable practices.
- Renewable Energy Integration and Low-Carbon Technologies: The adoption of renewable energy sources and low-carbon technologies is a critical use case for the carbon emissions market. Companies in the power generation, manufacturing, and transportation sectors are increasingly integrating solar, wind, and hydroelectric energy solutions to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels. Implementation of energy-efficient equipment, sustainable fuels, and smart energy management systems further supports emission reduction. This transition not only mitigates carbon emissions but also enhances operational efficiency, supports sustainability reporting, and aligns with global climate targets and net-zero commitments.
- Industrial Decarbonization and Process Optimization: Industrial decarbonization focuses on reducing emissions in sectors such as steel, cement, chemicals, and petrochemicals. Advanced process optimization, carbon capture, and utilization technologies are deployed to minimize CO₂, CH₄, and N₂O emissions during manufacturing and production. Companies are investing in the electrification of industrial processes, the adoption of green hydrogen, and material recycling to lower their environmental impact. This approach not only reduces regulatory risks but also improves competitiveness in global markets increasingly influenced by environmental performance and carbon compliance.
- Corporate Sustainability and Carbon Reporting: Corporate sustainability initiatives and carbon reporting practices are a major use case driving the global carbon emissions market. Organizations are implementing comprehensive carbon accounting frameworks, emission monitoring systems, and ESG reporting standards to quantify their carbon footprint and track progress toward reduction targets. Transparent reporting of emissions enables businesses to participate in carbon offset programs, improve investor confidence, and demonstrate environmental stewardship. This use case integrates financial, operational, and environmental strategies, making companies accountable for their carbon output and fostering the adoption of green policies across industries.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the global Carbon Emissions market
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the global carbon emissions market by enabling smarter monitoring, analysis, and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions across industries. AI-powered predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms allow organizations to track real-time carbon footprints, optimize energy consumption, and identify inefficiencies in industrial, transportation, and power generation sectors. These technologies support emission forecasting, automated reporting, and scenario analysis, helping companies and governments implement more precise decarbonization strategies while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
AI is also accelerating the adoption of low-carbon technologies by enhancing the performance of renewable energy systems, optimizing grid management, and improving energy storage solutions. In industrial processes, AI facilitates predictive maintenance, process automation, and energy-efficient operations, reducing CO₂, CH₄, and N₂O emissions.
Additionally, AI-driven platforms streamline carbon credit trading, emission offset verification, and sustainability reporting, creating a data-driven ecosystem that integrates environmental objectives with economic incentives. By leveraging artificial intelligence, the global carbon emissions market is becoming more efficient, transparent, and capable of meeting ambitious climate targets while supporting corporate sustainability and operational excellence.
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Stats & Facts
China (National Bureau of Statistics of China):
- In 2023, China's carbon dioxide emissions per 10,000 yuan worth of GDP remained the same as the previous year, indicating a stabilization in emission intensity.
- By the end of 2023, China's national carbon emissions trading market covered about 5.1 billion tons of annual carbon dioxide emissions and included 2,257 key emission units.
- In 2023, China's coal consumption surged due to drought and heatwave conditions, leading to increased energy demand and higher emissions.
- Despite a rapid deployment of renewables, China's emissions stabilized at near-record-high levels in 2024, following a sharp increase in fossil fuel consumption in 2023 after the lifting of zero-COVID policies.
- China's energy transition continues to reflect two seemingly opposing trends: rapid deployment of renewables and a surge in coal power construction, with 2024 marking the highest level in a decade due to the 2022-2023 permitting boom.
India (Press Information Bureau, Government of India):
- India's greenhouse gas emissions in 2020 were 2,959 million tonnes of CO₂ equivalent, excluding Land Use, Land-Use Change, and Forestry (LULUCF), marking a 7.93% reduction compared to 2019.
- In 2023, India's emissions grew faster than GDP, at slightly more than 7%, rising around 190 Mt to reach 2.8 Gt.
- India's per capita emissions remain very low, at around 2 tonnes, less than half the world average of 4.6 tonnes.
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that India's emissions will be around 4.4–4.6 GtCO₂e in 2030 under current policies, indicating an increase of around 8–11% since the last update.
- The IEA also notes that India's energy-related CO₂ emissions increased by 7% in 2023, driven by the continued rapid recovery in economic activity from the lows of the COVID-19 pandemic.
European Union (European Environment Agency):
- In 2023, the European Union achieved a net 8% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to the previous year, marking the largest annual drop in decades.
- The EU's natural carbon sink increased by 8.5% in 2023, reversing the declining trend of the past decade in the Land Use, Land Use Change, and Forestry (LULUCF) sector.
- In the fourth quarter of 2023, EU economy-wide greenhouse gas emissions were estimated at 897 million tonnes of CO₂-equivalents, a 4.0% decrease compared with the same quarter of 2022.
- The EU's gross domestic product remained stable, registering just a small increase (0.2%) in the fourth quarter of 2023, compared with the same quarter of 2022.
- The European Automobile Manufacturers' Association (ACEA) has urged the EU to relax its CO₂ emissions reduction targets for cars, vans, and trucks, citing industry challenges and global market pressures.
Russia (Russian Ministry of Economy):
- Starting from 2023, companies emitting more than 150,000 tons of CO₂ equivalent per year are required to report their emissions, aiming to enhance transparency and accountability.
- Russia's economy-wide emissions are expected to continue rising to 2030 or barely stabilizing, under current policies, instead of rapidly declining.
- In the last two years, the emissions absorption capacity of Russia's Land Use, Land Use Change, and Forestry (LULUCF) sector has nearly doubled, acting as a carbon sink of up to 1,172 MtCO₂e in 2023.
- Russia's 2025 inventory report indicated a significant increase in LULUCF emissions, reporting them as -750 MtCO₂e in 2021, compared to -505 MtCO₂e in the previous inventory.
- Under current policies, Russia's economy-wide emissions are projected to be between 2,067 and 2,145 MtCO₂e in 2030, excluding LULUCF.
Brazil (Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation):
- In 2023, Brazil's energy sector emissions reached 428 million tons of CO₂ equivalent, with a significant share from renewable sources.
- Brazil confirmed its absolute net greenhouse gas emission target in 2025 of 1.32 GtCO₂e, consistent with a reduction of 48.4% compared to 2005 levels.
- Brazil committed to an absolute net greenhouse gas emission target in 2030 of 1.20 GtCO₂e, consistent with a reduction of 53.1% compared to 2005 levels.
- Initial reports indicate a 36% decrease in primary forest loss in 2023 compared to 2022 due to strengthened law enforcement.
- Brazil's CO₂ emissions by fuel in 2022 showed that oil accounted for 72% of total CO₂ emissions from fuel combustion.
Japan (Ministry of the Environment, Japan):
- In 2023, Japan's national greenhouse gas emissions and removals were 1,017 million tonnes of CO₂ equivalent, showing a 4.2% decrease compared to 2022.
- This marks the lowest emissions and removals on record, continuing the decreasing trend towards Japan's target of achieving net zero by 2050.
- Japan's emissions and removals decreased by 27.1% compared to 2013 levels, indicating significant progress in emission reductions.
- The decrease in emissions is attributed to various factors, including energy efficiency improvements and increased use of renewable energy sources.
- Japan's national carbon emissions trading market has been instrumental in achieving these reductions, covering a significant portion of the country's emissions.
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Market Dynamics
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Driving Factors
Stringent Government Regulations and Carbon Policies
Governments globally are introducing stricter emission regulations, carbon taxes, and mandatory reporting standards to curb greenhouse gas emissions. These policies drive companies across energy, manufacturing, and transportation sectors to adopt emission reduction strategies, invest in renewable energy, and participate in carbon trading schemes. Regulatory frameworks, including emission caps and compliance reporting requirements, create a structured environment that encourages businesses to monitor their carbon footprint, implement energy-efficient solutions, and align with international climate agreements such as the Paris Accord.
Increasing Adoption of Low-Carbon Technologies
The global shift toward renewable energy, energy-efficient equipment, and carbon capture technologies is fueling growth in the carbon emissions market. Industries are deploying smart energy management systems, electrification of industrial processes, and sustainable fuel alternatives to reduce operational emissions. Adoption of advanced solutions like green hydrogen, solar and wind energy integration, and AI-driven emission monitoring helps organizations achieve decarbonization goals while optimizing production efficiency. The growing emphasis on sustainability and corporate social responsibility further reinforces the demand for low-carbon technologies.
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Restraints
High Capital Expenditure for Carbon Reduction Solutions
Implementation of renewable energy systems, carbon capture and storage infrastructure, and low-carbon industrial technologies requires significant upfront investment. Small and medium enterprises, in particular, face challenges in financing such projects, which can slow adoption rates. High initial costs, long payback periods, and limited access to financing options restrain widespread deployment of emission reduction initiatives, limiting the market growth potential despite regulatory incentives.
Limited Awareness and Technical Expertise
Many organizations still lack knowledge and technical expertise to effectively implement carbon management strategies. Insufficient awareness of carbon accounting, carbon offset programs, and emission monitoring tools restricts the ability of businesses to optimize energy use, participate in carbon trading, and meet compliance standards. This knowledge gap is particularly prevalent in developing regions, where sustainable energy adoption is slower, creating a barrier to market expansion.
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Opportunities
Expansion of Carbon Credit and Emissions Trading Markets
The growth of voluntary and compliance-based carbon markets offers substantial opportunities for businesses to monetize emission reduction efforts. Companies can invest in carbon credits, offset projects, and emission reduction certificates to meet sustainability goals while generating revenue streams. Increased demand for transparency, traceability, and verification of carbon offsets is driving technological innovations, blockchain-enabled carbon tracking, and digital platforms that enhance market efficiency and create investment potential.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and IoT in Emission Monitoring
AI, machine learning, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices provide actionable insights into energy consumption patterns, process optimization, and predictive maintenance. These technologies enable precise tracking of carbon emissions, identification of inefficiencies, and real-time optimization of industrial and energy systems. Integration of AI-driven platforms with smart grids and renewable energy assets opens new avenues for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and achieving net-zero targets while creating business opportunities in analytics and sustainability solutions.
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Trends
Adoption of Net-Zero and ESG Commitments
Corporations and governments are increasingly committing to net-zero carbon targets and integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into business operations. This trend is pushing industries to adopt renewable energy, sustainable supply chains, and transparent carbon reporting. Investors are prioritizing companies with strong ESG performance, which accelerates the adoption of carbon reduction strategies and supports long-term market growth.
Technological Advancements in Carbon Capture and Storage
Rapid innovation in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies is reshaping the global carbon emissions market. New solutions enable large-scale industrial facilities and power plants to capture CO₂ efficiently, convert it into usable products, or store it safely underground. These advancements reduce dependency on traditional fossil fuels, enhance energy efficiency, and create scalable pathways for achieving national and international climate targets while fostering industrial sustainability.
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Source Analysis
The energy sector is expected to be the dominant source segment in the global carbon emissions market, accounting for approximately 73.0% of the total market share in 2025. This dominance is driven by the heavy reliance on fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas for electricity generation, industrial operations, and transportation. Power plants, manufacturing facilities, and transportation networks contribute the largest portion of greenhouse gas emissions, making energy the central focus of emission reduction strategies.
Companies and governments are increasingly investing in low-carbon technologies, renewable energy sources, and energy-efficient solutions to curb emissions from this sector. Carbon trading schemes, emission monitoring systems, and regulatory compliance frameworks further emphasize the critical role of the energy sector in controlling global emissions and achieving net-zero targets.
Agriculture, forestry, and land use also play a significant role in the carbon emissions market, accounting for a considerable portion of global greenhouse gas outputs. Agricultural activities such as livestock rearing, fertilizer application, and rice cultivation release methane and nitrous oxide, which are potent greenhouse gases.
Deforestation and land conversion for agriculture reduce the planet’s natural carbon sinks, exacerbating the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. At the same time, sustainable land management practices, reforestation, and agroforestry initiatives offer opportunities to mitigate emissions within this segment. As countries implement policies to promote sustainable agriculture and protect forests, the agriculture, forestry, and land use segment is increasingly integrated into the broader carbon emissions market through carbon offset programs and environmental conservation initiatives.

ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
By Gas Type Analysis
Carbon dioxide is expected to account for the largest share in the gas type segment of the global carbon emissions market, capturing approximately 74.0% of the total market value. This high dominance is largely due to its widespread release from fossil fuel combustion in power generation, industrial processes, transportation, and residential energy use. Carbon dioxide is the primary contributor to the greenhouse effect and global warming, making it the central focus of emission reduction strategies globally.
Efforts to mitigate CO₂ emissions include the adoption of renewable energy sources, energy-efficient technologies, carbon capture and storage solutions, and participation in carbon trading schemes. Regulatory frameworks, carbon taxation, and corporate sustainability initiatives further reinforce the emphasis on reducing CO₂ output across major industrial and energy sectors.
Methane also plays a significant role in the gas type segment of the carbon emissions market, though its share is smaller compared to carbon dioxide. Methane is primarily released from agricultural activities, including livestock digestion and manure management, as well as from landfills, wastewater treatment, and the extraction and transport of fossil fuels.
Despite being present in smaller quantities, methane is a highly potent greenhouse gas, with a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide over a shorter time frame. The market is increasingly focusing on methane mitigation through improved agricultural practices, waste management systems, and leak detection and repair programs in oil and gas operations, which are critical for comprehensive greenhouse gas reduction efforts.
By End-Use Industry Analysis
The power generation industry is expected to maintain its dominant position in the end-use industry segment of the global carbon emissions market, accounting for approximately 31.0% of the total market share in 2025. This dominance is primarily driven by the extensive reliance on coal, natural gas, and oil to produce electricity and heat across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Power plants are among the largest emitters of carbon dioxide, making the sector a key focus for emission reduction strategies. The growing deployment of renewable energy technologies such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, along with energy efficiency measures and carbon capture solutions, is helping to mitigate emissions from this sector. Regulatory compliance, carbon pricing mechanisms, and corporate sustainability initiatives further reinforce the importance of power generation in achieving national and international climate targets.
The transportation and logistics sector also represents a significant portion of the end-use industry segment, contributing substantially to global greenhouse gas emissions. Emissions from road vehicles, aviation, shipping, and rail are primarily fueled by petroleum-based products, making this sector a major source of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
The market is increasingly emphasizing low-carbon transportation solutions, including the adoption of electric vehicles, biofuels, and optimized supply chain logistics to reduce fuel consumption. Intelligent transportation systems, route optimization, and fleet electrification are emerging as effective strategies for controlling emissions, while government policies and incentives further promote sustainable practices in freight, passenger transport, and logistics operations.
The Carbon Emissions Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following:
By Source
- Energy Sector
- Electricity & Heat Generation
- Transportation
- Industrial Energy Use
- Buildings
- Fugitive Emissions
- Agriculture, Forestry, and Land Use
- Agricultural Activities
- Deforestation and Land-Use Change
- Forestry and Other Land Sinks
- Industrial Processes and Product Use
- Cement Production
- Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
- Metal Production
- Other Industrial Processes
- Waste Sector
- Solid Waste Disposal
- Wastewater Treatment
By Gas Type
- Carbon Dioxide
- Methane
- Nitrous Oxide
- Fluorinated Gases
By End-Use Industry
- Power Generation
- Transportation & Logistics
- Manufacturing & Industrial Production
- Agriculture & Livestock
- Construction & Buildings
- Waste Management
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Regional Analysis
Region with the Largest Revenue Share
Asia Pacific is expected to lead the global carbon emissions market in 2025, accounting for approximately 52.0% of the total market revenue. This dominance is driven by rapid industrialization, high energy demand, and extensive use of fossil fuels across countries such as China, India, and Southeast Asian nations. The region’s power generation, manufacturing, and transportation sectors contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, making it a central focus for carbon reduction initiatives.
Growing investments in renewable energy, energy-efficient technologies, and carbon trading programs are being implemented to mitigate emissions, while regional policies and climate action plans are increasingly encouraging industries to adopt low-carbon practices. The combination of industrial growth, regulatory frameworks, and sustainability efforts positions Asia Pacific as the largest contributor to both global emissions and market revenue in the carbon emissions sector.

ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Region with significant growth
The Middle East and Africa region is expected to witness significant growth in the global carbon emissions market over the coming years. Rapid industrial expansion, growing energy demand, and large-scale investments in oil, gas, and power generation infrastructure are driving higher greenhouse gas emissions, creating a strong demand for carbon management solutions.
Governments and private sector players are increasingly adopting emission reduction strategies, carbon offset programs, and renewable energy projects to align with international climate commitments. Technological advancements in energy efficiency, carbon capture, and low-carbon industrial processes are further accelerating market growth, making this region a key emerging hub for investment and innovation in the carbon emissions market.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Competitive Landscape
The global carbon emissions market is highly competitive, with key players including Saudi Aramco, Chevron, Gazprom, ExxonMobil, BP, Royal Dutch Shell, PetroChina, and TotalEnergies actively participating in emission reduction initiatives, carbon trading, and renewable energy investments. Companies are increasingly focusing on low-carbon technologies, carbon capture and storage, and energy-efficient solutions to comply with stringent regulatory standards and meet corporate sustainability goals.
Strategic collaborations, mergers and acquisitions, and technological innovations are driving market differentiation, while emerging players in carbon offset programs and green energy solutions are creating additional competitive pressure. The landscape reflects a combination of traditional energy giants and innovative technology providers working to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions and capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable industrial practices.
Some of the prominent players in the global Carbon Emissions market are:
- Saudi Aramco
- Chevron
- Gazprom
- ExxonMobil
- National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC)
- BP
- Royal Dutch Shell
- Coal India
- Pemex
- Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA)
- PetroChina
- Peabody Energy
- ConocoPhillips
- Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC)
- Kuwait Petroleum Corporation
- Iraq National Oil Company
- TotalEnergies (Total SA)
- Sonatrach
- BHP (BHP Billiton)
- Petrobras
- Other Key Players
Global Carbon Emissions Market: Recent Developments
- June 2025: The World Bank reported that carbon pricing revenues exceeded USD 100 billion in 2024, with over half of this revenue generated for public budgets earmarked for environment, infrastructure, and development projects.
- November 2024: DevvStream Holdings Inc. announced the completion of its business combination with Focus Impact Acquisition Corp., securing up to USD 43 million of additional capital to execute growth plans aimed at democratizing access to carbon markets.
- October 2024: Terradot, a carbon removal company operating in Brazil, pioneered the use of enhanced rock weathering (ERW) to accelerate the natural process of carbon sequestration. By spreading fine basalt dust over agricultural land, the company aims to capture atmospheric CO₂ through chemical reactions in the soil.
- August 2024: Arch Resources and CONSOL Energy entered into an all-stock merger of equals to create Core Natural Resources, a premier North American natural resource company focused on global markets.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 988.2 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 6,276.0 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
22.8% |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 124.7 Bn |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| Forecast Data |
2026 – 2034 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Source (Energy Sector, Agriculture, Forestry, and Land Use, Industrial Processes and Product Use, Waste Sector), By Gas Type (Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Nitrous Oxide, Fluorinated Gases), By End-Use Industry (Power Generation, Transportation & Logistics, Manufacturing & Industrial Production, Agriculture & Livestock, Construction & Buildings, Waste Management) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, Rest of Europe; Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
Saudi Aramco, Chevron, Gazprom, ExxonMobil, National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC), BP, Royal Dutch Shell, Coal India, Pemex, Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA), PetroChina, Peabody Energy, ConocoPhillips, Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC), Kuwait Petroleum Corporation, and Others. |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the global Carbon Emissions market?
▾ The global Carbon Emissions market size is estimated to have a value of USD 988.2 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 6,276.0 billion by the end of 2034.
What is the size of the US Carbon Emissions market?
▾ The US Carbon Emissions market is projected to be valued at USD 124.7 billion in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 712.7 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 21.4%.
Which region accounted for the largest global Carbon Emissions market?
▾ Asia Pacific is expected to have the largest market share in the global Carbon Emissions market, with a share of about 52.0% in 2025.
Who are the key players in the global Carbon Emissions market?
▾ Some of the major key players in the global Carbon Emissions market are Saudi Aramco, Chevron, Gazprom, ExxonMobil, National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC), BP, Royal Dutch Shell, Coal India, Pemex, Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA), PetroChina, Peabody Energy, ConocoPhillips, Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC), Kuwait Petroleum Corporation, and Others.
What is the growth rate of the global Carbon Emissions market?
▾ The market is growing at a CAGR of 22.8 percent over the forecasted period.