Market Overview
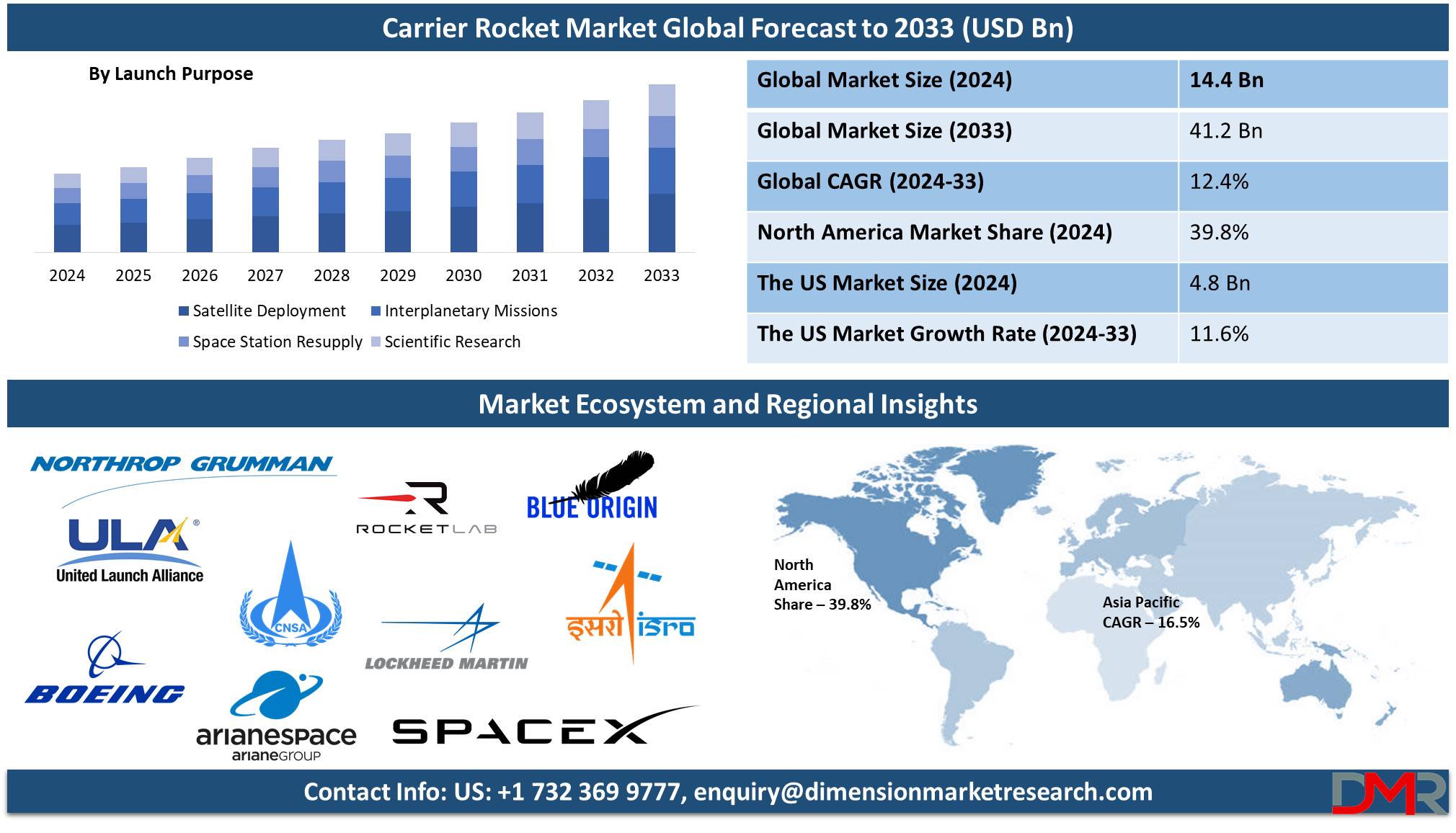
The Global Carrier Rocket Market size is expected to reach a value of USD 14.4 billion in 2024, and it is further anticipated to reach a market value of USD 41.2 billion by 2033 at a CAGR of 12.4%.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
The global carrier rocket market has witnessed a transformational growth pattern, driven by growing demand for satellite deployment and advancement in reusable rocket technology. The industry is also focusing on access and cost-effectiveness to complement the trend of smaller, dedicated launches for LEO satellites. Major players in the platform, such as Rocket Lab USA, Blue Origin, and SpaceX, complete the leading edge that is innovation with hybrid rocket fuel, advanced propulsion systems, and space reusability at record speed, reducing costs and environmental impacts.
Investments in launch infrastructure across emerging markets are boosting global accessibility and democratizing space exploration. This strong growth in the carrier rocket market is expected to be driven by the growing demand for internet connectivity and IoT services delivered through satellite constellations.
In addition to pursuing increasing demand in both government space missions and commercial businesses, the carrier rocket market size is expected to increase at a faster growth rate during the forecast period, backed by technological advancements and changing policies of space.
The market for carrier rockets does show a few very lucrative opportunities, especially in reusable rocket technology. Reusable rockets create game-changing advantages in costs due to lower launch costs, allowing frequent launches and opening access to space for small companies and countries.
This gives a good environment wherein innovative startups and emerging markets' entrance into the space industry might drive broader participation and investment. Besides that, due to ever-growing needs for internet coverage and IoT applications, wide opportunities are also opened in Low Earth Orbit and Medium Earth Orbit satellite constellations. This is further driven by increased global coordination, government funding, and private-area excitement that embolden vast possibilities of growth. The key factor acting positively on the carrier rocket market is the increase in collaboration between governments and private organizations, which speeds up the development concerning rocket technology.
Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin have made huge improvements in the capabilities of rockets, extending access to a wide range of space missions with the help of government contracts. Based on this, a basis for increased collaboration in mutual research activity and stimulation of advanced development in rocket propulsion, reusable technology, and hybrid fuel systems is created. As a result, the public-private synergy accelerates not only the pace of technical progress but also diminishes operational costs, making space launches viable and commercially more viable.
Moreover, the wide application spectrum of carrier rockets in areas like communications, earth observation, and scientific research adds fortitude to the market. As a result, diversification across various industries allows the carrier rocket market to be resistant to fluctuations in demand for certain segments of the industry, as it supports steady market growth and the expansion of service offerings for various end users. Despite good prospects for growth and development, the carrier rocket market faces several challenges, most of which principally stem from high R&D costs and strict regulatory requirements.
Indeed, carrier rockets and reusable technologies require huge investments in financing and technology to raise the barrier to entry for players other than established ones or well-funded new entrants. Thirdly, each launch needs to meet severe safety and environmental requirements that further increase the compliance and operation complexity. This might result in the reduction of competition and slowing down the pace of market innovation, which affects small and emerging companies in particular. Second, the uncontrollable nature that surrounds launching rockets, such as bad weather conditions and technical issues, can lead to very expensive delays, thus affecting profit as a whole. For companies involved in the business, these aspects highly add to financial risk in the long run and make project timelines very complicated.
The demand for small satellite constellations propelled into low and medium earth orbits to facilitate global internet coverage and IoT applications is an accelerating trend in the carrier rocket market. This is the trend that has been pursued by companies like SpaceX with its Starlink project, using sophisticated carrier rockets to fire off hundreds of satellites a year and build huge constellations of satellites in orbit.
It is also driven by the move to more frequent, dedicated launches at a note for small payloads, which supplies the increasing demand for prompt and less costly deployment. Besides, the development of miniaturized satellite technology will increase the ability for larger numbers of smaller satellites to be launched. This is also consistent with the trend of developing rockets specifically for those small payloads, as evidenced by Rocket Lab's Electron rocket. That emphasis shows another way in which the industry has shifted to pay even greater heed to frequency and affordability. This will continue to shape the carrier rocket market with each passing day as small satellite constellations take an ever-larger place in the modern space industry.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
The main customers will be the Department of Defense and major private space companies. It is expected that re-usability to introduce some economies into rockets, which will further open up accessibility by small commercial players. Within the global carrier rocket market, the value is expected to increase substantially by the end of the forecast period and its role in these industries will be cemented; from telecommunications to defense. These statistics certainly point to the strong growth that is foreseeable within the industry, since the demand for space-based services has seen an increase.
The US Carrier Rocket Market
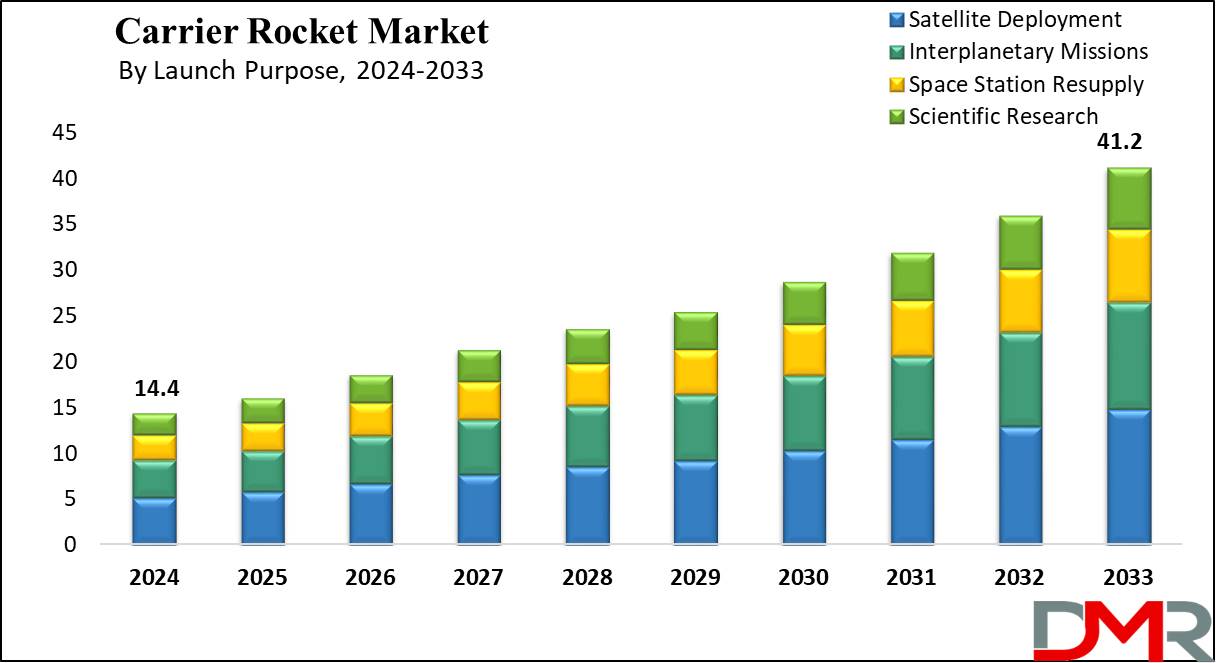
The US Carrier Rocket Market is projected to be valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2024. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 13.0 billion in 2033 at a CAGR of 11.6%.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
The carrier rocket market of the U.S., due to the enormous adjustment of investment by the government and private sector in the interests of space travel and launching satellites, leads the world. NASA and other agencies such as SpaceX, Rocket Lab USA, and Blue Origin make the US a completely different ball game with their pioneering projects on reusable rockets, advanced designing of payloads, and sustainable fuel for launching. Emphasis on reusable rockets, such as the SpaceX Falcon 9, made the U.S. pioneer both the reduction in launch cost and increased frequencies of missions.
Also, satellite infrastructure and surveillance programs by the U.S. government ensure enhanced national security, thereby fueling the requirement for dedicated launches by reliable rockets. Strong policies in support of commercial space ventures and government-private player partnerships further establish the U.S. market. Considering these factors, North America is likely to maintain its lead also during the forecast period in the market due to the intensity of innovation and launch frequency of companies based in the U.S.
This market expansion is attributed to the increasing demand for small satellites and a growing number of space expeditions, spurring the adoption of advanced carrier rocket technologies. The market is segmented by payload type and payload carrying capacity, with the rise of reusable rockets and advancements in hybrid rocket fuel expected to further fuel the growth of the carrier rocket market. Notably, major market players are focusing on developing reusable rocket technologies to optimize costs and meet the demand for carrier rockets across both government and commercial applications. The carrier rocket industry is also witnessing periodic maintenance requirements, which is expected to impact market trends as innovations in rocket technology continue.
Carrier Rocket Market: Key Takeaways
- Global Market Value: The Global Carrier Rocket Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 14.4 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 41.2 billion by the end of 2033.
- The US Market Value: The US Carrier Rocket Market is projected to be valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2024. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 13.0 billion in 2033 at a CAGR of 11.6%.
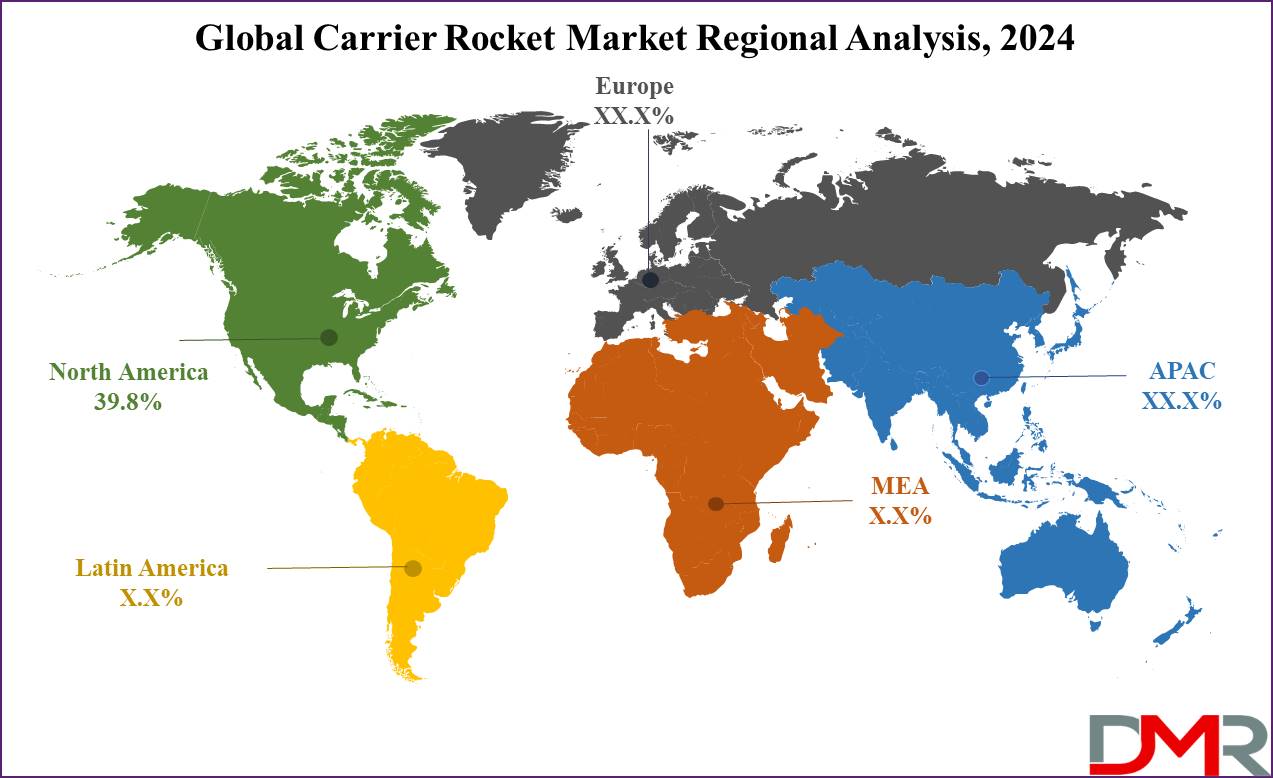
- Regional Analysis: North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Carrier Rocket Market with a share of about 39.8% in 2024.
- Key Players: Some of the major key players in the Global Carrier Rocket Market are SpaceX, Blue Origin, United Launch Alliance (ULA), Northrop Grumman, Arianespace, Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Rocket Lab, China National Space Administration (CNSA), and many others.
- Global Growth Rate: The market is growing at a CAGR of 12.4 percent over the forecasted period.
Carrier Rocket Market: Use Cases
- Satellite Deployment: Every time communications and observation satellites are launched, carrier rockets will always be required. These satellites allow for connectivity by enabling internet connectivity, remote sensing, and location; hence, carrier rockets are among the most important enablers in modern infrastructure.
- Space Exploration: The carrier rockets offer space missions, such as the exploration of the planets and manned flights to space. They provide the launch capability needed for exploratory missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
- Scientific Research: Rockets launch scientific instruments and telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, to make observations impossible from Earth's surface, thus enabling further insight into the structure of the universe.
- Defense and Security: In this, the government launches satellites through carrier rockets to provide surveillance, reconnaissance, and even secret communication for national protection and defense.
Market Dynamics
Trends in the Carrier Rocket Market
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and IoT
An increasing amount of AI and IoT-based technologies are being integrated into carrier rocket systems to improve pre-launch checks, optimize fuel consumption, and ensure precise mission control. Predictive maintenance by AI will reduce downtime and perhaps further improve the success rate of launches, while IoT sensors assist in real-time monitoring and communication from ground control. These developments reduce the difficulty during launching and improve reliability; therefore, AI and IoT integration is a developing trend in carrier rockets.
Expansion of Small Satellite Launch Capabilities
there will be an increasing need for small and medium-class carrier rockets given the forthcoming small and nano-satellite markets for communication and Earth Observation applications. This will create opportunities for smaller payloads to have dedicated launches at cheaper costs and allow other small entities and emerging economies access to space. The development of cost-effective rockets for dedicated or rideshare missions has been increasingly considered and developed for this class of payloads, a factor rapidly remodeling the commercial space sector.
Growth Drivers in the Carrier Rocket Market
Private Sector Investment in Space Ventures
The participation of private firms has brought about a sea change in the carrier rocket market by increasing investment and accelerating the pace of innovation. Private firms bring agility and resourcefulness, which enables much faster development of advanced rocket technologies. This is another important driver for cost reductions, especially with the development of reusable rockets. Successful models presented by such companies as SpaceX and Blue Origin among other global companies encourage more and more actors to join the game.
Global Push for Climate Observation and Disaster Monitoring
Several governments and private players are launching satellites to monitor climate change and also to predict the occurrence of natural disasters. Carrier rockets are vital for launching these satellites to monitor, in real-time, various environmental conditions such as deforestation, glacier melting, and hurricane formation. This focus on environmental awareness and protection is a significant growth driver for the carrier rocket market.
Growth Opportunities in the Carrier Rocket Market
Market Entry for Emerging Economies in Space Exploration
The emerging markets are now investing in space programs on a small scale, many times with the help of partnerships and technology sharing from established space agencies. Examples would include the United Arab Emirates and Brazil, which, to that effect, might go ahead and invest in localized satellite deployment missions for communications, surveillance, and weather observation. It creates new demand for affordable medium-payload rockets that are suited for these applications it encourages collaborative opportunities with established aerospace firms.
Development of Sustainable Fuel Alternatives
Hybrid and green propellant development continues to be a growth opportunity in carrier rockets. These classes of fuels are supposed to be clean, emitting less and causing less environmental harm upon launching rockets. This is the reason companies and governments invest in R&D for greener propellants that would result in compliance with global environmental standardization and which would therefore make the future of the industry eco-friendlier.
Restraints in the Carrier Rocket Market
Space Debris Management and Orbital Congestion
The more frequent the pace of launches, the graver the question of space debris, with potential future missions threatening active satellites operating in orbit. Consequently, the host of management issues regarding orbital space and the implementation of debris-mitigation strategies has come to the forefront. Growing pressure on companies and their regulatory bodies to address identifiable costs associated with managing debris.
Supply Chain Challenges in Rocket Components
The high level of dependence on specialty materials and sophisticated components-such as avionics, propulsion systems, and composites-places a bottleneck on supply. Delays and short supplies of these critical inputs will postpone production timelines, increase operational costs, and impact launch schedules. The geopolitics also extend to the supply chain, considering source materials emanating from regions experiencing instability.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Type Analysis
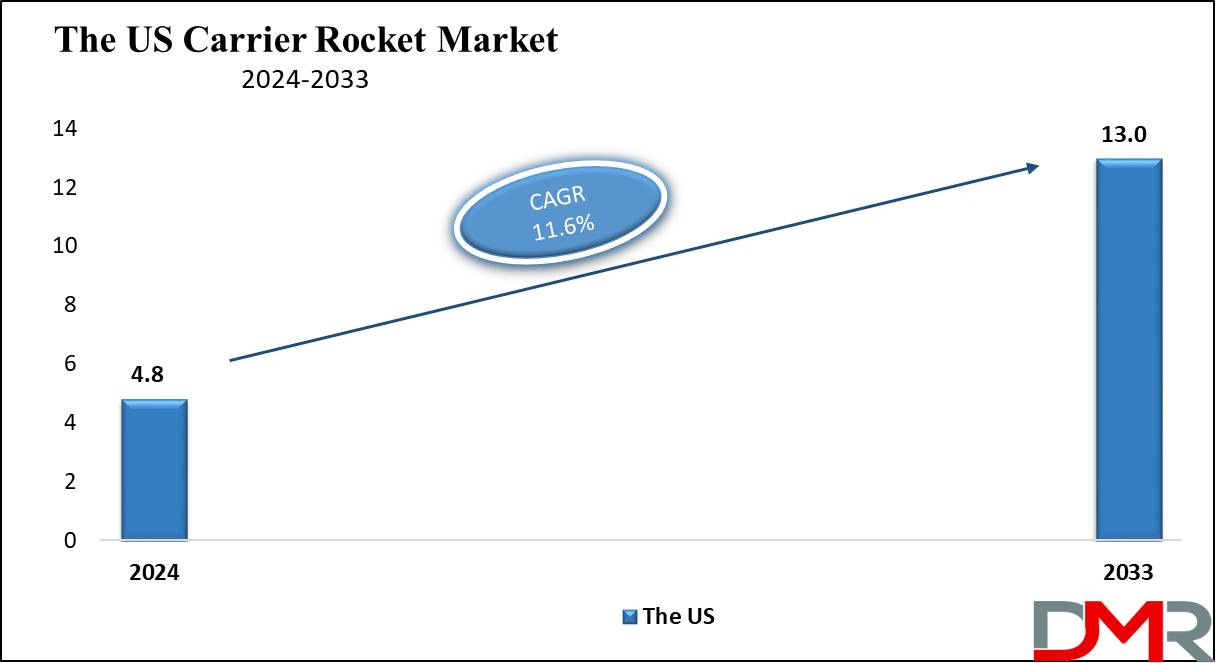
The high dependability of SRBs is projected to dominate the field of carrier rockets, forming tremendous output with much more economical expenditure. Compared to liquid-fueled rocket motors, the design of a solid rocket booster dealing with solid propellants is less complicated in design. This will directly result in fewer mechanical parts and less maintenance; as a result of which, all other operation and maintenance costs, too, will go down. Besides that, SRBs are well-known for being able to provide a quantity of thrust in a very short period, hence making them highly suitable for heavy-lift missions requiring rapid acceleration, as in the deployment of large-size or heavy payloads into low Earth orbit.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Further evidence of the inherent reliability of SRBs lies in their widespread use for high-profile missions, such as NASA's Space Shuttle program and several military satellite deployments. Because this launch sequence creates one extreme of temperature and pressure for these SRBs, designs are carried out in a manner that they always deliver as expected over a wide range of mission profiles. Besides, technological advances in the production of SRB technology have improved composite materials that enhance manufacturing processes for better efficiency and payload capacity.
These technological advances complement increasing the operating life of the SRBs, hence an environmentally friendly option for government and commercial missions. The segment of a solid rocket booster, therefore, secures considerable market share from ongoing innovations and the persistent demand for reliable heavy-lift capabilities in the carrier rocket market.
By Launch Purpose Analysis
Satellite deployment is the main application of carrier rockets, owing to the ever-increasing global demand for communication, earth observation, and navigation-related services. These satellites are being highly developed by both government and commercial organizations to enhance connectivity, strengthen their defense, and fascinatedly develop disaster management systems. Carrier rockets play a major role in deploying satellites with special features such as precise orbital insertion mechanisms to optimally position and operate the satellite.
Encouraged especially by constellations such as SpaceX's Starlink and Amazon's Project Kuiper, the proliferation of small satellites launched into space underlines the very important role that carrier rockets will play in establishing such wide networks for global access to the Internet and IoT infrastructure. These constellations require frequent, cost-effective launches, which carrier rockets are uniquely positioned to realize. Besides that, the economic benefits accruing from satellite deployment-from real data taken in real-time up to widening communication channels-make it one of the most feasible and profitable applications by carrier rockets.
As more and more industries become reliant on satellite data, relating to agriculture, transportation, and environmental monitoring, among others, so does the demand for effective and reliable satellite deployment services surge. Therefore, this sustained deployment of satellites into space for various purposes has positioned the industry as the primary motive behind the launch in the carrier rocket market, hence driving technology advancement and consequently market growth.
By Payload Capacity Analysis
Falling within the medium payload capacity category of 500 kg to 2,000 kg, the dominant position that the carrier rocket market holds is largely based on its exceptionally versatile and cost-effective nature. It is a perfect balance in this range, where the highest demand is recorded for a wide array of missions requiring flexibility and affordability. Medium-payload launchers are particularly suited for deploying small to medium-sized satellite constellations, which are increasingly in demand for such applications as Earth observation, scientific research, and communication networks.
Perhaps the most fundamental reason why medium payload launchers dominate space launch markets is that they can support a wide range of applications without the high costs associated with heavy-lift missions. This makes them most attractive to commercial entities and research institutions that seek to minimize their operational expenses while fulfilling the objectives of a mission. Added to this, the increasing trend in the utilization of medium-sized payloads in deploying commercial constellations, such as for global internet coverage, further reinforces its prominence in this category.
Medium-payload rockets accommodate specialized applications associated with environment monitoring and disaster management, among others, which require precise and reliable deployment. Its adaptability to mission requirements, coupled with the continuous improvement of rocket technology for better performance and lower costs, justifies its dominance in the carrier rocket market.
By Range Analysis
With its strategic advantage in communication, research, and earth observation satellites, Low Earth Orbit has emerged as the predominating range for carrier rockets. Since launching any payload to LEO requires considerably less energy than sending it to other orbits, for reasons of cost and efficiency, missions to LEO are preferable. Due to proximity with the Earth, reduced latency and faster data relay can be achieved for LEO-something very essential for applications like global internet services, real-time monitoring, and responsive communication networks.
The rise of satellite constellations to provide ubiquitous internet access, epitomized by projects such as SpaceX's Starlink and OneWeb, captures the essence of the significance of LEO in the carrier rocket market. These constellations require extremely frequent and dedicated launches just to maintain and expand their network's tendency which makes LEO an alluring range for consistent and reliable deployment. Besides, the relative accessibility of LEO makes replenishment of satellite fleets easier and more frequent to sustain operational capabilities and continuity of service. The emerging demands for real-time earth monitoring and remote sensing applications, dependent on LEO satellites, further cement its dominance.
We can expect this preference to persist as new technological developments continue to enhance the efficiency and capacity of missions in LEO, holding its central role in the carrier rocket market and continuing to drive market growth.
By Launch Frequency Analysis
The increasing need for personalized and flexible deployment of payloads has driven dedicated launches to surge to the forefront of a carrier rocket market that is seeing unprecedented growth. Unlike shared or rideshare launches, in the dedicated launches category, a carrier rocket exclusively avails one client with the precision of controlling the launch timeline, orbital parameters, and configuration of the payload. This tailored approach is of particular benefit for high-priority or sensitive payloads, which may require specific orbits and uncompromised launch schedules, such as those of national security satellites and critical commercial communications satellites.
In fact, to date, the growth of small satellites has promoted greater demand for dedicated launches to the point that many companies are looking for fast and individualized deployment solutions as their primary means for retaining and building up their satellite constellations. Advancing reusable rocket technology has increased availability and lowered the cost of dedicated launches, making them increasingly attractive. Dedicated launches from companies like SpaceX and Rocket Lab USA are available in a range of sizes from very small to a few thousand kilograms and satisfy a range of mission needs from low Earth orbit constellations to interplanetary missions.
It includes avoiding delays related to shared launches and ensuring mission-specific tailoring, both of which go well with the operational goals of government agencies and private enterprises. As a final consideration, faithful choices do make dedicated launches dominant in the carrier rocket market when it comes to frequency, reflecting the growing preference for reliable, efficient, and mission-aligned launch solutions.
By Industry Vertical Analysis
Government space agencies such as NASA, ESA, and Roscosmos remain the dominant verticals of the carrier rocket market owing to massive funding, huge infrastructure, and R&D facilities, with strategic imperatives in deploying satellites and space exploratory programs. It is also these space agencies that hold the focused prime resources and are in a situation to drive rocket technologies toward next-level payload capacities, fuel efficiency, and mission reliability. This means that their most crucial roles in national security, scientific research, and space exploration impose the necessity of employing highly reliable and advanced carrier rockets, further entrenching their lead in the market.
Space missions require considerable budgets invested by governments, continuously investable in the latest rocket technologies and space infrastructure. Financial support is reassuring for the development of new propulsion systems, sustainable fuel solutions, and advanced payload delivery mechanisms. Government-funded missions usually deal with long-term and high-stakes missions that require reliable launch services, thus tumbling the way for potential strong relationships between leading rocket manufacturers and launch service providers. Such collaboration ensures continuous technological advancement, where undisputedly state-of-the-art carrier rockets come into availability for certain mission requirements.
Moreover, the industrial standards and manufacture of carrier rockets are designated and regulated by government space agencies, further influencing market dynamics and driving quality improvements across the entire market. Examples include NASA's Artemis program and Earth observation missions by ESA. This demand, brought about by such strategic missions, is continuous and thus provokes continuous growth and advancement in the sector.
The Carrier Rocket Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Type
- Solid Rocket Boosters
- Liquid Rocket Engines
- Hybrid Rockets
- Cryogenic Rockets
By Launch Purpose
- Satellite Deployment
- Interplanetary Missions
- Space Station Resupply
- Scientific Research
By Payload Capacity
- Small Payload (up to 500 kg)
- Medium Payload (500 kg - 2,000 kg)
- Large Payload (2,000 kg - 10,000 kg)
- Heavy Payload (10,000 kg and above)
By Range
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO)
- High Earth Orbit (HEO)
- Interplanetary
By Launch Frequency
- Dedicated Launches
- Rideshare Missions
- Regularly Scheduled Launches
By Industry Vertical
- Government Space Agencies
- Private Aerospace Companies
- Educational and Research Institutions
- International Space Organizations
- Defense Agencies
- Commercial Enterprise
Regional Analysis
North America is projected to exert its dominance in the global carrier rocket market as it will hold 39.8% of the total market revenue by the end of 2024. North America, especially the United States, occupies the major share in the carrier rocket market, backed by heavy investment in space projects both from public and private operators. The leading position is underlined by pioneering firms like SpaceX, Rocket Lab USA, and Blue Origin which have led groundbreaking changes in rocket technology with innovative reusable rockets, sophisticated payload designs, and sustainable fuels for launching.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
SpaceX's Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets have already shown the disruptive impact that recoverable launch technology can have on launch costs and mission cadence and raised the bar in terms of industry benchmarks for cost efficiency and reliability. Government programs are a prime driver to maintaining North America's edge.
Major funding usually flows into either rocket development or satellite deployment programs with priorities in space exploration and national security by agencies like NASA and the Department of Defense. It is these high ambitions that spur such programs, forging key partnerships among government agencies and private firms and propelling not just technological advancement but also greatly influencing synergy to catapult the pace of innovation and market growth.
Besides, North America certainly offers a very conducive environment from the regulatory perspective for the private participation factor that brings significant motivation to entrepreneurship and competition in the space industry. Thereby, with the growing demand for satellite-based services across the globe, North America is in an ideal position to leverage new opportunities opening up, backed as it is by leading-edge capability and further investment currently being made in rocket technology.
Thus, this setting of focus for the region on sustainability through the development of eco-friendly fuels and reusable rocket technologies increases its standing within global environmental standards and therefore makes those more attractive in the international market. As a result, during the forecast period, North America is bound to continue holding the leading position in the carrier rocket market, given its holistic ecosystem of innovation, investment, and strategic collaboration.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Competitive Landscape
Competition in the carrier rocket market is characterized by dynamic interaction between established industry leaders and innovative entrants, each in pursuit of an important share in the burgeoning global demand for satellite deployment, space exploration, and defense. Major players like SpaceX, Rocket Lab USA, and Blue Origin have dominated the market with a relentless focus on technological innovation, cost-efficiency, and strategic partnerships.
SpaceX led them with pioneering reusable Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy, which shook the economics of space launches by drastically lowering their cost and enabling the quick turn-around of missions. Aggressive expansion by SpaceX into global satellite constellations and its successful track record for frequent, reliable launches consolidate its position as a market leader. In addition, the Starship project from SpaceX further expands its heavy-lift capability to further position the firm for deep-space missions.
Both international collaboration and strategic alliances are the two major facilitators that shape the competitive landscape and help in the exchange of technology, thereby enabling new market opportunities. Joint ventures and other forms of partnering by global actors enhance innovation and operational efficiencies, fostering a globally more integrated and competitive market. The investment in the carrier rocket market is also growing in the spheres of research and development, especially in reusable and sustainable rocket technologies. In effect, this has instigated continuous innovation that enables firms to press on with developing capacity for launches at reduced costs, hence increasing competition.
In the carrier rocket market, competition will be very dynamic since key players will strive incessantly to innovate in order to meet demands coming from government agencies, commercial clients, and scientific institutions around the world. Cost-efficiency, reliability, and technological excellence will remain the prime movers in the future shape of the market, shaping up an environment of robust competition and sustained growth.
Some of the prominent players in the Global Carrier Rocket Market are
- SpaceX
- Blue Origin
- United Launch Alliance (ULA)
- Northrop Grumman
- Arianespace
- Lockheed Martin
- Boeing
- Rocket Lab
- China National Space Administration (CNSA)
- Roscosmos
- ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation)
- Virgin Orbit
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In October 2024, SpaceX's Falcon 9 reusable rocket program reaches a milestone with its 50th successful launch, demonstrating significant advancements in reusability and cost reduction. This achievement underscores SpaceX's commitment to making space access more affordable and sustainable, setting a new standard for the industry.
- In September 2024, Rocket Lab announced the development of its Neutron rocket, a new heavy-lift model designed to accommodate the growing demand for medium-payload satellite launches. Neutron's enhanced lift capacity and rapid reusability features aim to capture a larger market share in both commercial and governmental sectors.
- In August 2024, Blue Origin enters a strategic partnership with NASA's Glenn Research Center to test and develop hybrid rocket fuel solutions. This collaboration focuses on creating more environmentally friendly propulsion systems, aligning with global sustainability goals and NASA's Artemis program objectives.
- In December 2023, The European Space Agency (ESA) successfully conducted its first operational mission using the Ariane 6 rocket, deploying a multi-spectral imaging satellite for advanced earth observation. This launch expands ESA's low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellation, enhancing capabilities in environmental monitoring and disaster management.
- In November 2023, NASA awards multiple contracts to emerging rocket companies, supporting innovations in low-cost and small payload launch technologies. This initiative aims to diversify the supply chain, foster new market entrants, and reduce overall launch costs through increased competition and technological advancements.
- In October 2023, Arianespace unveils the inaugural launch of the Vega C rocket, marking a significant upgrade in their small-to-medium payload launch capabilities. The Vega C's improved performance and cost-efficiency enhance Arianespace's competitiveness in the growing market for dedicated small satellite missions.
- In April 2023, India's Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) achieved a major milestone with the successful deployment of its Gaganyaan mission, utilizing its indigenous carrier rockets for manned spaceflight. This accomplishment highlights ISRO's growing capabilities and ambition in the global space arena.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2024) |
USD 14.4 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2033) |
USD 41.2 Bn |
| CAGR (2024-2033) |
12.4% |
| Historical Data |
2018 – 2023 |
| The US Market Size (2024) |
USD 4.8 Bn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Estimate Year |
2024 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors and etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Type (Solid Rocket Boosters, Liquid Rocket Engines, Hybrid Rockets, and Cryogenic Rockets), By Launch Purpose (Satellite Deployment, Interplanetary Missions, Space Station Resupply, and Scientific Research), By Payload Capacity (Small Payload (up to 500 kg), Medium Payload (500 kg - 2,000 kg), Large Payload (2,000 kg - 10,000 kg), and Heavy Payload (10,000 kg and above)), By Range (Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), Geostationary Orbit (GEO), High Earth Orbit (HEO), and Interplanetary), By Launch Frequency (Dedicated Launches, Rideshare Missions, and Regularly Scheduled Launches), By Industry Vertical (Government Space Agencies, Private Aerospace Companies, Educational and Research Institutions, International Space Organizations, Defense Agencies, and Commercial Enterprise) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – The US and Canada; Europe – Germany, The UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Europe; Asia- Pacific– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, & Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
SpaceX, Blue Origin, United Launch Alliance (ULA), Northrop Grumman, Arianespace, Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Rocket Lab, China National Space Administration (CNSA), Roscosmos, ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation), Virgin Orbit, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users) and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the Global Carrier Rocket Market?
▾ e Global Carrier Rocket Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 14.4 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 41.2 billion by the end of 2033.
What is the size of the US Carrier Rocket Market?
▾ The US Carrier Rocket Market is projected to be valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2024. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 13.0 billion in 2033 at a CAGR of 11.6%.
Which region accounted for the largest Global Carrier Rocket Market?
▾ North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Carrier Rocket Market with a share of about 39.8% in 2024.
Who are the key players in the Global Carrier Rocket Market?
▾ Some of the major key players in the Global Carrier Rocket Market are SpaceX, Blue Origin, United Launch Alliance (ULA), Northrop Grumman, Arianespace, Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Rocket Lab, China National Space Administration (CNSA), and many others.
What is the growth rate in the Global Carrier Rocket Market?
▾ The market is growing at a CAGR of 12.4 percent over the forecasted period.