Market Overview
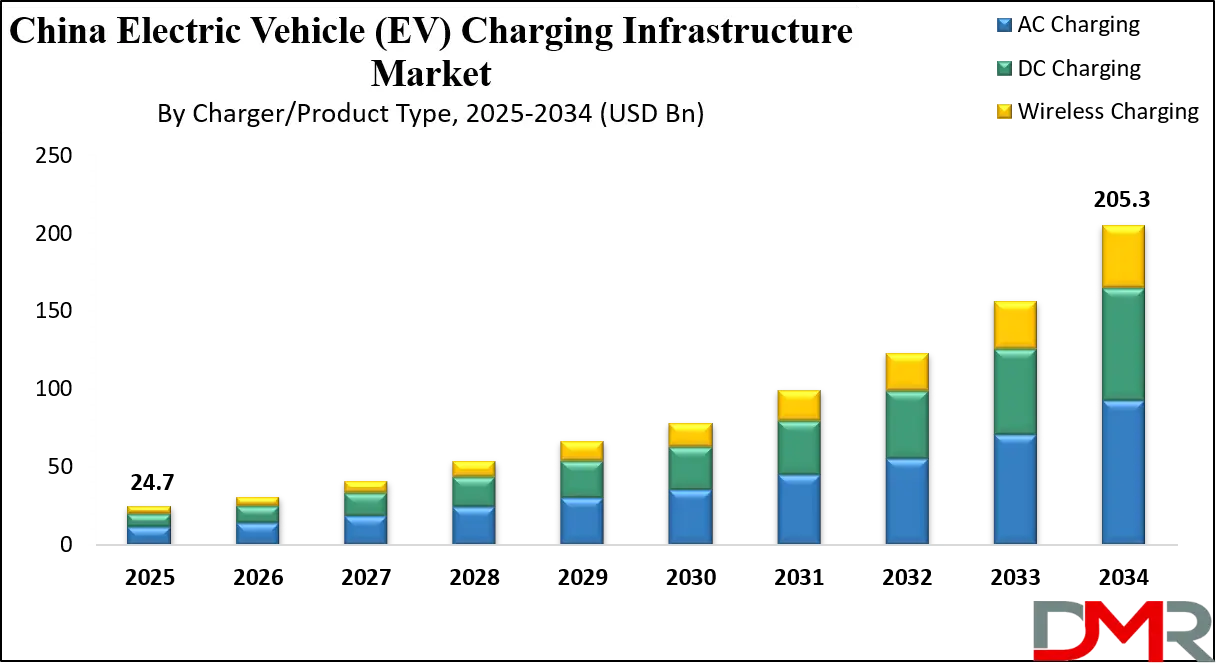
The China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market is projected to surge from USD 24.7 billion in 2025 to USD 205.3 billion by 2034, registering a remarkable CAGR of 26.5% during the forecast period. This exponential growth reinforces China’s status as the global epicenter of electrified mobility driven by robust state-backed industrial strategies, massive public investments, and unparalleled consumer adoption of electric vehicles.
Through aggressive policy frameworks, such as the 14th Five-Year Plan for Modern Energy Systems and the New Energy Vehicle (NEV) Industry Development Plan (2021–2035), China continues to advance a nationwide transition toward zero-emission transport supported by the world’s most extensive EV charging network.

ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
State-directed initiatives and partnerships between central ministries, provincial governments, and private enterprises are accelerating the deployment of AC Level 2, DC fast, and ultra-fast high-power charging systems across urban centers, expressways, logistics hubs, and industrial zones. Integration with renewable energy sources, AI-powered grid management, and IoT-enabled smart platforms ensures optimized load distribution and energy efficiency.
Market leaders such as State Grid Corporation of China, China Southern Power Grid, TELD, Star Charge, and NIO Power dominate deployment, leveraging AI-driven analytics, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) capabilities, and battery-energy-storage integration to enhance grid resilience. While AC Level 2 chargers prevail in residential and semi-public segments, DC ultra-fast chargers (150–350 kW and above) are rapidly expanding along national highways to support China’s enormous EV fleet.
China’s unwavering emphasis on digital connectivity, standardization, and renewable-powered charging ecosystems positions it as the global benchmark for smart, sustainable, and future-ready e-mobility infrastructure cementing its leadership in the global transition to clean transportation.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Key Takeaways
- Exponential Growth Trajectory: The market is projected to grow from USD 24.7 billion in 2025 to USD 205.3 billion by 2034, at a remarkable CAGR of 26.5%, fueled by strong policy, consumer adoption, and investment.
- Powerful Policy & Investment Engine: Aggressive government mandates and substantial state-level funding are accelerating public-private partnerships, ensuring rapid infrastructure deployment nationwide.
- Dual-Track Charging Deployment: While AC chargers dominate residential and workplace settings, DC ultra-fast chargers are being rapidly installed along major transport corridors to facilitate long-distance travel.
- Pioneering Intelligent Networks: China leads in smart, cloud-based charging ecosystems that utilize IoT and AI for grid load balancing, predictive maintenance, and system-wide operational efficiency.
- Dynamic, Collaborative Competition: The market is characterized by a mix of state-owned utility giants and agile private firms, including charging specialists and automakers, who are forming alliances to scale the network.
- Focused Geographic Rollout: Infrastructure development is prioritized in high-density megacities and along critical national highway networks to serve both urban dwellers and inter-city travel.
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Use Cases
- National Ultra-Fast Charging Corridor Network: China’s State Grid and Southern Power Grid are deploying 350–600 kW ultra-fast DC corridors linking major cities like Beijing–Shanghai. These enable sub-20-minute charging, renewable integration, and nationwide EV mobility, advancing intercity electrification and logistics decarbonization.
- Smart City Charging and Energy Management Ecosystems: Cities like Shanghai and Shenzhen employ AI, IoT, and OCPP-compliant systems for intelligent charging management, balancing load demand, integrating renewables, and applying time-of-use pricing supporting China’s New Infrastructure strategy toward grid efficiency, decarbonization, and smart mobility transformation.
- Fleet and Logistics Depot Electrification: Operators including SF Express, Didi, and JD Logistics deploy centralized DC charging hubs using AI for scheduling, load optimization, and battery health monitoring reducing operational costs, emissions, and energy peaks while advancing logistics fleet electrification goals.
- Commercial and Destination Charging Integration: Retailers and property developers like Alibaba and Wanda integrate AC/DC chargers in malls, offices, and hotels enhancing customer dwell time, sustainability branding, and user convenience through mobile payments, real-time availability apps, and loyalty program integration.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) and Renewable Integration Pilots: NIO, BYD, and State Grid test V2G pilots enabling EVs to discharge power during peaks, stabilize grid frequency, and support renewable microgrids creating bi-directional energy ecosystems aligned with China’s 2060 carbon-neutrality commitment.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market
- AI-Powered Energy Distribution Forecasting: Artificial intelligence models forecast regional energy demand based on EV density, climate patterns, and grid data optimizing electricity dispatch, preventing overloads, and aligning renewable integration strategies across China’s expanding ultra-fast and residential charging infrastructure network.
- Adaptive Charging Speed Control Systems: AI dynamically regulates power output according to battery state, charger capacity, and grid stability ensuring optimal charging speed, reducing energy waste, and extending EV battery life while maintaining system efficiency across China’s public and private charging ecosystems.
- Real-Time Fault Detection and Predictive Repairs: AI-driven diagnostic platforms detect anomalies in charging equipment using sensor analytics and predictive algorithms triggering automated maintenance alerts, minimizing service downtime, and ensuring consistent charger reliability across high-demand urban and expressway networks in China.
- Intelligent Pricing and Demand Response Management: AI-powered systems apply time-of-use pricing and demand response signals to shift user behavior during peak hours optimizing grid balance, enhancing profitability for operators, and supporting China’s carbon neutrality roadmap through efficient electricity consumption management.
- AI-Enhanced Interoperability and Data Security: Through blockchain-integrated AI algorithms, charging networks ensure secure authentication, prevent data breaches, and maintain interoperability between multiple operators strengthening trust, transparency, and cybersecurity resilience across China’s smart, connected, and vehicle-to-grid EV infrastructure ecosystem.
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Stats & Facts
National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) & Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT)
- China’s industrial plans target over 40 million new energy vehicles on the road by 2030.
- To support this, the country is building the world's largest charging network, with targets for millions of public charging points by the end of the decade.
State Council & Ministry of Finance
- Billions of USD in direct subsidies, tax exemptions, and local government incentives have been allocated to promote EV purchases and expand charging networks.
- Various provincial and municipal programs offer significant grants covering the installation costs of private and public charging points.
China Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Promotion Alliance (EVCIPA)
- China’s public charging network expanded by over 40% in 2024, adding hundreds of thousands of new points.
- As of Q4 2024, China operated over 2 million public charging points, representing the vast majority of the global total.
- The number of ultra-rapid chargers (≥150 kW) is growing exponentially, with a doubling of installations seen in 2024 alone.
- Key economic zones like the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, Yangtze River Delta, and Pearl River Delta host the majority of China’s public charging infrastructure.
International Energy Agency (IEA)
- China accounts for over 60% of the world's public slow and fast charging points.
- The density of high-power charging capability is rapidly increasing, with significant investments focused on ultra-fast technology.
State Grid Corporation of China (Corporate Report)
- State Grid installed thousands of public chargers per month in 2024, with tens of thousands of new stations under construction or in the planning pipeline across the country.
EVCIPA Joint Data
- By December 2024, China recorded over 2.5 million public charging points, a year-on-year increase of over 50%.
- A significant and growing proportion of new installations are in the 50–250 kW and 250kW+ power ranges, demonstrating the rapid mainstreaming of ultra-fast charging.
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Market Dynamics
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Driving Factors
Formidable Government Support and State-Led Investment
A key catalyst driving China’s EV charging infrastructure expansion is the powerful, top-down national strategy. China’s latest Five-Year Plans and the "Dual Carbon" goals (Carbon Peak, Carbon Neutrality) allocate immense financial and policy resources toward building a comprehensive charging network.
This state-led capital infusion and regulatory mandate have de-risked private sector investments and enabled a rollout at a scale unmatched elsewhere. Furthermore, national mandates such as the New Energy Vehicle (NEV) credit system and long-term targets for NEV dominance provide an irreversible regulatory push for automakers and infrastructure developers. Together, these policies are fueling a decisive transformation of the entire mobility ecosystem.
World's Largest Electric Vehicle Fleet and Mass Consumer Adoption
China’s colossal and rapidly growing electric vehicle fleet forms the foundational demand for charging infrastructure. National and local purchase incentives, license plate privileges, and extensive model availability have made EVs the default choice for millions of new car buyers.
As more EVs enter the market, the requirement for a ubiquitous and reliable charging network intensifies. This creates a powerful virtuous cycle: a denser charging network eliminates range anxiety, which further accelerates EV adoption. This, in turn, stimulates more investment into network expansion, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem that supports China’s national energy security and technological leadership ambitions.
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Restraints
Regional Infrastructure Disparities
Despite massive national progress, China faces significant geographic disparities in charging infrastructure distribution. Affluent coastal provinces and megacities enjoy extremely dense charging networks, while some central, western, and rural regions have less developed infrastructure. These "charging gaps" can constrain nationwide electric mobility and deter consumer confidence in less developed areas. Ensuring equitable access across all provinces remains a challenge to achieving truly uniform national electrification.
Grid Integration Challenges at Scale
The sheer scale and speed of China's EV infrastructure rollout present unique challenges for grid integration. While the national grid is robust, local distribution networks in some fast-developing urban areas can experience congestion. Coordinating the connection of hundreds of thousands of high-power chargers requires meticulous planning and upgrades to local grid infrastructure. Managing the simultaneous energy demand from numerous ultra-fast chargers, especially during peak hours, is a complex task that requires continuous investment and smart management solutions to prevent localized instability.
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Opportunities
Deep Integration with Renewable Energy and Storage
A major growth avenue for China lies in fully merging its world-leading EV charging network with its equally massive renewable energy sector. Co-locating charging hubs with solar and wind generation, coupled with giant stationary battery storage facilities, creates resilient microgrids that can offset peak grid demand. This model lowers operational energy costs, supports national carbon neutrality goals, and enhances energy independence. This synergy positions China as the global benchmark for integrating sustainable energy generation with e-mobility consumption.
Commercialization of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) at Scale
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology represents a transformative opportunity within China’s world-leading EV and energy landscape. With the largest fleet of EVs potentially acting as a distributed energy storage system, V2G can provide unprecedented grid flexibility. Chinese utilities, tech giants, and automakers are positioned to pilot and commercialize V2G systems at a scale impossible elsewhere, transforming EVs into a national energy asset that supports grid stability. This innovation could redefine EV economics by creating new revenue streams and advancing China’s transition toward a decentralized, intelligent energy ecosystem.
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Trends
Massive Expansion of High-Power Charging Corridors
China’s market is defined by the rapid deployment of ultra-fast charging networks along its entire national expressway system (G-series highways). This evolution is strategically focused on enabling effortless long-distance Electric Vehicle travel across the vast country. Operators are investing heavily in high-power stations at service areas to provide refueling times comparable to traditional vehicles. This trend signifies the market's maturity, shifting focus from basic availability to high-performance, high-accessibility, and seamless interoperability on a continental scale.
Total Digitalization and Smart Grid Integration
The Chinese EV charging market is a global leader in digital intelligence. Cloud-based platforms, IoT sensors, and AI-driven analytics are standard, enabling advanced functionalities like predictive maintenance, dynamic load balancing, and fully integrated mobile payments. Super-apps like WeChat and Alipay provide real-time charger availability, reservation, and seamless payment across different providers. This deep digitalization enhances operational efficiency on a massive scale, optimizes national energy consumption, and is the bedrock for advanced applications like V2G, positioning China at the forefront of the global intelligent charging ecosystem.
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Charger / Product Type Analysis
AC charging is expected to dominate this market but DC fast charging is also demonstrating explosive growth and is increasingly dominant in China's EV charging landscape, particularly in public and commercial applications. While AC charging remains widespread in residential areas due to its lower cost and suitability for overnight charging, the market is defined by the rapid deployment of DC fast and ultra-fast chargers.
This shift is driven by the need to support China's massive EV fleet, reduce range anxiety for long-distance travel, and align with the capabilities of newer EV models from domestic leaders like BYD and NIO that support high-power charging. State-owned grid operators and private CPOs are prioritizing DC charger rollouts along national expressways (G-series highways) and in urban hubs to create a comprehensive charging network.
The government's "V2G + Ultra-Fast Charging" pilot programs and substantial subsidies for high-power public infrastructure further accelerate this trend. Although AC chargers will remain a staple in homes and workplaces, the scale, speed, and strategic focus of China's infrastructure build-out are solidifying DC charging's leading role in the market's next growth phase.
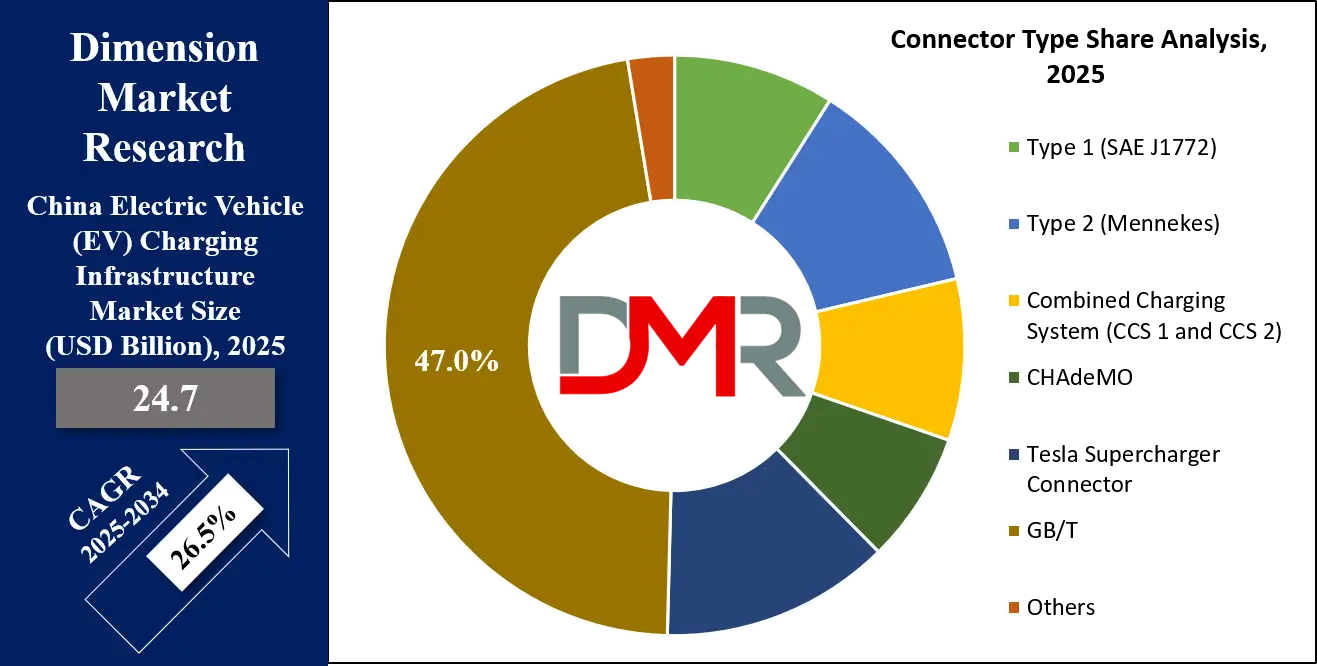
By Connector Type Analysis
GB/T (GuoBiao/T national standard) connectors are projected to be the undisputed dominant standard across China's EV charging network. Mandated by national policy, the GB/T standard ensures complete interoperability within China's domestic market. The AC GB/T connector is universally used for slow and accelerated charging, while the DC GB/T connector is the standard for all fast-charging stations deployed by State Grid, China Southern Power Grid, and private operators like TELD and Star Charge.
This unified standard has been critical for the rapid and scalable deployment of infrastructure, eliminating compatibility confusion for consumers and operators alike. While international standards like CCS2 and CHAdeMO are occasionally found, often to support imported vehicles, they represent a negligible fraction of the market. The dominance of GB/T underscores China's strategy of developing a self-contained, technologically independent EV ecosystem. The standard continues to evolve, with updates supporting higher power levels and V2G functionality, ensuring its centrality in China's electrification roadmap through 2034 and beyond.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
By Installation / Deployment Type Analysis
Fixed charging stations are poised to form the absolute backbone of China's EV charging infrastructure, constituting the vast majority of all operational units. The scale of China's ambition necessitates permanent, high-capacity installations integrated directly into the national and local power grids. Massive investments from state-owned utilities and private companies are focused on building extensive networks of fixed stations, from roadside AC posts to dedicated DC charging parks with dozens of stalls.
These fixed installations are prioritized in national and provincial infrastructure plans, receiving direct subsidies and regulatory support. They are essential for providing the power levels required for ultra-fast charging and for integrating with smart grid management systems. While portable chargers are included as a standard accessory with EV purchases for emergency use, they play no significant role in the public infrastructure strategy. The permanence, reliability, and high capacity of fixed stations are indispensable for supporting the daily charging needs of millions of EVs and enabling long-distance travel across the country, making them the dominant and unquestioned deployment model.
By Charging Level Analysis
DC Fast Charging (Level 3) is the focal point of current market expansion and investment in China. While AC Level 2 charging is prevalent in residential and some workplace settings, the strategic growth and majority of new public investment are directed towards DC fast and ultra-fast chargers. The Chinese government and industry players are focused on solving the "charging time" barrier to mass adoption.
Consequently, there is a massive push to deploy 150kW, 350kW, and even higher-power chargers along all major transportation corridors and in urban centers. This strategy is designed to make EV refueling as quick and convenient as refueling a conventional vehicle, thereby eliminating range anxiety.
The high utilization rates of public chargers in dense urban environments also make the faster turnaround time of DC charging economically imperative for operators. Although AC charging will continue to serve the important overnight "refueling" segment, the growth trajectory, policy support, and technological advancements are squarely aimed at establishing China's leadership in DC fast charging infrastructure on a global scale.
By Operation and Connectivity Analysis
Smart and connected charging solutions are the default standard in China's EV infrastructure market. Nearly all new public and commercial charging stations are equipped with 4G/5G connectivity, integrated payment systems (often via super-apps like WeChat or Alipay), and cloud-based management platforms. Chinese CPOs are global leaders in deploying large-scale, IoT-enabled networks that allow for real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, dynamic load balancing, and predictive maintenance.
This deep connectivity is crucial for managing the immense energy demand from millions of EVs and preventing local grid congestion. Furthermore, it enables advanced features like reservation systems, seamless "plug-and-charge" identification, and integration with renewable energy sources. The national push for a "New Infrastructure" that includes smart grids and IoT ensures that connectivity is not an optional feature but a foundational element. This smart, data-driven approach is essential for optimizing the operational efficiency of the world's largest charging network and for pioneering future technologies like V2G.
By Application Analysis
The Public Charging segment is the projected to be the dominant and most dynamically growing application in China. While private charging in residential complexes is widespread, the scale and visibility of public infrastructure are unparalleled. This includes massive charging plazas on the outskirts of cities, dedicated stations within public parking facilities, and, most critically, extensive networks along China's national expressway system.
The government's strategy explicitly prioritizes the development of a ubiquitous public network to assure current and potential EV owners that charging is always accessible, thereby fueling further EV adoption. This segment is driven by intense competition among private CPOs (TELD, Star Charge) and automakers (NIO, Xpeng) building their own branded networks, as well as by state-owned grid companies ensuring coverage in strategic locations.
The commercial application, which includes charging at malls, hotels, and for fleets, is a significant subset of this public domain. The sheer volume of EVs in dense urban centers, where home charging is not always available, makes a robust, high-utilization public network not just a convenience but a necessity, solidifying its dominance in the market.
The China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following:
By Charger / Product Type
- AC Charging
- Level 1 (120V standard home charging)
- Level 2 (240V commercial and residential charging)
- DC Charging
- DC Fast Charger (50–150 kW)
- Ultra-Fast / Supercharger (>150 kW)
- Wireless Charging
- Static Wireless Charging
- Dynamic Wireless Charging (on-road charging)
By Connector Type
- Type 1 (SAE J1772)
- Type 2 (Mennekes)
- Combined Charging System (CCS 1 and CCS 2)
- CHAdeMO
- Tesla Supercharger Connector
- GB/T
- Others
By Installation / Deployment Type
- Fixed Charging Stations
- Publicly Accessible Stations
- Semi-Public Stations
- Private Stations
- Portable Charging Units
- Mobile EV Chargers
- Temporary Event Chargers
By Charging Level
By Operation and Connectivity
- Operation Mode
- Mode 1
- Mode 2
- Mode 3
- Mode 4
- Connectivity
- Connected Charging Stations
- Non-Connected Charging Stations
By Application
- Residential
- Individual Homes
- Multi-Dwelling Units
- Commercial
- Corporate Offices
- Retail Outlets
- Hospitality & Malls
- Public
- Municipal Parking Areas
- Roadside & Street Charging Points
- Highway Charging Corridors
- Fleet / Transport Hubs
- Public Transit Depots
- Logistics & Delivery Hubs
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of China's EV charging infrastructure market is a dynamic and fiercely contested arena, characterized by a unique public-private partnership model. Leadership is shared between state-owned behemoths and agile private champions. State Grid and China Southern Power Grid form the foundational backbone, leveraging their vast grid access and capital to deploy extensive public networks, particularly along national expressways and in key urban centers.
In the private sector, specialized Charging Point Operators (CPOs) like TELD and Star Charge have achieved massive scale and market penetration through aggressive expansion and strategic alliances. They dominate many public charging plazas and collaborate widely with commercial property developers.
A distinct and influential competitive force comes from automakers themselves. NIO has differentiated itself with a comprehensive ecosystem, including its proprietary Battery Swap stations and high-power chargers exclusively for its users. BYD, as the world's leading EV seller, is also a significant player, often providing charging solutions for its vast fleet.
This ecosystem is further crowded by technology giants and energy companies, such as CATL, which are investing in next-generation technologies like ultra-fast charging and battery storage integration. The intense competition is driving rapid innovation in charging speed, digital user experience, and business models, as players vie for dominance in the world's largest EV market. The landscape is consolidating, with leaders leveraging data, network effects, and strategic partnerships to secure their positions.
Some of the prominent players in the China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market are:
- State Grid (SGCC)
- China Southern Power Grid (CSG)
- TELD
- Star Charge
- Yun Fast Charge
- EV Power (a subsidiary of Beijing New Energy Vehicle)
- Anyo Technology
- Potevio New Energy Co., Ltd.
- NIO
- BYD
- Tesla
- Xpeng
- CATL (EVOGO battery swap and charging)
- China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC)
- China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec)
- Beijing HuaTian Power Technology Co., Ltd.
- XJ Electric Co., Ltd.
- NARI Technology Co., Ltd.
- Shenzhen INVT Electric Co., Ltd.
- WiTricity
- Other Key Players
China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market: Recent Developments
May 2025
- NIO surpasses 2,500 Power Swap battery swap stations deployed globally, the vast majority in China, and announces a new partnership with GAC Group to co-develop battery swap standards and networks.
April 2025
- CATL launches its latest "God-like Speed" charging technology, claiming to enable a 400 km range charge in 10 minutes, and signs agreements with multiple EV makers and CPOs to deploy the technology.
- TELD and Star Charge announce a major interoperability agreement to deepen data sharing and payment integration across their combined network of over 400,000 chargers.
March 2025
- State Grid unveils a massive investment plan for 2025, focusing on building 4,000 new ultra-fast charging stations along national highways and piloting the integration of large-scale grid-level energy storage at charging hubs.
- Sinopec announces the completion of its 3,000th "Oil-Gas-Hydrogen-Electric" integrated service station, highlighting the rapid co-location of charging with traditional fuel services.
February 2025
- BYD and Shell officially open their first joint-venture mega charging station in Shenzhen, featuring over 100 DC fast chargers, marking a significant step in oil-auto industry collaboration.
January 2025
- The 2nd World New Energy Vehicle Congress (WNEVC) in Haikou features a major exhibition on charging and battery swap tech, with keynotes from CATL, State Grid, and NIO on the future of ultra-fast charging and V2G.
December 2024
- China Southern Power Grid completes a pilot V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) project in Guangzhou, allowing a fleet of 50 EVs to successfully discharge power back to the grid during peak demand.
November 2024
- The 2024 China International Green Vehicle & Charging & Battery Swap Facilities Expo is held in Shanghai, showcasing the latest hardware and software solutions from leading CPOs and manufacturers.
- NIO and Changan Automobile formally sign a strategic cooperation agreement on battery swap, agreeing to share NIO's swap network and co-develop compatible vehicle platforms.
October 2024
- Star Charge secures a new round of funding worth several hundred million USD, earmarked for expanding its high-power charging network and international market presence.
- Geely Auto launches its own branded public charging network, "Geely Charging," aiming to build 1,000 stations by 2025, intensifying competition in the automaker-led CPO space.
September 2024
- Huawei launches its "FusionCharge" solution at the Huawei Connect conference, a full-stack offering for CPOs that includes power modules, power management, and cloud services.
August 2024
- TELD announces a strategic collaboration with Tencent Cloud to leverage its cloud computing and AI capabilities to optimize charging network operations, predictive maintenance, and user experience.
July 2024
- NIO and Volkswagen Group (China) sign a technical partnership agreement, granting Volkswagen access to NIO's battery swap system for its future models in China.
June 2024
- CATL's EVOGO battery swap service network expands to its 10th major city in China, promoting its modular "chocolate battery" swap model.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 24.7 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 205.3 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
26.5% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| Forecast Data |
2026 – 2034 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Charger/Product Type (AC Charging, DC Charging, and Wireless Charging), By Connector Type (Type 1, Type 2, CCS 1 & 2, CHAdeMO, Tesla Supercharger, GB/T, Others), By Installation/Deployment Type (Fixed Charging Stations, Portable Charging Units), By Charging Level (Level 1, Level 2, Level 3), By Operation and Connectivity (Operation Mode, Connectivity), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Public, Fleet/Transport Hubs). |
| Regional Coverage |
China |
| Prominent Players |
State Grid (SGCC), China Southern Power Grid (CSG), TELD, Star Charge, Yun Fast Charge, EV Power, Anyo Technology, Potevio New Energy Co., Ltd., NIO, BYD, Tesla, Xpeng, CATL (EVOGO), China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (Sinopec), Beijing HuaTian Power Technology Co., Ltd., XJ Electric Co., Ltd., NARI Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen INVT Electric Co., Ltd., WiTricity, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market?
▾ The China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 24.7 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 205.3 billion by the end of 2034.
What is the growth rate of the China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market?
▾ The market is growing at a CAGR of 26.5 percent over the forecasted period.
Who are the key players in the China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market?
▾ Some of the major key players in the China Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Infrastructure Market are State Grid (SGCC), China Southern Power Grid (CSG), TELD, Star Charge, Yun Fast Charge, EV Power, Anyo Technology, Potevio New Energy Co., Ltd., and Others.