Market Overview
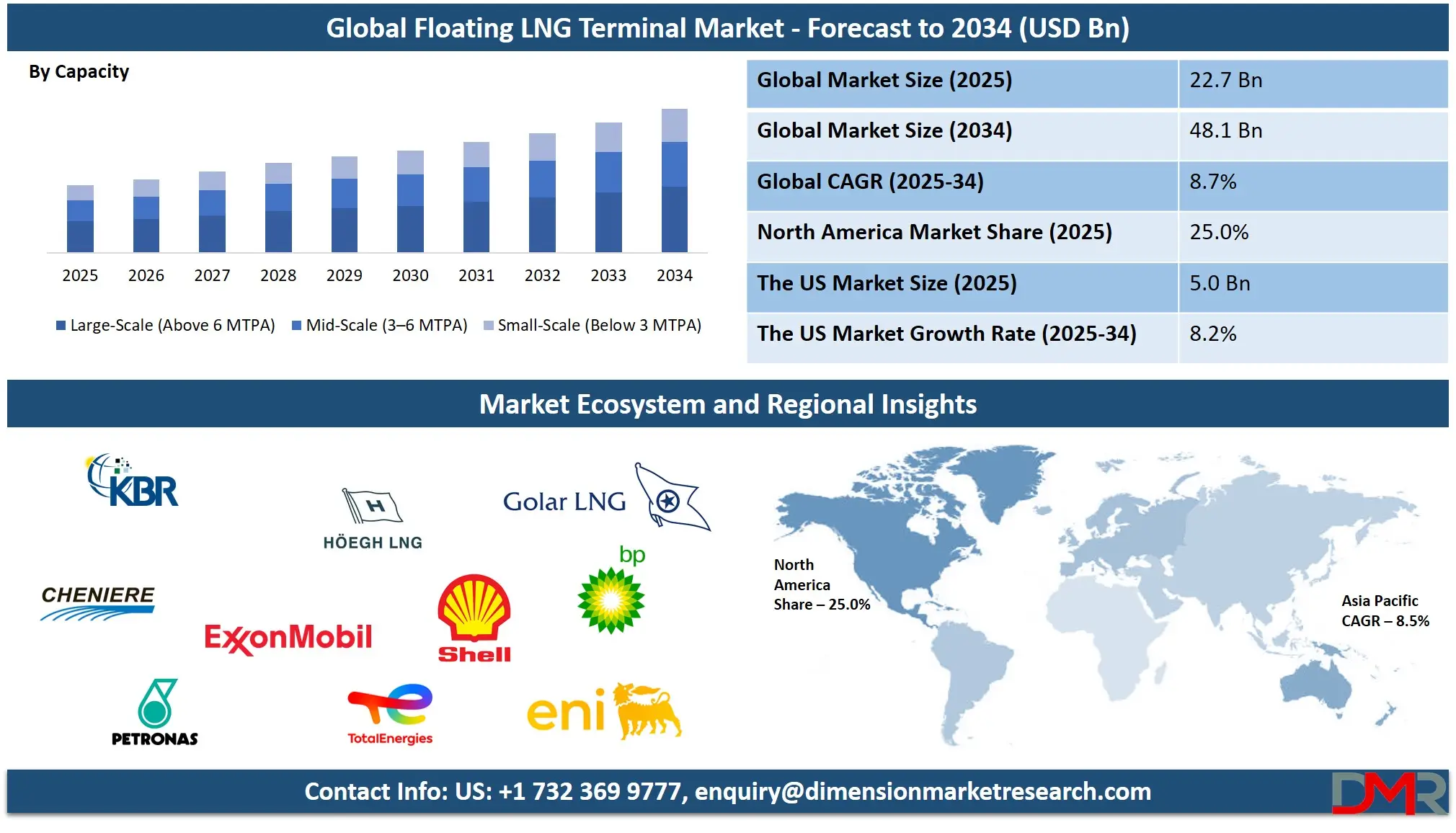
The Global Floating LNG Terminal Market size is projected to reach USD 22.7 billion in 2025 and grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.7% to reach a value of USD 48.1 billion in 2034.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
A Floating LNG Terminal is an offshore liquefied natural gas infrastructure system designed to liquefy, store, regasify, and transfer natural gas without relying on permanent onshore facilities. It includes Floating Storage and Regasification Units, Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Units, and Floating Storage Units operating in nearshore or offshore environments. These terminals integrate cryogenic storage tanks, regasification equipment, marine transfer systems, and specialized mooring technologies. Their modular and mobile design allows rapid deployment, relocation, and scalability, making them suitable for offshore gas processing, LNG import and export operations, and energy supply in regions with limited land availability.
The Floating LNG Terminal Market has gained strategic importance as countries focus on energy security, fuel diversification, and reduced reliance on coal and oil. Floating terminals support the adoption of cleaner-burning natural gas while accommodating fluctuating demand and supply uncertainties. Their flexibility and shorter construction timelines make them attractive for emerging LNG-importing nations and export-oriented gas producers. Shifts in global LNG trade routes and geopolitical supply risks have further increased demand for adaptable offshore LNG infrastructure solutions.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Changes in energy policy and infrastructure planning continue to influence market growth. Large adoption of modular terminal designs, improvements in cryogenic containment systems, and enhanced offshore safety standards are supporting long-term deployment. Rising LNG demand in Asia and Europe, along with accelerated project execution, is encouraging governments and energy companies to prioritize floating LNG terminals within medium- and long-term energy strategies.
The US Floating LNG Terminal Market
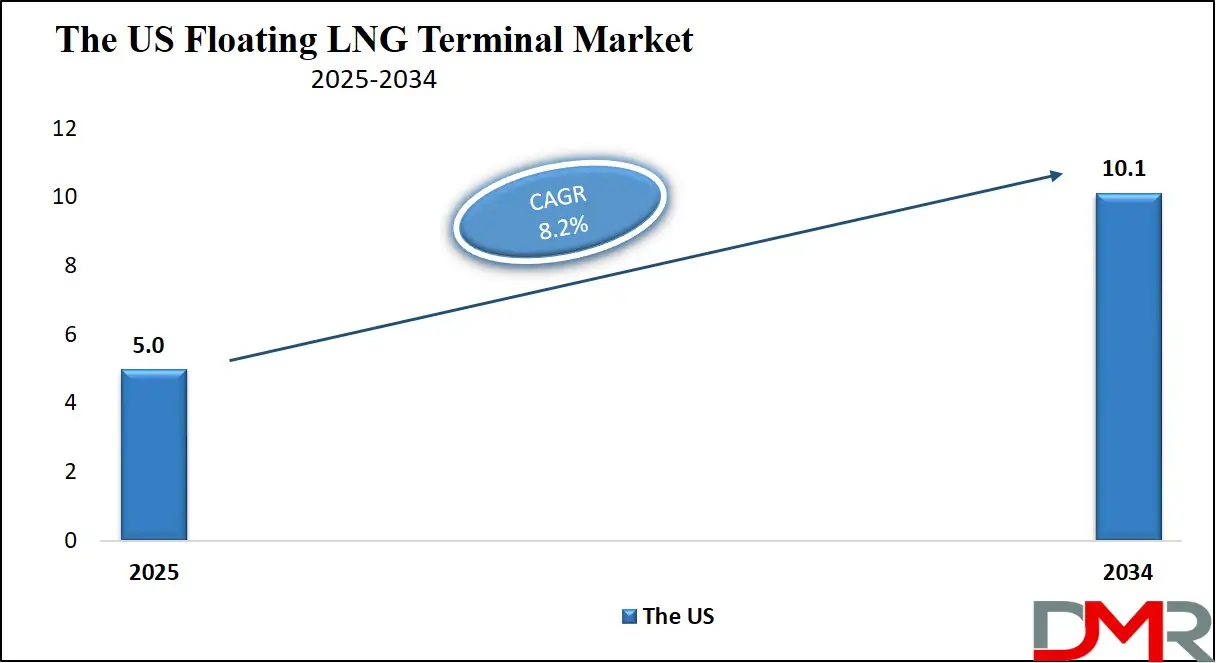
The US Floating LNG Terminal Market size is projected to reach USD 5.0 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 8.2% over its forecast period.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
The United States Floating LNG Terminal Market is shaped by strong natural gas production capacity, export-oriented energy policy, and advanced offshore engineering capabilities. The US benefits from extensive shale gas reserves and established pipeline networks that support LNG liquefaction and export through floating terminals, particularly in the Gulf Coast region. Government permitting reforms, offshore leasing frameworks, and export approvals have encouraged investment in floating LNG infrastructure as a flexible alternative to large onshore terminals. Energy companies in the US favor long-term charter and tolling models to manage price volatility and capital exposure. The presence of experienced maritime contractors and LNG technology providers further supports innovation and scalability in the market.
Europe Floating LNG Terminal Market
Europe Floating LNG Terminal Market size is projected to reach USD 4.5 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 8.0% over its forecast period.
The Europe Floating LNG Market is driven by energy diversification goals, supply security concerns, and regional de-carbonization strategies. Several European countries have adopted floating regasification units to rapidly expand LNG import capacity without constructing permanent onshore facilities. Regulatory alignment with regional climate objectives and cross-border energy cooperation has influenced deployment decisions. Floating terminals are used to stabilize gas supply during peak demand periods and reduce dependency on single-source imports. However, environmental permitting processes and public scrutiny create operational challenges. Despite this, continued policy support for energy resilience and infrastructure flexibility sustains steady market growth across key European coastal economies.
Japan Floating LNG Terminal Market
Japan Floating LNG Terminal Market size is projected to reach USD 1.6 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 7.6% over its forecast period.
Japan’s Floating LNG Terminal Market is supported by high LNG dependency, limited domestic energy resources, and strong government backing for supply stability. Floating terminals are used extensively for LNG import, peak shaving, and coastal power generation, helping utilities manage seasonal demand fluctuations. The market benefits from advanced shipbuilding expertise, strict safety standards, and long-term LNG procurement strategies. Government initiatives promoting energy resilience and cleaner fuels have encouraged continued investment in floating infrastructure. Challenges include high operational costs and space constraints, but Japan’s focus on technological efficiency and reliability continues to create growth opportunities within the floating LNG segment.
Floating LNG Terminal Market: Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Floating LNG Terminal Market size is expected to grow by USD 23.7 billion, at a CAGR of 8.7%, during the forecasted period of 2026 to 2034.
- By Capacity: The large scale segment is anticipated to get the majority share of the Floating LNG Terminal Market in 2025.
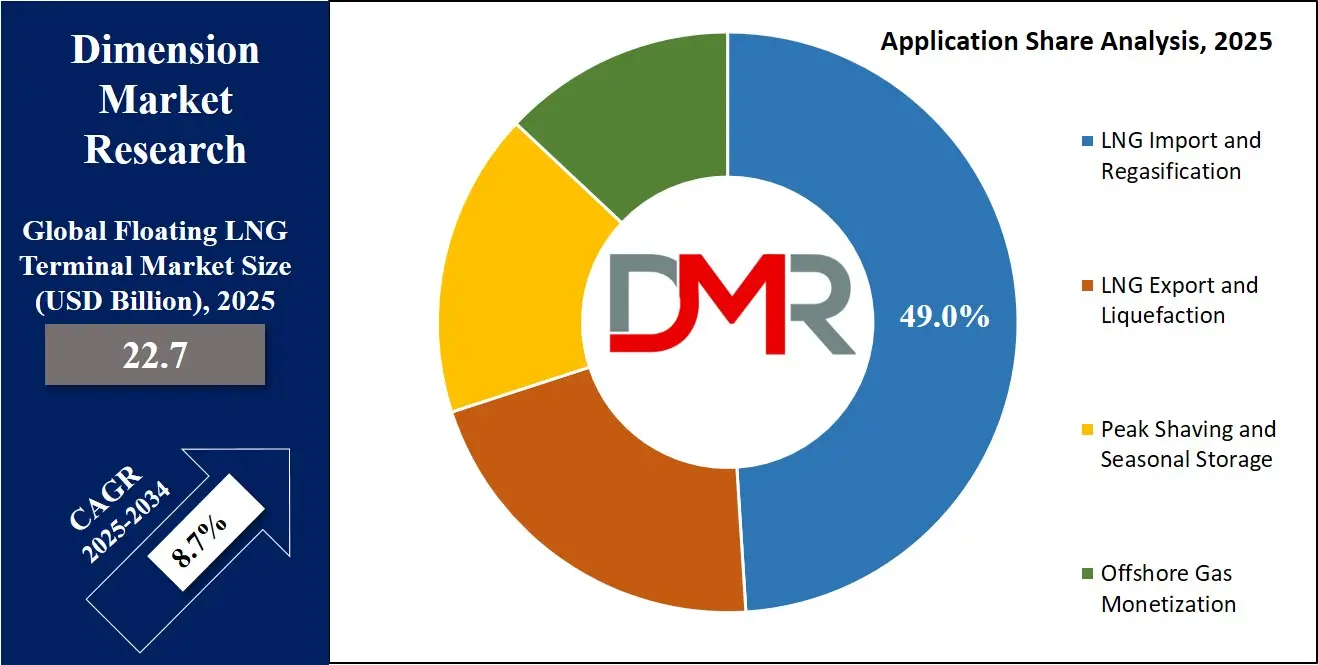
- By Application: LNG import & regasification segment is expected to get the largest revenue share in 2025 in the Floating LNG Terminal Market.
- Regional Insight: Asia Pacific is expected to hold a 48.0% share of revenue in the Global Floating LNG Terminal Market in 2025.
- Use Cases: Some of the use cases of Floating LNG Terminal include energy import security, offshore gas monetization, and more.
Floating LNG Terminal Market: Use Cases
- Energy Import Security: Floating terminals enable rapid LNG imports for countries seeking immediate diversification of gas supply sources without permanent infrastructure.
- Offshore Gas Monetization: FLNG units allow gas producers to liquefy and export offshore gas fields that are uneconomical for onshore development.
- Seasonal Demand Management: Floating storage and regasification units support peak shaving during high-demand periods, especially for power generation.
- Temporary Infrastructure Deployment: Floating terminals provide interim solutions for emerging markets before long-term onshore facilities are developed.
Stats & Facts
- International Energy Agency reports that global LNG trade exceeded 410 million metric tons in 2024.
- International Energy Agency states floating regasification capacity accounted for over 20 percent of global LNG import infrastructure in 2024.
- International Gas Union confirms that more than 50 million tons per annum of floating LNG capacity was under construction globally in 2025.
- US Energy Information Administration reports LNG exports from the United States averaged over 12 billion cubic feet per day in 2024.
- US Energy Information Administration notes that natural gas accounted for approximately 43 percent of US electricity generation in 2024.
- European Commission energy data shows LNG imports supplied over one-third of Europe’s total gas demand in 2024.
- Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Japan reports LNG imports exceeded 65 million tons in 2024.
- International Maritime Organization confirms floating LNG terminals must comply with updated offshore safety codes implemented in 2025.
- International Energy Agency projects global natural gas demand growth of over 2 percent annually through 2025.
- World Bank energy statistics indicate LNG infrastructure investment surpassed USD 90 billion globally in 2024.
Market Dynamic
Driving Factors in the Floating LNG Terminal Market
Energy Security and Supply Diversification
One of the primary drivers of the Floating LNG Terminal Market is the increasing emphasis on energy security and diversification of gas supply sources. Floating terminals enable countries to quickly access global LNG markets without the need for land-based facilities, thereby reducing geopolitical risk exposure. Governments view these assets as strategic tools to stabilize domestic energy systems during supply disruptions. The ability to relocate terminals enhances resilience, allowing operators to respond to changing demand patterns and regional supply imbalances. As the global gas trade becomes more interconnected, floating LNG terminals play a crucial role in enhancing supply flexibility and national energy independence.
Technological Advancements in Offshore LNG Systems
Advancements in offshore engineering, cryogenic containment, and modular processing systems have significantly improved the efficiency and safety of floating LNG terminals. Modern designs reduce construction timelines and operational risks while lowering lifecycle costs. Innovations in mooring systems, digital monitoring, and regasification technology enhance reliability and throughput. These improvements make floating terminals increasingly competitive with onshore alternatives, particularly in regions with limited land availability or strict environmental regulations. As technology matures, the market continues to attract investment from both public and private stakeholders.
Restraints in the Floating LNG Terminal Market
High Capital and Operating Costs
Despite their flexibility, floating LNG terminals involve substantial capital investment, including vessel construction, offshore installation, and specialized equipment. Operating costs related to maintenance, crew, and compliance with maritime safety standards can be high, particularly in harsh offshore environments. These financial barriers limit adoption among smaller economies and private operators. Cost overruns and financing constraints can delay projects and reduce return on investment, impacting market growth. Managing these expenses remains a key challenge for market participants.
Regulatory and Environmental Challenges
Floating LNG terminals must comply with complex regulatory frameworks covering maritime safety, environmental protection, and offshore operations. Environmental concerns related to marine ecosystems, emissions, and coastal impacts can lead to prolonged approval processes. Regulatory uncertainty and public opposition may delay deployment or restrict terminal locations. These challenges increase project risk and complicate long-term planning for developers, particularly in environmentally sensitive regions.
Opportunities in the Floating LNG Terminal Market
Expansion in Emerging LNG Import Markets
Emerging economies with rising energy demand present significant opportunities for floating LNG terminals. These countries often lack established gas infrastructure and benefit from the rapid deployment capabilities of floating solutions. Floating terminals enable governments to transition from coal and oil to cleaner natural gas while avoiding large upfront land investments. As urbanization and industrialization accelerate, demand for flexible LNG infrastructure is expected to grow substantially in these regions.
Integration with Energy Transition Strategies
Floating LNG terminals offer opportunities to support energy transition goals by enabling cleaner fuel adoption and complementing renewable energy systems. Natural gas serves as a bridge fuel, providing grid stability while renewable capacity expands. Floating terminals can be integrated with hybrid energy systems and future low-carbon technologies, enhancing their long-term relevance. Policy incentives and sustainability initiatives further strengthen this opportunity.
Trends in the Floating LNG Terminal Market
Increased Adoption of Lease and Charter Models
A notable trend in the market is the shift toward lease and charter-based business models. Instead of owning assets, operators increasingly prefer long-term leasing arrangements that reduce capital exposure and improve financial flexibility. This trend enables faster project execution and allows countries to test LNG demand before committing to permanent infrastructure. Leasing also supports asset mobility, aligning with evolving market needs.
Digitalization and Automation of Operations
The integration of digital technologies is transforming floating LNG terminal operations. Advanced monitoring systems, predictive maintenance tools, and automation improve efficiency, safety, and uptime. Data-driven decision-making enables operators to optimize performance and reduce operational risks. Digitalization also supports regulatory compliance and environmental monitoring, making floating terminals more sustainable and competitive.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Floating LNG Terminal Market
- Predictive Maintenance: AI systems analyze equipment data to anticipate failures and reduce downtime.
- Operational Optimization: Machine learning improves regasification efficiency and fuel consumption.
- Safety Monitoring: AI-driven surveillance enhances offshore safety and incident prevention.
- Supply Chain Management: AI optimizes LNG logistics and vessel scheduling.
- Demand Forecasting: Algorithms improve LNG demand prediction for better capacity planning.
- Energy Efficiency: AI supports emission reduction through optimized operational control.
- Regulatory Compliance: Automated reporting systems streamline compliance with safety standards.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Terminal Type Analysis
Floating Storage and Regasification Units dominate the Floating LNG Terminal Market, accounting for approximately 52 percent market share in 2025, due to their rapid deployment capability and comparatively lower capital investment than onshore terminals. FSRUs are particularly suitable for LNG-importing countries seeking fast-track solutions to enhance energy security and diversify gas supply sources. Their modular configuration allows easy integration with existing gas networks, while leasing and charter-based models reduce financial risk for operators. These units are widely used for peak demand management and seasonal supply balancing, especially in regions transitioning from coal and oil to natural gas. Long-term agreements with utilities and national gas companies further reinforce their commercial viability and sustained market leadership.
Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Units represent the fastest-growing segment in the Floating LNG Terminal Market, driven by rising offshore gas discoveries and increasing global LNG export demand. FLNG facilities enable the liquefaction, storage, and export of natural gas directly at offshore production sites, eliminating the need for extensive onshore infrastructure. This capability significantly reduces development timelines and environmental footprint, making FLNG attractive for monetizing remote or stranded gas reserves. Technological advancements in liquefaction efficiency, hull design, and safety systems have improved project reliability and operational performance. Growing investments from international energy companies and supportive government policies for offshore resource development are expected to further accelerate the adoption of FLNG units globally.
By Capacity Analysis
Large-scale floating LNG terminals, with capacities above 6 million tons per annum, held around 46 percent market share in 2025, supported by economies of scale and strong demand from long-term LNG trade agreements. These terminals are primarily used for high-volume LNG export and import operations, serving major power generation markets and industrial consumers. Their large processing capacity enables lower unit costs and improved profitability over extended contract periods. Large-scale terminals are commonly associated with national energy strategies and long-term supply security objectives. Despite higher initial investment requirements, their ability to handle consistent and large LNG volumes makes them a preferred choice for established LNG-producing and consuming nations.
Mid-scale floating LNG terminals are experiencing rapid growth due to their balanced combination of capacity, flexibility, and cost efficiency. These terminals are well suited for emerging LNG markets, regional supply hubs, and countries with moderate but growing natural gas demand. Lower capital requirements compared to large-scale facilities make mid-scale terminals attractive for governments and private developers seeking manageable investment exposure. Their adaptability allows deployment in diverse geographic locations, including nearshore and offshore settings. Additionally, mid-scale capacity aligns well with regional power generation needs and industrial gas consumption, enabling faster adoption and scalability as demand increases over time.
By Application Analysis
LNG import and regasification accounted for approximately 49 percent market share in 2025, driven by increasing LNG imports and heightened focus on energy security across multiple regions. Floating regasification terminals provide an efficient and time-sensitive solution for countries seeking to diversify gas supply sources without constructing permanent onshore facilities. These terminals are particularly valuable during supply disruptions and peak demand periods, offering flexibility and rapid commissioning. Their use supports the transition toward cleaner energy by enabling natural gas adoption in power generation and industrial sectors. Government-backed energy diversification programs and growing LNG trade volumes continue to strengthen this segment’s dominance.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
LNG export and liquefaction applications are expanding steadily, fueled by offshore gas development and rising global LNG consumption. Floating liquefaction terminals enable gas producers to access international markets directly from offshore fields, reducing reliance on coastal infrastructure. This application is especially relevant for remote gas reserves that are otherwise uneconomical to develop. Increasing investment in offshore exploration, coupled with advancements in liquefaction technology, has improved operational efficiency and reduced project risk. As global demand for LNG continues to rise, export-oriented floating terminals are expected to play a critical role in meeting supply requirements.
By Deployment Mode Analysis
Nearshore deployment led the Floating LNG Terminal Market with around 55 percent share in 2025, benefiting from easier access to coastal infrastructure and lower operational complexity. Nearshore terminals offer reduced installation and maintenance costs compared to fully offshore facilities, while still providing flexibility and rapid deployment. Proximity to shore allows smoother integration with existing pipelines and power plants, enhancing operational reliability. These terminals are widely adopted for LNG import and regasification applications, particularly in densely populated coastal regions. Favorable regulatory conditions and lower environmental risk further support nearshore deployment as the preferred option for many LNG-importing nations.
Offshore deployment is the fastest-growing segment, driven by increasing offshore gas monetization and export-oriented projects. Offshore floating terminals enable direct processing of gas at production sites, reducing transportation and infrastructure costs. This deployment type is particularly advantageous for remote gas fields and deepwater developments. Technological advancements in offshore mooring, safety systems, and remote operations have improved feasibility and reduced risk. As exploration moves further offshore and demand for flexible LNG export solutions grows, offshore deployment is expected to gain significant traction in the coming years.
By End User Analysis
Power generation companies accounted for approximately 44 percent market share in 2025, reflecting the growing role of natural gas in electricity generation and grid stability. Floating LNG terminals supply reliable fuel to gas-fired power plants, particularly in regions transitioning away from coal and oil. These terminals support base-load and peak-load power generation, ensuring consistent electricity supply. Increasing electrification, urbanization, and renewable energy integration further boost gas demand for balancing purposes. Long-term supply contracts between terminal operators and power utilities enhance market stability and reinforce this segment’s dominant position.
Oil and gas companies represent a rapidly growing end-user segment due to increased offshore production and LNG export strategies. These companies utilize floating LNG terminals to monetize gas reserves, optimize supply chains, and expand global market reach. Floating terminals offer flexibility, reduced development timelines, and lower environmental impact compared to onshore facilities. Rising exploration activity and strategic investments in LNG infrastructure strengthen this segment’s growth outlook.
The Floating LNG Terminal Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following:
By Terminal Type
- Floating Storage and Regasification Unit (FSRU)
- Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Unit (FLNG)
- Floating Storage Unit (FSU)
By Capacity
- Small-Scale (Below 3 MTPA)
- Mid-Scale (3–6 MTPA)
- Large-Scale (Above 6 MTPA)
By Application
- LNG Import and Regasification
- LNG Export and Liquefaction
- Peak Shaving and Seasonal Storage
- Offshore Gas Monetization
By Deployment Type
By End User
- Power Generation Companies
- Oil & Gas Companies
- Industrial Gas Consumers
- National Gas Utilities
Regional Analysis
Leading Region in the Floating LNG Terminal Market
Asia-Pacific led the Floating LNG Terminal Market with approximately 48 percent market share in 2025, driven by rapid industrialization, growing urban populations, and a high dependency on imported liquefied natural gas. Many countries in the region lack sufficient domestic gas resources, making floating LNG terminals a strategic solution for ensuring energy security and supply diversification. Governments actively support LNG infrastructure development through favorable policies and long-term procurement strategies. Floating terminals are widely used for peak demand management and grid stability, particularly in power generation. Strong growth in industrial gas consumption, combined with the transition from coal to cleaner fuels, further reinforces Asia-Pacific’s dominant position in the global market.
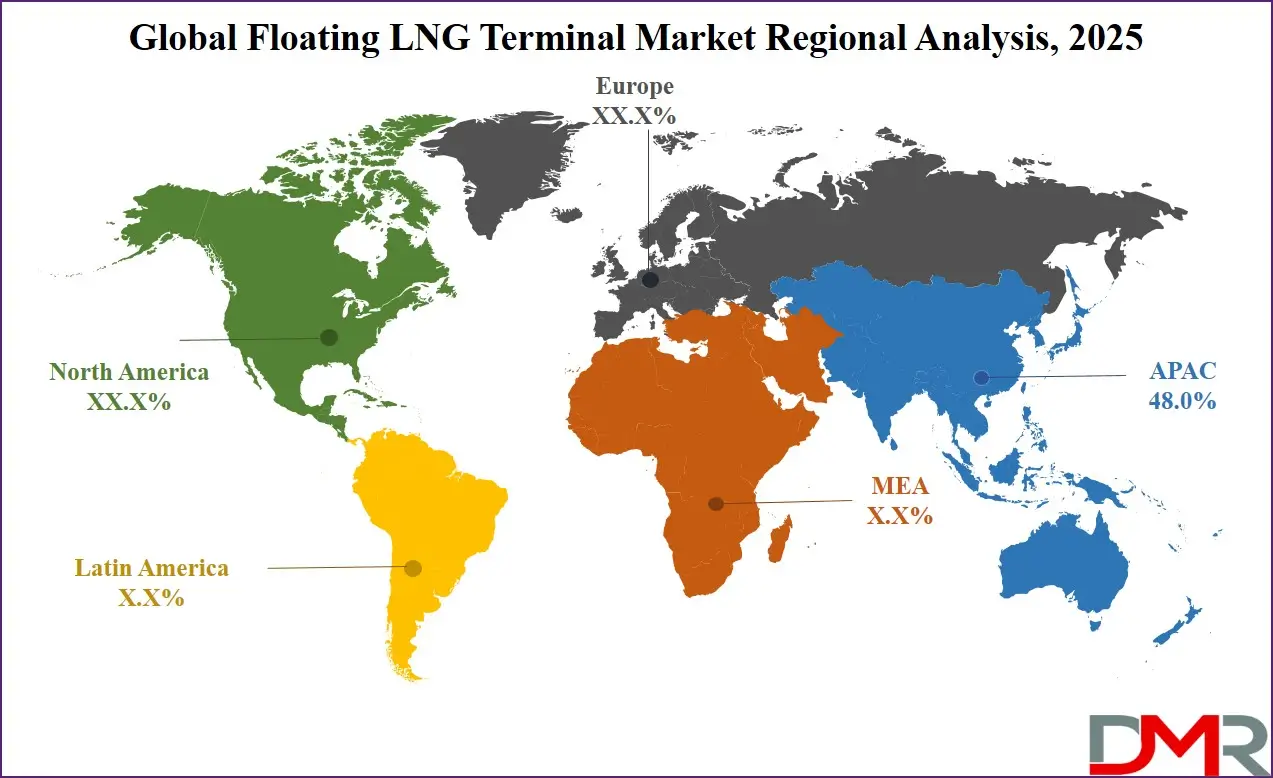
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Fastest Growing Region in the Floating LNG Terminal Market
The Middle East and Africa region is witnessing the fastest growth in the Floating LNG Terminal Market due to significant offshore gas discoveries and export-driven energy strategies. Floating liquefaction terminals enable countries to monetize offshore and remote gas reserves efficiently while reducing reliance on extensive onshore infrastructure. Governments across the region are encouraging LNG development through investment incentives, regulatory support, and national energy diversification plans. International partnerships with global energy companies are accelerating technology transfer and project execution. Growing global demand for LNG exports, coupled with expanding exploration and production activities, positions the Middle East and Africa as a high-growth region for floating LNG terminal deployment.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Competitive Landscape
The Floating LNG Terminal Market is characterized by high entry barriers, capital intensity, and strong technological differentiation. Market participants focus on strategic partnerships, long-term contracts, and continuous innovation to maintain competitiveness. Emphasis on operational efficiency, safety, and flexible business models enables companies to secure market share. Investments in R&D and digitalization further strengthen competitive positioning.
Some of the prominent players in the global Floating LNG Terminal are:
- Shell plc
- ExxonMobil Corporation
- Chevron Corporation
- TotalEnergies SE
- BP plc
- Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS)
- Eni S.p.A.
- Cheniere Energy, Inc.
- Golar LNG Limited
- Höegh LNG Holdings Ltd.
- Excelerate Energy L.P.
- Technip Energies
- Samsung Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.
- Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.
- Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd.
- Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. (MOL)
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Saipem S.p.A.
- KBR, Inc.
- JGC Corporation
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In January 2026, Eni along with its partners, China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), ENH, KOGAS and XRG announced the hull launch of the Coral North FLNG, fully in line with the project schedule. Coral North will be the second state-of-the-art floating LNG facility to be deployed in the Rovuma Basin waters, offshore Cabo Delgado, north of Mozambique, and will bring to production the gas from the northern part of Coral gas reservoir.
- In September 2025, GTT unveiled that it received an order from the shipyard Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) for the tank design of a new Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) unit, which will be deployed in the Africa region. As GTT will design the cryogenic membrane containment system for the LNG storage tanks, with a total capacity of 238,700 m³. The tanks will be fitted with GTT’s Mark III technology, and will highlight its central role in enabling major floating LNG developments in new markets and demonstrates how FLNG solutions can rapidly deliver offshore liquefaction capacity without relying on onshore infrastructure.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 22.7 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 48.1 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
8.7% |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 5.0 Bn |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| Forecast Data |
2026 – 2034 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors and etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Terminal Type (Floating Storage and Regasification Unit (FSRU), Floating Liquefied Natural Gas Unit (FLNG), and Floating Storage Unit (FSU)), By Capacity (Small-Scale (Below 3 MTPA), Mid-Scale (3–6 MTPA), and Large-Scale (Above 6 MTPA)), By Application (LNG Import and Regasification, LNG Export and Liquefaction, Peak Shaving and Seasonal Storage, and Offshore Gas Monetization), By Deployment Type (Nearshore and Offshore), By End User (Power Generation Companies, Oil & Gas Companies, Industrial Gas Consumers, and National Gas Utilities) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – The US and Canada; Europe – Germany, The UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Europe; Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, & Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
Shell plc, ExxonMobil Corporation, Chevron Corporation, TotalEnergies SE, BP plc, Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), Eni S.p.A., Cheniere Energy, Inc., Golar LNG Limited, Höegh LNG Holdings Ltd., Excelerate Energy L.P., Technip Energies, Samsung Heavy Industries Co., Ltd., Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd., Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd., Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. (MOL), Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Saipem S.p.A., KBR, Inc., JGC Corporation, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users) and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the Global Floating LNG Terminal Market?
▾ The Global Floating LNG Terminal Market size is expected to reach USD 22.7 billion by 2025 and is projected to reach USD 48.1 billion by the end of 2034.
Which region accounted for the largest Global Floating LNG Terminal Market?
▾ Asia Pacific is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Floating LNG Terminal Market, with a share of about 48.0% in 2025.
How big is the Floating LNG Terminal Market in the US?
▾ The US Floating LNG Terminal market is expected to reach USD 5.0 billion by 2025.
Who are the key players in the Floating LNG Terminal Market?
▾ Some of the major key players in the Global Floating LNG Terminal Market include Shell, BP, Eni, and others.
What is the growth rate in the Global Floating LNG Terminal Market?
▾ The market is growing at a CAGR of 8.7 percent over the forecasted period.