The Indian tractor market is one of the largest in the world, with the country's predominantly agrarian economy. The sector has grown rapidly over the past decades as mechanization in farming increases, the government implements initiatives to boost agricultural productivity, and rising rural incomes. Tractors are essential for increasing efficiency in farming operations and are increasingly used for non-agricultural purposes such as construction and goods transport. Subsidies on farming equipment, access to financing, and development of rural infrastructure are some key growth drivers.
The Tractor Market in India is a fragmented landscape with multiple domestic and international players competing across different horsepower categories to meet the unique requirements of Indian farmers. High initial costs, fragmented land holdings, and dependence on monsoons hinder market growth. Despite these challenges, the Tractor Market in India is still evolving, leveraging technology to develop products that are more efficient and affordable than those in other countries, and tailored specifically to meet local agricultural needs.
The Indian tractor market is growing steadily as the pace of mechanization continues to be supported by government policies for agriculture. The market is further pushed by improving rural infrastructure and farmers' preference for better farming techniques. In recent years, the market has shifted toward higher-horsepower
tractors as farmers look to increase productivity. Several factors impact the market expansion. For example, the scope of the rising commercial applications related to infrastructure development makes up a proportionate share of the market scope.
However, some of these issues include rising inflationary pressure, supply chain disruption, erratic monsoons, and further challenges in tractor prices, thus influencing procurement decisions. More specifically, despite such challenges, high tractor prices are still preventing small-scale farmers from purchasing, thus affecting this Indian tractor market. With rural demand stabilizing and government policies favoring mechanization, the market is in a good position for long-term growth.
Key Takeaways
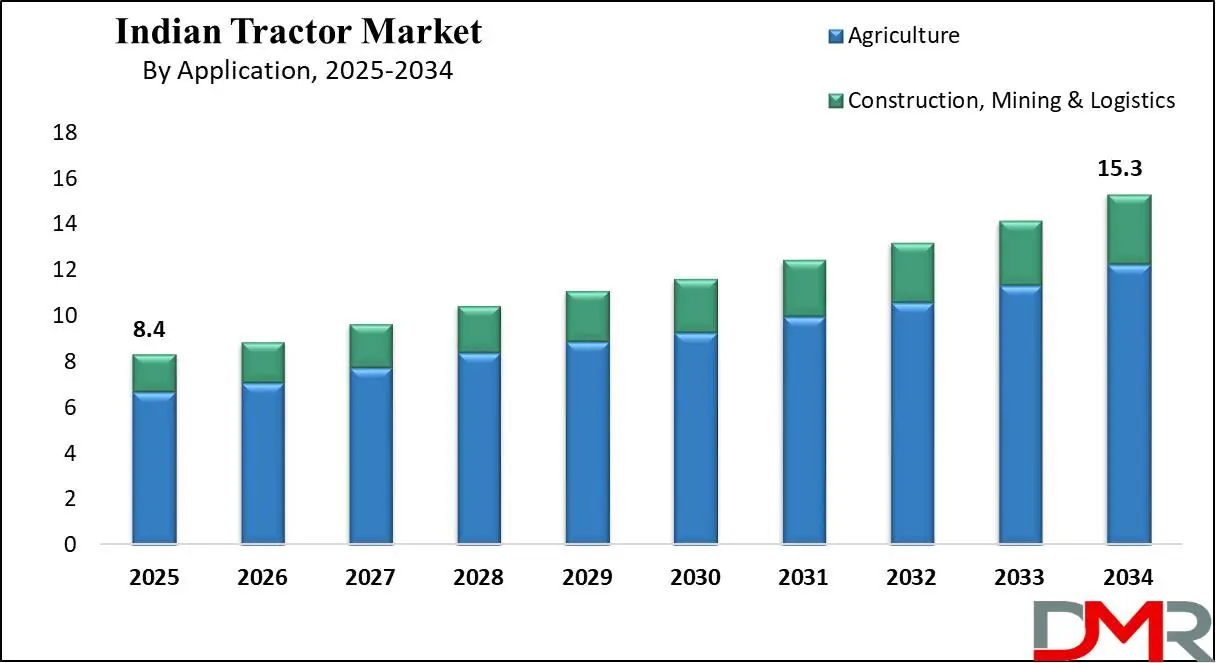
- Market Value: The Indian tractor market size is expected to reach a value of USD 15.3 billion by 2034 from a base value of USD 8.4 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of 7.0%.
- By Drive Type: 2- Wheel Drive is projected to maintain its dominance in the drive type segment, capturing 63.1% of the market share in 2025.
- By Application: The agriculture channel is expected to dominate the application segment in the Indian tractor market, holding 80.0% of the market share in 2025.
- Key Players: Some major key players in the Indian tractor market are, Mahindra & Mahindra Limited, John Deere India Private Limited, CNH Industrial Pvt. Ltd, TAFE Ltd, and Other Key Players.
Use Cases
- Agriculture Use: Tractors allow the adoption of sophisticated techniques such as multi-crop farming and precision agriculture with attachments like seed drills, rotavators, and sprayers. Tractors provide an economical alternative as labor scarcity increases and labor-intensive farming costs are on the rise. Incentives like subsidies on tractors and attachments through government schemes have also accelerated their adoption. The tractors are being tailored for crop-specific needs, including sugarcane harvesting and cotton planting.
- Commercial Use in Infrastructure and Construction: Tractors are widely used in infrastructure and construction projects in India beyond agriculture. They are versatile, capable of handling rough terrains, and useful for tasks such as transporting materials, leveling ground, and powering heavy-duty equipment. Tractors also facilitate rural road-building schemes and government initiatives such as the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana, which seeks to enhance connectivity in rural areas. Rural infrastructure development increases the demand for tractors with special attachments used for construction work.
- Haulage and Goods Transportation: Outside agriculture, the tractors find utility in a wide range of rural enterprises like dairy farming, and small-scale industries. Using trailers, tractor units can take heavy loads consisting of bricks, sand, or timber and still be relatively logistically efficient without the hassle and expense of accessing large transport vehicles due to regional impediments. Durability and the ease with which they can traverse unpaved rural roads make tractors the preferred machines for short-distance transport.
- Adoption of Advanced Farming Technologies: Precision agriculture has integrated advanced technologies into tractors to make farming more efficient. Modern tractors are equipped with GPS, telematics, and sensors to perform tasks such as automated steering, field mapping, and yield monitoring. These technologies are slowly being adopted in India as farmers understand the value of a data-driven farming market to support the sustainable and technologically driven practice of agriculture to ensure long-term growth and efficiency.
Stats & Facts
- Market Size and Growth: The Indian market is the biggest in the world, with annual production estimated at over 1 million units as of 2024, accounting for about 40% of worldwide tractor sales. The 31-40 HP segment dominates the Indian market, being used by small and medium-sized farms while the demand is growing for tractors with more than 50 HP owing to mechanization in larger farm operations and use in nonagricultural areas.
- Horsepower (HP) Segment Trends: The major markets for tractors are North India, especially in states like Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh, which have extensive agriculture. Southern and Western regions also have a growth in demand as farming practices vary.
- Regional Demand Distribution: North India, particularly states like Punjab, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh, contributes significantly to tractor sales due to extensive agricultural activities. Southern and Western regions are also witnessing a surge in demand due to diversified farming practices.
- Export Contribution: India is a major exporter of tractors, with exports exceeding 125,000 units annually, catering to markets in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, driven by affordable and durable tractor models.
Market Dynamic
Driving Factors
Government Support and PoliciesThe Indian government propels the tractor market with benefiting policies and schemes. Subsidies on tractors and agriculture equipment help farmers ease the financial burden, thereby making mechanization more accessible for them. For example,
schemes like PM-Kisan, which give farmers direct income support, help the farmers invest in modern machinery. Subsidized loans through NABARD encourage the purchase of tractors through institutions, and they also facilitate low-cost finances.
Programs like Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana ensure crop insurance, thus reducing the financial risks faced by farmers and enabling them to focus on productivity. Government-backed custom hiring centers help farmers rent tractors and other machinery at economical rates, which is helpful for small and marginal farmers who cannot afford outright purchases. Improvement in rural infrastructure through initiatives such as
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana will increase the utility of tractors, including electric tractors, in both farm operations and haulage. All these measures will encourage tractor adoption especially the use of modern, sustainable technologies like
electric tractors while fostering the overall growth of agriculture by making modern technologies more accessible.
Rising Mechanization in Agriculture
Mechanization in Indian agriculture has transformed the whole sector to enhance efficiency and productivity. The use of tractors in this process leads to the displacement of labor-based practices by advanced and efficient operations. Since labor shortages and rising wages make labor-intensive farming costlier, mechanized solutions have become a solution for farmers in optimizing their operations. Tractors are no longer restricted to large farms, compact models designed for small and fragmented landholdings are gaining popularity among small-scale farmers.
Implements like plows, rotavators, seed drills, and sprayers attached to tractors further increase their utility. Mechanization reduces the time and effort taken in sowing, plowing, and harvesting, thus ensuring timely crop cycles and higher yields. Moreover, with modern tractors equipped with advanced technologies GPS, and sensors in modern tractors, farmers can apply precision agriculture for the best resource usage in the farm. Also, with increased awareness of mechanized farming and its advantages along with support from the government, demand for tractors continues to rise.
Restraints
High Initial Cost
One of the significant restraints in the Indian tractor market is the high upfront cost for purchasing tractors. While mechanization offers numerous benefits, many small and marginal farmers, who constitute a large portion of the Indian agricultural workforce, cannot afford the initial investment. Tractors, along with necessary attachments like plows and rotavators, often cost high investments, making them inaccessible to a significant segment of farmers. Even though loan facilities and subsidies are available, the procedure is lengthy, involving many complicated stages, which further hampers the availability for farmers without collateral or documentation.
Furthermore, higher input prices owing to inflation, supply chain constraints, or raised import duties on components lead to increased costs. Therefore, the majority of the farmers are stuck with conventional, time-consuming practices or sometimes hire tractors on a lease basis, thereby restraining market development.
Fragmented Land Holdings
The agricultural landscape in India is dominated by highly fragmented landholdings, which impose a major constraint on tractor adoption. More than 80% of Indian farmers have less than 2 hectares of land, making the use of tractors economically unviable. Tractors are most effective on larger farms where their operational costs can be spread over extensive land areas. On smaller plots, it makes more sense to use manual labor or animal-drawn equipment.
Fragmentation also creates difficulties in utilizing high-horsepower tractors, which would be ideal for large-scale operations. Although models of cooperative farming and shared ownership of tractors are emerging, the lack of awareness and logistical challenges limit their adoption. This fragmentation continues to impede the market's potential for expansion.
Opportunities
Rising Demand for Precision Agriculture
The increasing adoption of precision agriculture in India offers an enormous opportunity to the tractor market. Precision farming focuses on the optimization of input use such as water, fertilizers, and seeds, thus leading to increased productivity and sustainability. Advanced technologies like GPS, sensors, and telematics are integral parts of tractors for implementing such practices. They allow farmers to carry out operations such as field mapping, automated steering, and real-time monitoring of soil conditions.
With the government focusing on modern agricultural practices and providing subsidies for advanced machinery, there is a growing awareness among farmers about the benefits of precision farming. Moreover, startups and agri-tech companies are entering the space, providing accessible technology solutions tailored to Indian farming needs. The integration of IoT and AI in tractors is further driving this trend. As farmers increasingly seek to reduce costs and improve yields, the demand for smart tractors designed for precision agriculture is expected to rise, creating a robust growth avenue for manufacturers.
Expansion of Non-Agricultural Applications
The diversification of tractor applications into non-agricultural sectors is a promising opportunity. Tractors are increasingly being utilized in industries such as construction, logistics, and infrastructure development. The affordability, versatility, and ability to operate on rugged terrains make them perfect for tasks such as material handling, goods transportation, and site leveling. Due to the government initiatives for rural infrastructure development, in which the country has launched such schemes as Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana, it is increasing demand for tractors in construction activity.
Additionally, the growth in rural entrepreneurship and small-scale industry has increased the demand for durable machinery. Tractors with attachments in the form of loaders, trailers, and backhoes have become essential elements in these fields. This shift stabilizes the market during agricultural downturns but also brings in new revenues for manufacturers. By offering multi-utility tractors and customized solutions for non-agricultural use, companies can tap into this expanding market and ensure long-term growth.
Trends
Shift towards Higher Horsepower Tractors
The Indian tractor market has seen a growing demand for higher horsepower (HP) tractors, especially in the 50 HP and above range. Traditionally, the Indian tractor market was dominated by smaller tractors, especially in the 31-40 HP segment, which was ideal for small and marginal farmers. However, the commercialization and mechanization of Indian agriculture will increase the need for higher HP tractors for more extensive areas and more challenging operations. The larger tractors can accommodate a large variety of attachments, such as larger plows, harvesters, and sprayers, to allow farmers to operate faster and more efficiently.
Furthermore, as farm sizes expand and more farmers invest in mixed farming or diversified activities like construction and transport, the demand for tractors capable of handling such diversified activities is also on the increase. Moreover, higher HP tractors are becoming versatile and, hence, are essential for non-agricultural sectors such as rural infrastructure development and goods transportation. The performance of these tractors is enhanced, with improved fuel efficiency and faster work rates, making them more suitable for larger and more demanding operations. In response to the increased demand, manufacturers are introducing new models combining higher power with fuel efficiency, making it an appealing solution for modern farmers and contractors.
Adoption of Electric and Hybrid Tractors
The adoption of electric and hybrid tractors is an emerging trend in the Indian tractor market, driven by eco-friendly agriculture, as it helps bring down costs without compromising efficiency. Electric tractors are emerging to be the potential alternative to conventional diesel machines. These tractors save a lot of fuel costs because electricity is relatively cheaper than diesel, and it also requires less maintenance as it has fewer moving parts. Additionally, electric tractors produce less noise and air pollution, thus being cleaner and more sustainable, which is critical in India's effort to reduce its carbon footprint.
These tractors can significantly reduce fuel expenses, as electricity is typically cheaper than diesel, and they require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts. Furthermore, electric tractors generate less noise and air pollution, making them a cleaner and more sustainable option, which is crucial in India’s drive towards reducing its carbon footprint. The Indian government is also offering incentives for electric vehicles, which include agricultural machinery, further driving the shift toward electric and hybrid solutions. Hybrid tractors, which combine conventional internal combustion engines with electric power, improved fuel efficiency and the flexibility to operate in areas where electricity infrastructure may be lacking.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Drive Type
The 2-wheel Drive (2WD) segment is expected to maintain its dominance in the Indian tractor market, capturing 63.1% of the market share by 2025. Such 2WD tractors have preferences due to being cheaper and well-suited to small and medium-sized farms. They are less heavy, require less fuel, and are also cheaper to maintain in comparison to the 4WD variants. The farmers, in such areas where the terrain is not as difficult, or with smaller land holdings, account for a majority share of Indian agricultural land. Also, 2WD tractors are versatile and quite adequate for various agricultural operations like plowing, sowing, and hauling lighter loads, making them a very practical solution for farmers looking for cost-effective mechanization.
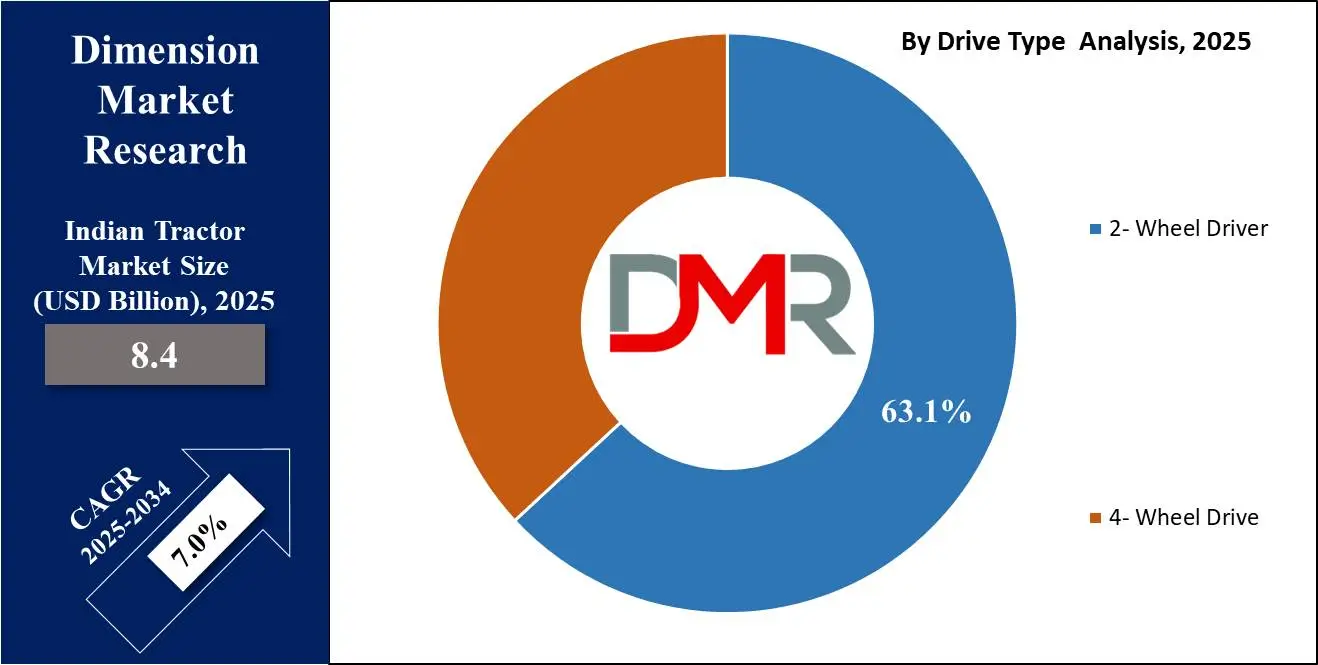
Additionally, 2WD tractors are easier to handle and require less technical expertise to operate, making them more accessible to the average farmer. The cost of the initial purchase is relatively low, hence affordable for even small-scale farmers who are often dependent on government subsidies or financing schemes. Government policies aimed at promoting mechanization in agriculture in India further help to support demand for 2WD tractors, which will be easier entry points for most farmers who will want to change their traditional agriculture practices. Consequently, the 2WD segment is going to retain the leadership in the market.
By Application
The agriculture channel is expected to maintain its dominance in the application-type segment of the Indian tractor market, capturing 80.0% of the market share by 2025. This dominance is because India's agricultural sector remains the backbone of the economy, with more than 50% of the population working in this sector and contributing highly to GDP. Tractors are mainly used for a variety of agricultural tasks such as plowing, tilling, sowing, irrigation, and harvesting, which are necessary for increasing productivity and reducing labor costs. While non-agricultural applications like construction and haulage are growing in importance, agriculture remains the primary use for tractors in India with vast agricultural land, small-scale farms, and a shift toward commercial farming practices.
Demand for tractors in agriculture is boosted by the increasing mechanization of farming operations, especially in light of labor shortages, increases in wages, and efforts to increase crop yields. As more farmers become susceptible to adopting modern practices of farming that promote efficiency, the use of tractors is bound to be common. The Indian government further promotes agricultural mechanization through offering subsidies and financing to farmers at all levels of income as a result the agriculture channel is projected to maintain its substantial share of the market, driving consistent demand for tractors in the coming years.
By Power Output
The 30-40 HP tractors are expected to dominate the power output segment with a market share of 40.0% in 2025 driven by the country’s agriculture landscape and mechanization needs. This segment strikes the right balance between affordability, power, and versatility, making it the preferred choice for the majority of Indian farmers, especially those with medium-sized landholdings. Tractors in the 30-50 HP range are suitable for a wide variety of agricultural tasks such as plowing, sowing, hauling, and irrigation.
They can easily handle a variety of implements such as rotavators, seed drills, and harrows for raising soil health, crop management, and productivity maximization. Since farm holding size distribution has a vast proportion of small and medium-sized farms in India, tractors with this range of horsepower are the most practical and affordable for farmers who want to gear up without heavy upfront investment.
The 30-50 HP segment is also more fuel efficient than the higher horsepower variants, and this makes it more economical for resource-constrained farmers. It is also much more maneuverable than the other tractors, which is crucial in India's fragmented and uneven agricultural terrain. Compact yet powerful, they are best suited for narrow fields and irregular land shapes that are characteristic of rural areas.
Government initiatives also contribute to the segment’s dominance. The Indian government has subsidies and other financial assistance programs for small and marginal farmers. Therefore, the tractors falling in this category are easily affordable. The rising awareness of mechanization benefits and labor scarcity further fuel the demand for 30-50 HP tractors. This is a dominant segment in the market. Furthermore, with the improvement in farming methods and contract farming, this range of horsepower will be needed for a broad variety of uses from traditional crop cultivation to modern farming.
The Indian Tractor Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Power Output
- Less than 30 HP
- 30-50 HP
- 51-100 HP
- More than 100 HP
By Drive Type
- 2- Wheel Drive
- 4- Wheel Drive
By Application
- Agriculture
- Construction, Mining & Logistics
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the Indian tractor market is highly dynamic, driven by a mix of domestic and international players competing on price, performance, innovation, and after-sales service. Key domestic manufacturers like Mahindra & Mahindra, TAFE Motors, and Swaraj Tractors, dominate the market, leveraging strong brand recognition, an extensive dealer network, and a deep understanding of local agricultural needs. Such firms offer a whole array of models for tractors that vary between horsepower categories, particularly in the 30-50 HP segment, which holds the largest market share.
Mahindra & Mahindra leads the Indian tractor market, famous for its long-lasting and fuel-efficient tractors, especially in the 30-50 HP range. In terms of innovation, they lead the market, with smart features like GPS tracking and telematics. The other major player is Tafe Motors, offering a mix of compact and higher-horsepower tractors tailored for different farming practices.
International brands such as John Deere, Kubota, and New Holland are also competing in the market. These global players focus on advanced technology, quality, and high-performance models, especially in the higher horsepower categories like 51–100 HP and above 100 HP. John Deere, for instance, has introduced smart farming solutions in its tractors, targeting progressive farmers who seek high-tech farming equipment. The Tractor Market Share in India is influenced by such innovations and brand positioning. The competitive environment shall remain focused on offering value through affordable, efficient, and durable tractors, with an increasing emphasis on customer service and financing options catering to India's large base of small and medium farmers.
Some of the prominent players in the Indian Tractor Market are
- Mahindra & Mahindra Limited
- John Deere India Private Limited
- CNH Industrial Pvt. Ltd
- TAFE Ltd
- International Tractors Limited (Sonalika)
- Preet Tractors Limited
- Escorts Kubota Limited
- Indo Farm Equipment Limited
- VST Tillers Tractors Limited
- Captain Tractors Private Limited
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- December 2024: Kubota announced a partnership with a local Indian company to develop electric tractors for the Indian market. This collaboration aims to produce environmentally friendly tractors suited for India’s farming conditions, capitalizing on the increasing demand for sustainable farming solutions.
- October 2024: Mahindra & Mahindra launched the eMax 20 S, an electric tractor designed for small and medium-scale farmers. The tractor is powered by a lithium-ion battery, providing an eco-friendly, cost-efficient alternative to traditional diesel-powered tractors. This launch marks Mahindra’s commitment to green farming solutions in India.
- June 2024: New Holland launched its new T7 Series tractor in India. The T7 series is designed for both high-performance agricultural tasks and non-agricultural applications. Equipped with advanced features such as automatic transmission, fuel-efficient engines, and precision farming capabilities, the T7 series is aimed at the expanding demand for versatile, higher-horsepower tractors in India.
- July 2023: John Deere launched its new 5E Series tractors in India, designed for small and medium farmers. The new range focuses on providing advanced features, including fuel-efficient engines, ergonomic designs, and ease of use. This product launch aligns with John Deere’s strategy of catering to the diverse needs of Indian farmers, particularly in the 30-50 HP segment.
- March 2023: Tafe Motors (part of the TAFE Group) completed the acquisition of the Italian tractor manufacturer Landini. This acquisition is part of TAFE's strategy to expand its global footprint and strengthen its portfolio in the high-power and specialty tractor segments, offering advanced machinery to both Indian and international markets.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 8.4 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 15.3 Bn |
| CAGR (2025-2034) |
7.0% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| Forecast Data |
2026 – 2034 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors and etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Power Output (Less than 30 HP, 30-50 HP, 51-100 HP, and More than 100 HP), By Drive Type (2- Wheel Drive and 4- Wheel Drive), By Application (Agriculture and Construction, Mining & Logistics) |
| Regional Coverage |
The US
|
| Prominent Players |
Mahindra & Mahindra Limited, John Deere India Private Limited, CNH Industrial Pvt. Ltd, TAFE Ltd, International Tractors Limited (Sonalika) and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (, to 5 Users) and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days and 5 analysts working days respectively. |