Market Overview
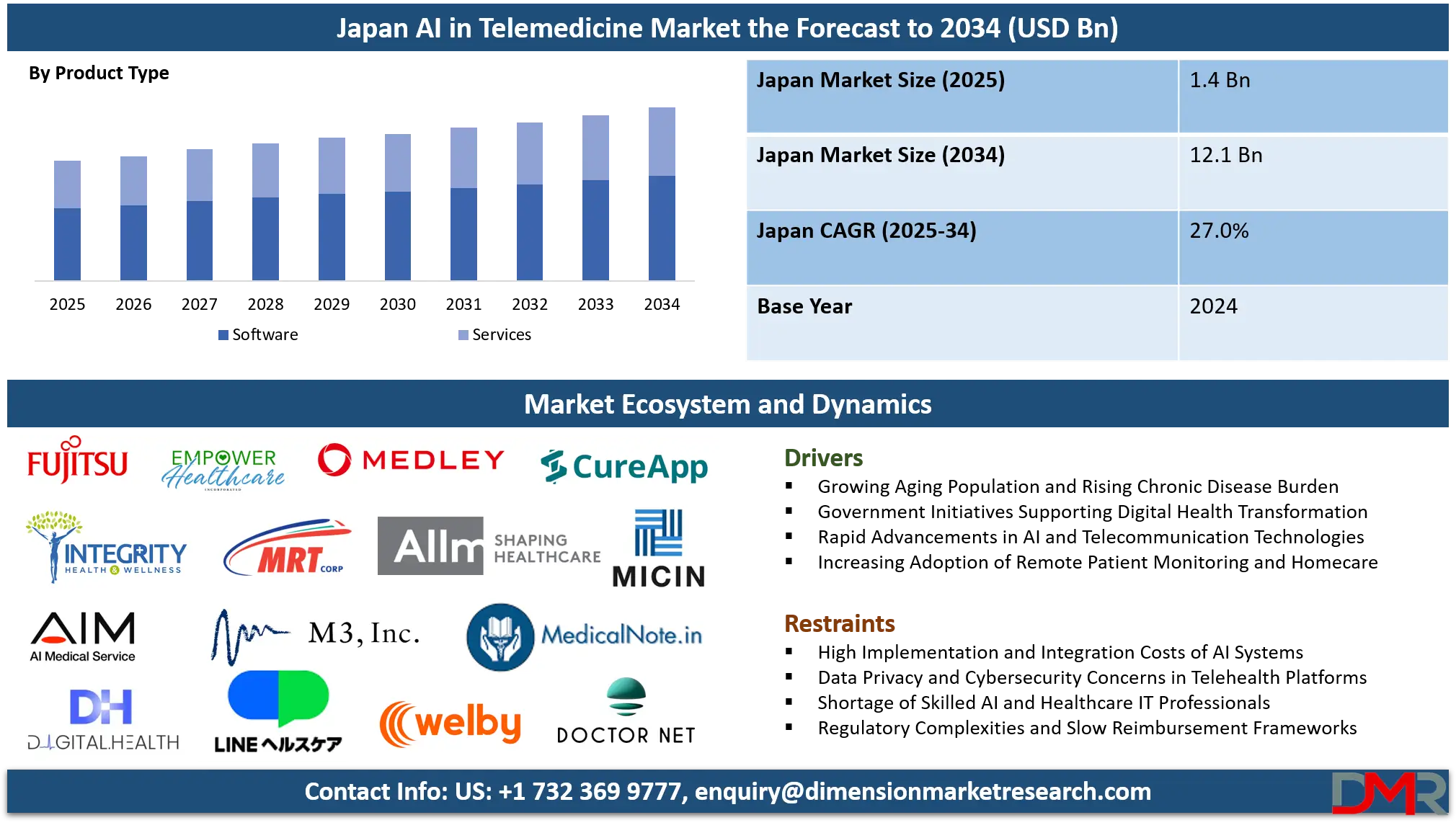
The Japan AI in Telemedicine Market is projected to reach USD 1.4 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to grow at a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.0% from 2025 to 2034, attaining an estimated market value of USD 12.1 billion by 2034.
This significant growth is driven by Japan’s rapidly aging population, rising demand for remote healthcare services, and government initiatives promoting digital transformation in the medical sector. The integration of artificial intelligence in teleconsultations, diagnostics, and remote patient monitoring is reshaping Japan’s healthcare ecosystem, enabling precision care and efficient medical resource utilization. The market’s strong trajectory reflects advancements in AI-based clinical decision support, predictive analytics, and telehealth infrastructure, positioning Japan as a leading hub for next-generation telemedicine innovation in Asia.
The integration of artificial intelligence within Japan's telemedicine sector is accelerating, driven by a potent convergence of demographic pressures and technological advancement. The nation's rapidly aging population, with a high prevalence of chronic diseases, is placing unprecedented strain on traditional healthcare delivery models.
This has catalyzed a strategic pivot towards digital health solutions, with AI emerging as a critical enabler for enhancing the efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility of remote care. The market is witnessing a shift from basic video consultations to sophisticated, AI-powered platforms that offer predictive diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, and automated administrative functions, fundamentally transforming the patient-provider dynamic.
A significant trend is the proliferation of AI-driven diagnostic support tools. These systems, often leveraging computer vision, analyze medical images from X-rays, CT scans, and retinal photographs with remarkable precision, aiding physicians in early detection of conditions like cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and strokes.
Concurrently, natural language processing algorithms are being deployed to sift through vast repositories of electronic health records and unstructured clinical notes. This not only automates administrative burdens but also uncovers subtle patient patterns, facilitating more informed clinical decision-making and contributing to the development of personalized medicine protocols tailored to Japan's unique patient demographics.
The market presents substantial opportunities, particularly in addressing the nation's critical shortage of healthcare professionals in rural areas. AI-powered triage and symptom-checking chatbots can serve as a first line of defense, directing patients to the appropriate level of care and alleviating pressure on overburdened clinics.

Furthermore, the burgeoning field of AI for remote patient monitoring offers a paradigm shift in managing chronic illnesses. By continuously analyzing data from wearable devices and smart sensors, these systems can predict potential health deteriorations, such as congestive heart failure episodes, enabling preemptive interventions and reducing hospital readmissions.
Japan AI in Telemedicine Market: Key Takeaways
- Robust Market Expansion: The Japan AI in Telemedicine Market is set to expand significantly from USD 1.4 billion in 2025 to USD 12.1 billion by 2034, registering a CAGR of 27.0%. This strong upward trajectory is fueled by Japan’s aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic illnesses, and rising demand for accessible, remote healthcare services powered by AI technologies.
- Software Segment Leadership: The software segment dominates Japan’s AI in the telemedicine landscape owing to its scalability, seamless integration with electronic medical record (EMR) systems, and capability to provide real-time insights. AI-based telehealth platforms, predictive analytics software, and digital diagnostic tools form the foundation of Japan’s telemedicine modernization efforts.
- Remote Monitoring & Predictive Analytics Drive Applications: Remote monitoring and predictive analytics represent the leading application segment. AI algorithms process real-time health data from connected devices and wearables, allowing healthcare providers to detect abnormalities early, predict potential health risks, and enable timely medical intervention key priorities in Japan’s preventive care model.
- · Healthcare Facilities as Core End Users: Hospitals and medical institutions are the leading end users, extensively deploying AI solutions for teleconsultations, diagnostics, and patient management. The sector’s investment capacity, operational complexity, and emphasis on quality outcomes make healthcare facilities central to AI telemedicine adoption across Japan.
- Enhancing Workforce Productivity: AI automation tools are helping Japan’s healthcare sector address staff shortages and burnout by streamlining documentation, triage, and administrative processes. This improves clinical efficiency and allows physicians to focus more on patient care.
- Favorable Government and Regulatory Environment: Japan’s Society 5.0 vision, Digital Health Promotion Policy, and MHLW-led telemedicine reforms are fostering AI integration across the healthcare system. These initiatives promote data interoperability, regulatory clarity, and sustained public–private investment in AI-enabled telehealth innovation.
Japan AI in Telemedicine Market: Use Cases
- AI-Powered Triage for Rural Clinics: In depopulated regions, an AI chatbot conducts initial patient interviews via a telemedicine platform. Using NLP, it analyzes symptoms, medical history, and severity. It then prioritizes cases for the limited physicians, recommends self-care for minor issues, and schedules urgent video consultations.
- Remote Diabetic Retinopathy Screening: Patients at local clinics undergo retinal imaging. An AI algorithm with computer vision analyzes the images in real-time, detecting microaneurysms and hemorrhages indicative of diabetic retinopathy. It instantly flags positive cases for immediate ophthalmologist review via telemedicine, enabling early intervention.
- Predictive Analytics for Heart Failure Management: Hospitals discharge congestive heart failure patients with Bluetooth-enabled weight scales and blood pressure monitors. An AI model continuously analyzes this data alongside EHR information.
- AI-Enhanced Mental Health Support Platforms: A telepsychiatry platform incorporates an AI-powered mental health chatbot. It provides users with Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques and mood tracking between sessions. The AI analyzes user inputs for linguistic markers of declining mental state, alerting a human therapist if a high-risk pattern is detected.
- Automated Medical Transcription and Coding: During a teleconsultation, an AI tool using advanced speech-to-text and NLP transcribes the doctor-patient conversation in real-time. It automatically identifies and extracts key diagnoses, prescriptions, and procedures, populating the Electronic Health Record (EHR) and assigning accurate medical billing codes.
Japan AI in Telemedicine Market: Stats & Facts
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC)
- As of 2021, the percentage of medical institutions in Japan that have introduced telemedicine was 25.3%.
- In 2021, the telemedicine utilization rate among individuals in Japan was 25.6%.
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW)
- Japan's total national medical expenditure reached approximately 44.2 trillion yen in FY2021.
- The number of physicians per 100,000 population in Japan is 260.2, highlighting a maldistribution issue.
- Over 28% of Japan's population is aged 65 or over, representing one of the world's most aged societies.
- The MHLW estimates that by 2025, there will be a shortage of approximately 270,000 care workers for the elderly.
- The Japanese government has set a target for 90% of prescriptions to be digitally transmitted by the end of FY2024.
- The MHLW's "Health Japan 21" initiative promotes the use of data and technology for preventive healthcare.
Cabinet Office, Government of Japan
- The government's budget for Society 5.0-related initiatives, which integrates AI and IoT into all societal sectors, including healthcare, was over 1 trillion yen in the 2021 fiscal year.
Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- AMED has funded numerous projects in the "Program for Bridging the Gap between R&D and the Ideal Society," including several focused on AI diagnostics and telemedicine integration.
- Funding for AI-based medical image diagnosis research and development has been a consistent priority for AMED in recent years.
World Health Organization (WHO)
- The WHO Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025 encourages member states to prioritize the development and adoption of digital health technologies.
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- Japan has one of the highest numbers of CT scanners and MRI units per capita among OECD countries, generating vast volumes of image data suitable for AI analysis.
- Japan's health spending per capita is above the OECD average.
International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Japan has one of the highest percentages of fiber-optic broadband subscriptions among developed countries, providing critical infrastructure for high-quality telemedicine.
Japan Medical Association
- Surveys by the JMA have indicated physician concerns regarding patient safety and the clarity of liability in telemedicine and AI-assisted diagnosis.
Japan Pharmaceutical Association
- Online pharmacy sales in Japan have seen a consistent increase, facilitated by telemedicine consultations and digital prescriptions.
Statistics Bureau of Japan
- The percentage of households with internet access in Japan exceeded 95% in recent years.
National Institute of Population and Social Security Research
- Japan's population is projected to fall below 100 million by 2056, exacerbating the healthcare workforce shortage.
Japan Tourism Agency
- The government is promoting "medical tourism," for which integrated telemedicine platforms for pre- and post-consultation are becoming a key component.
Financial Services Agency
- The FSA has been involved in discussions regarding the regulatory sandbox for fintech and insurtech, which can include health-tech applications and data usage.
Personal Information Protection Commission
- The PPOC provides guidelines for the handling of personal information, including special care-required information such as medical data under the APPI law.
Japan AI in Telemedicine Market: Market Dynamics
Driving Factors in Japan AI in Telemedicine Market
Demographic Pressures and Healthcare System Strain
The most powerful driver for AI adoption in Japan's telemedicine market is the nation's profound demographic challenge. With the world's most aged population, where over 28% are 65 or older, there is a correspondingly high prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions. This demographic reality places an unsustainable burden on the healthcare system, exacerbating a well-documented shortage and maldistribution of physicians, particularly in rural areas. This strain creates an urgent, systemic need for efficiency-enhancing solutions.
AI in telemedicine directly addresses this by automating administrative tasks, triaging patients, and supporting diagnostics, thereby multiplying the effectiveness of the existing clinical workforce. The government and healthcare providers are compelled to invest in these technologies as a strategic imperative to maintain the quality and accessibility of care for its citizens in the face of a shrinking workforce and growing elderly demographic.
Supportive Government Policies and Digital Transformation Initiatives
Active promotion and regulatory modernization by the Japanese government serve as a critical accelerant for the market. Following the temporary relaxation of telemedicine regulations during the COVID-19 pandemic, the government has moved to make many of these changes permanent, providing a stable regulatory foundation for growth. Central to this is the national "Society 5.0" vision, which explicitly aims to integrate advanced technologies like AI and IoT into all industrial and social sectors, with healthcare being a primary focus.
Furthermore, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare's (MHLW) "Health Care Policy of New Form" and its push for digital transformation (DX) in medicine are creating a fertile environment. These initiatives are backed by substantial funding for R&D through agencies like AMED and include efforts to standardize data formats and promote the secure exchange of medical information, thereby directly facilitating the development and integration of AI-driven telemedicine solutions.
Restraints in Japan AI in Telemedicine Market
Stringent Data Privacy Regulations and Data Silos
The development and training of robust AI models in healthcare are contingent on access to large, high-quality, and diverse datasets. In Japan, this is significantly restrained by the stringent Act on the Protection of Personal Information (APPI), which classifies medical data as "special care-required personal information." The compliance burden for collecting, anonymizing, and sharing this data is high, creating a complex regulatory environment that can stifle innovation and collaboration between institutions and technology firms.
Compounding this issue is the pervasive existence of data silos within the healthcare system. Patient data is often fragmented across hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies using incompatible legacy IT systems. This lack of interoperability makes it exceptionally difficult to aggregate the comprehensive datasets needed to train unbiased and generalizable AI algorithms, creating a major bottleneck for the advancement of sophisticated telemedicine applications.
Clinical Validation Hurdles and Physician Adoption Resistance
For AI tools to be integrated into standard clinical workflow, they must undergo rigorous validation to demonstrate not just algorithmic accuracy but also clinical efficacy and improved patient outcomes. This process is time-consuming, expensive, and requires extensive collaboration with medical institutions. The "black box" nature of some complex AI models, where the reasoning behind a diagnosis is not easily explainable, poses a significant barrier to earning the trust of physicians who are ultimately liable for patient care.
This leads to resistance in adoption, as clinicians may be hesitant to rely on recommendations they do not fully understand. Furthermore, integrating these novel AI systems into existing, often outdated, hospital IT infrastructure presents significant technical and financial challenges, requiring substantial investment in system upgrades and staff training, which can be a major deterrent for many healthcare providers, especially smaller clinics.
Opportunities in Japan AI in Telemedicine Market
Expansion of Personalized and Preventive Care Models
A significant growth frontier lies in leveraging AI to transition from a standardized, reactive healthcare model to a highly personalized and preventive one. By integrating and analyzing multimodal data streams, including genetic information, longitudinal EHR data, and real-time lifestyle metrics from wearables, AI can generate deeply personalized health insights and risk profiles. This enables the development of bespoke wellness plans, tailored medication regimens, and proactive screening schedules delivered via telemedicine platforms.
For Japan's cost-conscious system, this represents a paradigm shift towards value-based care, focusing on preventing the onset or progression of expensive chronic diseases common in its aging populace. Telemedicine companies can evolve into continuous health management partners, offering subscription-based services for personalized coaching and monitoring, thereby unlocking new revenue streams while simultaneously improving public health outcomes and reducing long-term medical expenditures.
Addressing Specialist Shortages in Rural and Geriatric Care
There is a substantial, unmet opportunity to deploy specialized AI telemedicine solutions to bridge the healthcare access gap in rural Japan and within geriatric care facilities. AI-powered diagnostic support tools can empower general practitioners and nurses in remote clinics to perform at a higher specialist level, for instance, by using smartphone-based retinal imaging with AI analysis to screen for diabetic retinopathy, eliminating the need for immediate ophthalmologist availability.
Similarly, in nursing homes, AI-driven fall detection sensors, combined with predictive analytics for conditions like sepsis or delirium, can enable remote monitoring by central clinical teams. This model allows a few specialists to oversee the health of a large, distributed patient population efficiently. Developing and scaling such targeted applications represents a critical opportunity to ensure equitable healthcare access and improve the quality of life for Japan's most vulnerable demographics.
Trends in Japan AI in Telemedicine Market
Proliferation of AI-Powered Diagnostic and Clinical Decision Support Tools
The market is witnessing a significant shift from basic teleconsultation platforms to sophisticated systems embedded with AI-driven diagnostic capabilities. A primary trend is the widespread adoption of computer vision for medical image analysis. AI algorithms are now routinely deployed to interpret X-rays, CT scans, and mammograms, achieving high accuracy in detecting pathologies such as lung nodules, fractures, and early-stage cancers. This not only augments the radiologist's capabilities, reducing diagnostic time and human error, but also helps address the geographical maldistribution of specialist doctors in Japan.
Concurrently, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is being leveraged to mine unstructured data within Electronic Health Records (EHRs). These systems extract critical information from physician notes, lab reports, and medical literature, providing clinicians with evidence-based, personalized treatment recommendations and risk assessments at the point of care, thereby enhancing the overall quality and efficiency of remote diagnostics.
Integration of Predictive Analytics and Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
A transformative trend is the deep integration of AI with Remote Patient Monitoring technologies, moving telemedicine from reactive consultations to proactive, predictive healthcare. AI algorithms are increasingly used to analyze continuous, real-time data streams from a growing ecosystem of connected devices, including wearable sensors, smart blood pressure cuffs, and Bluetooth-enabled glucometers. By establishing individual patient baselines, these systems can detect subtle deviations and identify complex patterns predictive of adverse health events.
For instance, AI can forecast potential heart failure exacerbations by analyzing weight and vital sign trends, or predict hypoglycemic episodes in diabetics. This enables preemptive interventions through telehealth channels, such as a nurse calling to adjust medication, thereby preventing hospitalizations and improving long-term outcomes for Japan's aging population with chronic conditions, fundamentally changing the chronic disease management paradigm.
Japan AI in Telemedicine Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Product Type Analysis
Software is expected to dominate the product type segment in the Japan AI in Telemedicine Market, driven by the country’s rapid digital transformation and emphasis on smart healthcare infrastructure. Japan’s healthcare ecosystem relies heavily on AI-powered telemedicine platforms, clinical decision support systems (CDSS), predictive analytics tools, and EHR-integrated management software, all of which enable more efficient, accurate, and personalized care.
These software solutions support real-time patient monitoring, virtual consultations, and diagnostic automation capabilities that are crucial in Japan’s aging society with high demand for remote medical access.
Unlike service-based solutions, which primarily focus on implementation and maintenance, AI software platforms provide continuous operational and analytical value, allowing for seamless scalability across hospitals and clinics. Integration with Japan’s existing health IT systems, wearables, and IoT medical devices ensures comprehensive patient data flow and informed clinical decision-making.
Furthermore, frequent AI algorithm updates and cloud-based deployment models allow healthcare institutions to adapt quickly to new medical regulations and patient care standards. The long-term cost efficiency and adaptability of software-driven solutions make this segment the backbone of Japan’s AI telemedicine ecosystem.
By Application Analysis
Remote Monitoring & Predictive Analysis is projected to lead the application segment in Japan’s AI in telemedicine market. With a rapidly aging population and increasing chronic disease prevalence, the need for continuous, proactive health management has surged. AI algorithms in this segment analyze patient data from wearables, home healthcare IoT devices, and remote diagnostic systems to detect abnormalities and forecast potential health issues. These predictive tools enable early intervention, reduce hospital readmissions, and support Japan’s nationwide push toward preventive and community-based care.
Applications such as virtual nursing assistants, diagnostics, and AI imaging are also gaining traction, but remote monitoring delivers the most tangible outcomes by providing uninterrupted insights into patient health. Hospitals and physicians in Japan use these platforms to enhance clinical efficiency and optimize patient management, while patients benefit from personalized health alerts and recommendations. As IoT integration deepens and predictive models advance, remote monitoring and predictive analytics will remain the most impactful and widely implemented AI telemedicine applications in Japan.

By End User Analysis
Healthcare Facilities are anticipated to remain the dominant end-user segment in Japan’s AI in telemedicine market. Hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers across Japan are investing in AI-enabled platforms to manage remote consultations, automate diagnostics, and deliver personalized treatment plans. These institutions have the financial capacity and digital infrastructure to integrate AI systems at scale, supporting the government’s broader vision of a data-driven healthcare ecosystem.
While home care adoption is expanding, especially among the elderly, limitations such as high device costs, technological literacy gaps, and inconsistent internet coverage in rural areas hinder large-scale use. In contrast, institutional healthcare settings benefit from centralized data management, advanced AI analytics, and multi-department interoperability, improving both operational efficiency and clinical outcomes.
Other end users, such as corporate wellness programs and government telehealth initiatives, contribute modestly but are expected to grow as Japan’s health digitization deepens. Overall, healthcare facilities are the driving force behind AI telemedicine adoption, leveraging technology to streamline workflows, enhance patient satisfaction, and sustain Japan’s leadership in next-generation digital healthcare delivery.
Japan AI in Telemedicine Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following:
By Product Type
- Software
- AI-powered Telemedicine Platforms
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
- AI-based Patient Management & EHR Integration Tools
- Predictive Analytics Software
- Services
- AI Implementation & Integration Services
- Remote Patient Monitoring Services
- Consultation & Training Services
- Managed AI Telemedicine Services
By Application
- Diagnostics & Medical Imaging
- AI Imaging Interpretation & Analysis
- AI-based Diagnostic Tools (Radiology, Pathology, etc.)
- Medication Adherence & Treatment Plans
- AI Reminders & Personalized Treatment Plans
- Digital Therapeutics Integration
- Teleconsultation Enhancement
- AI-assisted Video Consultations
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Medical Documentation
- Remote Monitoring & Predictive Analysis
- AI-driven Wearables & IoT Monitoring
- Predictive Analytics for Chronic Disease Management
- Virtual Nursing Assistant
- AI Chatbots & Symptom Checkers
- Personalized Patient Interaction Systems
- Other Application
By End User
- Homecare / Patients at Home
- Chronic Disease Patients
- Elderly Care
- Post-Surgery Care
- Healthcare Facilities
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Diagnostic Centers
- Specialty Care Centers
- Other End Users
Japan AI in Telemedicine Market: Competitive Landscape
The Japan AI in Telemedicine Market is characterized by an increasingly competitive and innovation-driven environment, shaped by Japan’s aging population, technological sophistication, and strong governmental support for digital healthcare transformation. Key domestic players such as MICIN Inc., Medley Inc., Allm Inc., and CureApp Inc. are leading the development of AI-driven telemedicine solutions tailored to Japan’s healthcare needs.
MICIN focuses on AI-enabled remote consultations and patient monitoring systems; Medley Inc. offers digital platforms connecting patients with medical professionals; Allm Inc. specializes in AI-powered mobile health communication tools; and CureApp Inc. develops AI-driven digital therapeutics for chronic disease management.
Major technology firms like NEC Corporation, Fujitsu Limited, NTT Data Corporation, and SoftBank Corp. are integrating AI analytics, 5G connectivity, and cloud computing to enhance the performance and scalability of telemedicine solutions. These companies collaborate with healthcare institutions to optimize clinical workflows, improve diagnostic precision, and enable real-time remote care. The competitive intensity is further fueled by the emergence of innovative startups such as AI Medical Service Inc., Fast Doctor Inc., and Welby Inc., which are advancing AI-assisted diagnostics, remote monitoring, and personalized treatment management.
Strategic partnerships, investments, and government-backed digital health initiatives under Japan’s Society 5.0 framework are accelerating market expansion. Regulatory support from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) and nationwide efforts to expand telehealth accessibility have positioned Japan as a leading hub for AI-driven healthcare innovation in Asia. Overall, the market is witnessing strong momentum from technology integration, cross-sector collaborations, and patient-centric digital solutions.
Some of the prominent players in the Japanese AI in Telemedicine Market are:
- MICIN Inc.
- Medley Inc.
- Allm Inc.
- CureApp Inc.
- LINE Healthcare
- M3 Inc.
- Medical Note Co., Ltd.
- Welby Inc.
- Fast Doctor Inc.
- Doctor Net Inc.
- Kids Public Inc.
- MRT Inc.
- Empower Healthcare K.K.
- Digital Health Co., Ltd.
- AI Medical Service Inc.
- Integrity Health
- NEC Corporation
- Fujitsu Limited
- SoftBank Corp.
- NTT Data Corporation
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments in Japan's AI in Telemedicine Market
- October 2025: MICIN Inc. announced a collaboration with Fujitsu Limited to integrate AI-based predictive analytics into remote monitoring platforms, improving chronic disease management and hospital readmission prevention.
- September 2025: CureApp Inc. secured Series D funding from SoftBank Ventures Asia to expand its AI-driven digital therapeutics for hypertension and smoking cessation across Japan.
- August 2025: Allm Inc. partnered with NTT Data Corporation to develop an AI-powered telehealth infrastructure supporting cross-hospital data sharing and physician collaboration.
- July 2025: Medley Inc. launched a new AI triage platform, enabling hospitals to automate patient prioritization and optimize virtual consultation workflows.
- June 2025: AI Medical Service Inc. received regulatory approval for its AI-based endoscopic diagnostic software from Japan’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA).
- April 2025: NEC Corporation introduced an AI telemedicine module leveraging 5G and edge computing for real-time video consultations in rural areas.
- March 2025: LINE Healthcare partnered with Welby Inc. to integrate AI-enabled health tracking into its digital consultation app, enhancing patient engagement and continuity of care.
- February 2025: NTT Data Corporation announced the launch of a nationwide telehealth cloud platform powered by AI for data analysis, hospital integration, and remote diagnostics.
- December 2024: SoftBank Corp. invested in Digital Health Co., Ltd. to expand AI-based medical data platforms, supporting healthcare interoperability and patient data security.
- October 2024: Fujitsu Limited showcased its AI-driven telemedicine solutions at the CEATEC Japan Expo, highlighting advancements in remote diagnostics, speech recognition, and AI triage systems.
- August 2024: Welby Inc. introduced an AI-enabled self-care platform designed for patients with diabetes, integrating wearable device data with physician monitoring tools.
- June 2024: Doctor Net Inc. collaborated with AI Medical Service Inc. to co-develop AI diagnostic imaging tools aimed at improving early cancer detection through telepathology services.
- April 2024: M3 Inc. expanded its AI-supported teleconsultation platform to include multilingual services for international patients, leveraging machine translation and clinical AI algorithms.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 1.4 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 12.1 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
27.0% |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 4.2 Bn |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| Forecast Data |
2026 – 2034 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Product Type (Software, Services), By Application (Virtual Nursing Assistant, Remote Monitoring & Predictive Analysis, Diagnostics & Medical Imaging, Medication Adherence & Treatment Plans, Teleconsultation Enhancement, and Other Applications), and By End User (Homecare / Patients at Home, Healthcare Facilities, and Other End Users) |
| Regional Coverage |
Japan |
| Prominent Players |
MICIN Inc., Medley Inc., Allm Inc., CureApp Inc., LINE Healthcare, M3 Inc., Medical Note Co. Ltd., Welby Inc., Fast Doctor Inc., Doctor Net Inc., Kids Public Inc., MRT Inc., Empower Healthcare K.K., Digital Health Co. Ltd., AI Medical Service Inc., Integrity Health, NEC Corporation, Fujitsu Limited, SoftBank Corp., NTT Data Corporation, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The Japan AI in Telemedicine Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 1.4 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 12.1 billion by the end of 2034.
The market is growing at a CAGR of 27.0 percent over the forecasted period of 2025.
Some of the major key players in the Japanese AI in Telemedicine Market are MICIN Inc., Medley Inc., Allm Inc., CureApp Inc., LINE Healthcare, M3 Inc., Medical Note Co. Ltd., Welby Inc., Fast Doctor Inc., Doctor Net Inc., and many others.