Market Overview
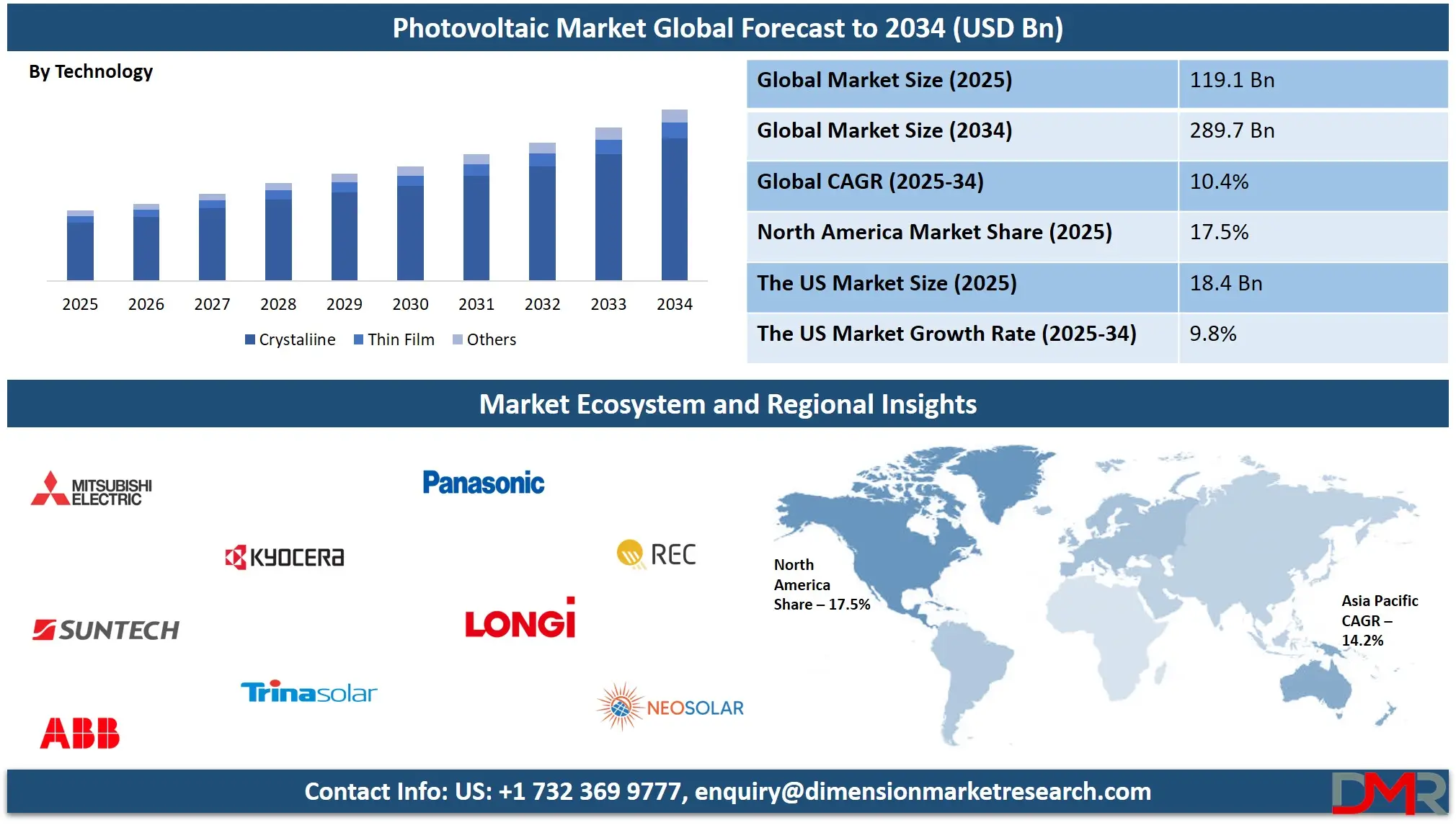
The Global Photovoltaic Market is projected to reach
USD 119.1 billion in 2025 and grow at a compound annual growth rate of
10.4% from there until 2034 to reach a value of
USD 289.7 billion.
Photovoltaic technology, often called PV, converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar cells made of materials like silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it knocks loose electrons that create an electrical current. These cells can then be combined into solar panels, which can then be installed on rooftops, open land areas, or buildings with minimal impact to the environment. PV is an environmentally friendly alternative way of creating power that produces no pollution when producing power without harming nature in any way.
In recent times, photovoltaic energy demand has seen steady increases. One key driver behind this is an increasing need for clean and renewable sources of energy - governments, companies, and individuals all over the world seek ways to decrease pollution while transitioning away from fossil fuels; solar PV systems offer an efficient means to do just this. Also, as more people become aware of climate change, they are opting to install PV panels in their homes or businesses in order to make a difference.
Photovoltaic technology is rapidly improving. Owing to new materials and designs, solar panels are producing more electricity even on cloudy days than before, while lightweight and flexible panels have made installation simpler than ever before. Battery storage technologies also play a huge role; batteries allow solar energy to be stored for use at night or cloudy days when necessary. Some companies have even integrated photovoltaic panels into everyday objects like windows or roof tiles.
Over the past several years, several countries have undertaken major solar energy initiatives. This includes installing large solar farms that produce electricity for entire cities. Governments across several nations have passed laws supporting the use of PV as part of an international effort to combat climate change and assist people and businesses with installation costs. International conferences have also advocated the need to embrace clean energy - PV in particular - for its climate-altering benefits.
Today, photovoltaic systems can be found almost anywhere - homes, schools, factories and even calculators and lights use solar power. Some cars and boats have even been designed to run partly on solar energy; showing that PV doesn't just belong in big projects but can become part of daily life too. As technology improves and costs decline, more people should expect to take up solar energy in future.
Photovoltaic energy's future looks bright. Experts predict solar will become one of the main sources of electricity around the globe, creating more jobs in manufacturing, installation and maintenance of PV panels. Meanwhile, scientists are working towards making them last longer and be easier to recycle - all contributing towards building a greener and more sustainable world through PV technology.
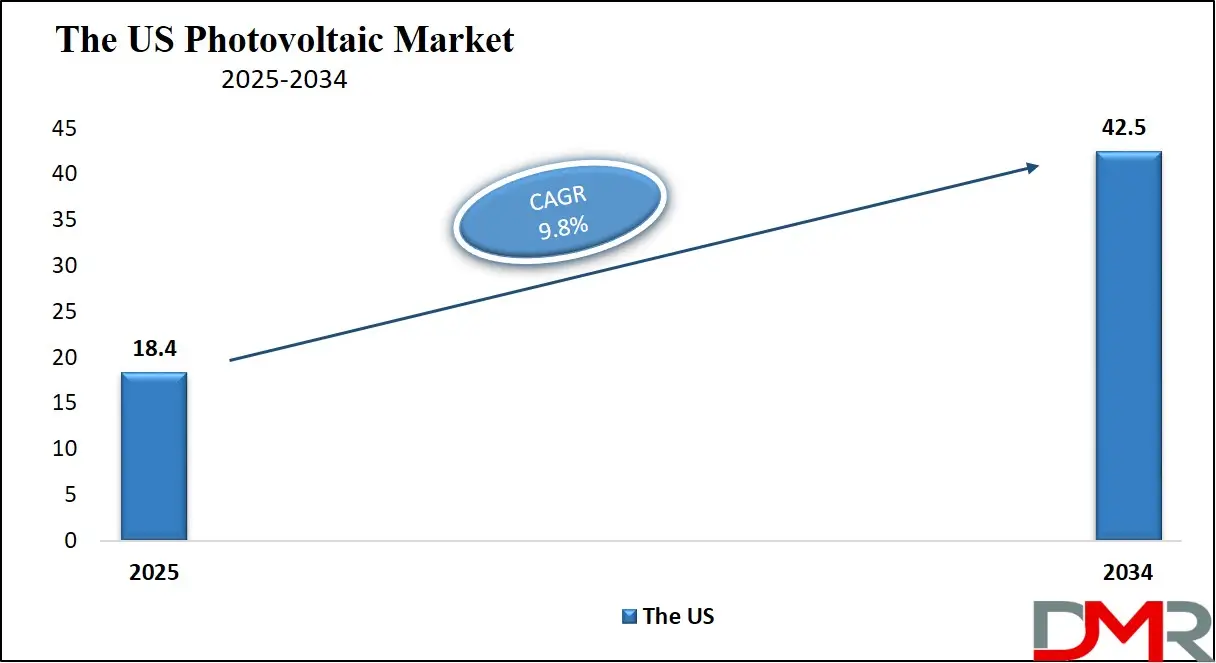
The US Photovoltaic Market
The US Photovoltaic Market is projected to reach USD 18.4 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 9.8% over its forecast period.
The U.S. photovoltaic market provides growth opportunities through increased federal and state incentives, expanding solar farms, and technological advancements. The shift towards clean energy, coupled with rising demand for residential and commercial solar installations, creates a favorable environment. Additionally, the growing adoption of energy storage solutions and electric vehicles enhances the potential for solar power integration across various sectors.
Further, the market is strong with government incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, which make solar installations more affordable. However, a key restraint is the challenge of grid integration, as the U.S. power grid needs significant upgrades to handle large-scale solar energy efficiently. Additionally, supply chain issues and high initial installation costs can slow down widespread adoption.
Photovoltaic Market: Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Photovoltaic Market size is expected to grow by 159.5 billion, at a CAGR of 10.4%, during the forecasted period of 2026 to 2034.
- By Technology: The Crystalline segment is anticipated to get the majority share of the Photovoltaic Market in 2025.
- By Application: The electric generation segment is expected to get the largest revenue share in 2025 in the Photovoltaic Market.
- Regional Insight: Asia Pacific is expected to hold a 54.3% share of revenue in the Global Photovoltaic Market in 2025.
- Use Cases: Some of the use cases of Photovoltaic include commercial & industrial use, residential power supply, and more.
Photovoltaic Market: Use Cases
- Residential Power Supply: Photovoltaic systems are commonly used on rooftops to power homes. They minimize dependency on the main electricity grid and help lower monthly energy bills. Homeowners also benefit from backup power during outages when combined with storage batteries.
- Commercial and Industrial Use: Businesses and factories use photovoltaic systems to cut energy costs and support sustainability goals. Large buildings mostly have the space to install many solar panels, making them ideal for generating significant amounts of electricity, which also helps reduce their carbon footprint.
- Remote and Off-Grid Applications: Photovoltaic energy is useful in remote areas where traditional electricity access is limited or unavailable. Solar panels can power schools, clinics, and homes in off-grid regions, which helps improve quality of life without needing expensive infrastructure.
- Portable and Small Devices: Photovoltaic technology powers small electronics like calculators, solar lamps, and portable chargers. It provides a clean and simple energy source for everyday gadgets. These uses are especially helpful during travel or emergencies when plug-in power isn’t available.
Stats & Facts
- According to EPJ Photovoltaics, in 2023 global renewable energy investments rose by 8% to USD 623 billion, with solar energy securing the largest share—63% or USD 393 billion. This marked a 12% increase in solar investment compared to the previous year, reaffirming solar’s dominant position in the renewable sector.
- As reported by the IEA, solar PV electricity generation surged by 320 TWh in 2023—an impressive 25% year-on-year growth—reaching a total generation of over 1,600 TWh globally. This was the largest absolute growth among all renewables, nearly matching the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario projections.
- EPJ Photovoltaics notes that by the end of 2023, total installed global solar PV capacity had surpassed 1.6 terawatts-peak (TWp), with more than 420 GWp added that year alone. The number of countries installing at least 1 GWp annually has now increased to 35, indicating rapid global uptake of solar power.
- Ember estimates that the world will install 593 GW of solar panels in 2024 if current rates hold, which is 29% higher than 2023 installations. Notably, 292 GW had already been installed by the end of July 2024, underscoring the sector’s strong upward momentum even after an 87% growth surge in 2023.
- According to EPJ Photovoltaics, after price hikes in 2022, 2023 saw declining costs in solar PV and battery storage hardware markets. This drove reductions in levelised costs of electricity (LCOE) for non-tracking solar PV systems and battery storage, enhancing the economic competitiveness of solar solutions globally.
- However, EPJ Photovoltaics also highlighted that the global benchmark LCOE for tracking PV systems increased in 2023. This was largely driven by costlier labour, balance of systems (BoS), and financing conditions, particularly in the United States.
- From IEA data, it’s clear that sustained solar expansion hinges on more than just technological and cost improvements—doubling annual capacity additions by 2030 will require stepped-up policies, investment in grid infrastructure, and resolution of regulatory and financing barriers.
- Ember's mid-year snapshot of 2024 shows that over 292 GW of solar capacity was installed globally by July, suggesting another record-breaking year. If this pace continues, 2024 could outperform even the massive 87% growth rate seen in 2023, reinforcing solar's exponential trajectory.
- IEA indicates that growth in solar capacity is being turbocharged by stronger policy backing and resilient supply chains—especially in China, the U.S., EU, and India—which are collectively shaping a robust global expansion pathway for PV technologies.
- EPJ Photovoltaics stresses that while 2024’s outlook remains bullish, driven by increased electrification of heating, transport, and industry—this alone won’t suffice to limit warming to 1. °C. Rapid acceleration in renewables deployment is urgently needed to align with climate targets.
- The IEA warns that even though current solar generation growth is tracking closely with its NZE Scenario for 2023–2030, maintaining this trajectory requires unwavering ambition from governments and private stakeholders alike, especially on the integration and financial sustainability fronts.
- Based on EPJ Photovoltaics data, 2023 marked a pivotal return to falling system costs after the 2022 inflationary shock, positioning solar as an even more viable choice for meeting rising electricity demand in both developed and emerging markets.
Market Dynamic
Driving Factors in the Photovoltaic Market
Government Support and PoliciesOne of the strongest growth drivers of the photovoltaic market is the increasing support from governments around the world. Many countries have introduced policies, tax incentives, and subsidies to encourage the use of solar energy. These programs help reduce the upfront cost of installing solar panels, making them more affordable for both individuals and businesses. In addition, several regions have set clean energy targets that require a shift away from fossil fuels. This pushes more investment into solar projects. Some governments also provide feed-in tariffs, where people get paid for the excess solar energy they send back to the grid. All these steps create a strong foundation for long-term growth in the photovoltaic market.
Technological Advancements and Falling Costs
Another major factor driving the photovoltaic market is the steady improvement in technology and the dropping costs of solar systems. Over the years, solar panels have become more efficient, meaning they can produce more electricity from the same amount of sunlight. At the same time, the cost to produce and install these systems has gone down due to better manufacturing processes and larger production scales. Battery storage systems are also improving, allowing solar energy to be stored and used later, which increases its reliability. As solar power becomes more efficient and affordable, it becomes an attractive option for more people, leading to wider adoption across different regions and industries.
Restraints in the Photovoltaic Market
High Initial Installation Costs
One of the key restraints in the photovoltaic market is the high initial cost of purchasing and installing solar systems. Although prices have dropped over the years, the upfront investment is still a barrier for many households and small businesses. Costs include not only the solar panels but also inverters, batteries, wiring, and installation labor. In areas without government incentives or financial support, the return on investment may take several years. This delay can discourage people from switching to solar energy. Even though solar power saves money in the long term, the challenge of managing the early expenses continues to slow down adoption in some regions.
Weather Dependence and Energy Storage Challenges
Photovoltaic systems rely on sunlight, making them less effective in areas with frequent cloud cover, rain, or snow. Energy production can be inconsistent during different seasons or weather conditions, which can reduce reliability. To deal with this, users often need energy storage systems like batteries to store power for nighttime or cloudy days. However, these batteries can be expensive and may not be widely available in all markets. Limited storage capacity and added costs make it harder for some users to fully depend on solar energy. These challenges can limit the overall growth and performance of the photovoltaic market, especially in less sunny regions.
Opportunities in the Photovoltaic Market
Expansion in Emerging Markets
A major opportunity for the photovoltaic market lies in its expansion into emerging and developing regions. Many countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America have high solar potential due to abundant sunlight but limited access to reliable electricity. Photovoltaic systems offer a clean and cost-effective solution for powering rural homes, schools, and health centers without the need for expensive grid infrastructure. As global organizations and governments invest in energy access projects, solar technology is expected to play a leading role. Local job creation in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance also adds economic value. With rising demand for energy and increasing awareness, these markets present strong growth opportunities for the solar industry.
Integration with Smart Technologies
The combination of photovoltaic systems with smart technologies is creating exciting new possibilities in the energy sector. Smart grids, energy management apps, and AI-based systems allow users to monitor and control their solar energy use more efficiently, which helps in optimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and improving overall system performance. Also, integrating solar power with electric vehicle charging stations and home automation systems is gaining popularity. These smart solutions make solar power more convenient, reliable, and appealing to modern consumers. As technology advances and becomes more accessible, it opens the door for new business models and wider use of solar energy in both homes and industries.
Trends in the Photovoltaic Market
Growth of Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
A rising trend in the photovoltaic market is the adoption of building-integrated photovoltaics, or BIPV. This technology involves embedding solar panels directly into building materials such as windows, roofs, or facades. It allows buildings to generate electricity without needing separate solar panel installations. BIPV not only saves space but also adds to the aesthetic and energy efficiency of structures. Architects and developers are increasingly using it in smart buildings and eco-friendly construction projects. As awareness of sustainable design grows, BIPV is gaining popularity in both residential and commercial sectors. It represents a smart way to blend solar technology with modern architecture.
Rise of Floating Solar Installations
Another recent trend is the growth of floating solar power systems, where photovoltaic panels are installed on bodies of water like lakes, reservoirs, or even the sea. These systems are ideal for countries with limited land space for large solar farms. Floating solar panels can also improve panel performance by staying cooler over water, which boosts electricity output. Additionally, they help reduce water evaporation and limit algae growth. Governments and private developers are exploring these systems as part of larger renewable energy plans. As the technology becomes more proven and cost-effective, floating solar is expected to become a key part of the global solar expansion.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Technology Analysis
Crystalline silicon is expected to lead the photovoltaic market in 2025, holding a share of 82.9%. This technology is widely adopted due to its reliability, efficiency, and long lifespan. It comes in two main types—monocrystalline and polycrystalline—which both offer strong performance in different environmental conditions. Crystalline silicon panels are also easy to produce at scale, making them cost-effective over time. As a result, many homes, businesses, and solar farms rely on this technology for consistent electricity generation. With ongoing advancements in manufacturing processes and cell design, crystalline silicon continues to play a dominant role in the global transition to clean energy.
Further, thin film technology is expected to experience significant growth throughout the forecast period, becoming an increasingly important player in the photovoltaic market. This technology is lightweight, flexible, and can be easily installed on surfaces where traditional panels may not be suitable, such as buildings, vehicles, and portable solar products.
Thin film performs better in low-light and high-temperature conditions, making it particularly valuable in diverse climates. While it is not as efficient as crystalline silicon, its lower production costs and ability to be used in large-scale installations where space and weight are critical give it a competitive edge. As the market expands and seeks more versatile solar solutions, thin film technology is gaining recognition for its unique benefits.
By Grid Type Analysis
Utility-scale deployment is expected to lead the photovoltaic market in 2025, holding a share of 57.9%. These large solar power plants generate electricity on a massive scale, often providing power to thousands of homes and businesses through the grid. Typically built on open land, they utilize advanced tracking systems to follow the sun, optimizing energy production. Utility-scale projects benefit from economies of scale, which lower the cost per unit due to large installations and bulk purchasing of equipment.
Both governments and private companies are investing heavily in these projects to meet clean energy targets and reduce carbon emissions. As the demand for renewable energy rises and policy support strengthens, utility-scale solar is rapidly expanding and playing a leading role in establishing solar energy as a major contributor to the global electricity supply.
Residential deployment is expected to see significant growth throughout the forecast period, emerging as a key driver of the photovoltaic market. An increasing number of homeowners are opting to install solar panels on their rooftops to cut electricity bills and reduce reliance on traditional power sources.
Solar energy systems for homes have become more affordable and easier to install, making them increasingly popular. Financial support and incentives from governments are also encouraging families to transition to solar. Additionally, home solar systems can be paired with batteries, allowing households to store excess energy for use during the night or in case of power outages. This growth in residential solar adoption is not only helping homeowners save money but also contributing to the broader goal of clean and sustainable energy for all.
By Deployment Analysis
In 2025, grid-connected systems are expected to lead the photovoltaic market, holding a share of 92.9%. These systems are directly linked to the public electricity network, allowing users to draw power when solar energy is insufficient and send excess energy back to the grid. This configuration is popular for homes, businesses, and large solar farms because it provides a stable and reliable power supply.
It also allows users to earn credits or money through net metering, making solar investments more financially attractive. Grid-connected systems are easier to maintain and more cost-effective compared to off-grid alternatives. With strong governmental support, improved infrastructure, and increasing awareness of clean energy, more people are opting for grid-connected solar systems, further driving the global expansion of solar power.
Also, Off-grid photovoltaic systems are expected to see significant growth over the forecast period, becoming increasingly important, especially in remote and rural areas. These systems are not connected to the main electricity grid and rely entirely on solar power, often supplemented by batteries for energy storage. They are particularly useful in locations where building grid infrastructure is challenging or costly.
Off-grid systems help provide electricity to homes, schools, and health centers in isolated regions, improving quality of life and creating new economic opportunities. With advancements in technology and decreasing costs of solar panels and batteries, off-grid solutions are becoming more practical and affordable. Their ability to deliver clean electricity to hard-to-reach areas makes them a growing contributor to the global solar energy movement.
By Installation Type Analysis
Ground-mounted installations are expected to lead the photovoltaic market in 2025, holding a share of 67.1%. These systems are typically set up on open land and are often used in large solar farms that supply electricity to the grid. Ground-mounted systems offer easy maintenance and can be positioned in areas with strong sunlight to maximize energy production. They can also incorporate tracking systems that follow the sun, further enhancing efficiency.
These installations are ideal for utility-scale projects and help meet increasing energy demands in a clean, cost-effective manner. With strong government support and rising demand for renewable energy, ground-mounted solar systems continue to be a popular choice in many regions, making them a vital component in the global expansion of solar power.
In addition, floating solar installations are expected to see significant growth throughout the forecast period, gaining recognition as an innovative way to expand solar energy without using land. These systems are deployed on water bodies such as lakes, reservoirs, and ponds, making them particularly valuable in countries with limited land availability. Floating solar panels benefit from being cooler on water, which can enhance their performance and energy output.
Additionally, they help reduce water evaporation and prevent algae growth, providing environmental advantages. Both governments and private companies are investing in floating solar to optimize unused water surfaces. As technology continues to evolve and costs decrease, floating solar is becoming an increasingly popular solution, particularly in regions where space is limited but the demand for clean energy remains high.
By Component Analysis
Modules are anticipated to lead the photovoltaic market in 2025, holding a share of 48.4%. These are the core components of a solar power system where sunlight is converted into electricity. Solar modules are made up of multiple solar cells connected together, available in various types like monocrystalline and polycrystalline. As technology continues to evolve, modules are becoming more efficient, durable, and cost-effective, enabling more individuals and businesses to adopt solar energy.
They are used in applications ranging from small home systems to large-scale solar farms. With increasing demand for clean energy and strong support for renewable energy sources, the need for high-quality solar modules continues to rise. Their performance is directly linked to the amount of electricity generated, making them essential to the success and expansion of solar power worldwide.
Balance of system (BoS) components are expected to experience significant growth throughout the forecast period, becoming increasingly important in the photovoltaic market. These components include all parts of a solar energy system aside from the modules, such as inverters, wiring, mounting structures, and monitoring devices. BoS components are crucial for managing, converting, and delivering the electricity produced by the solar panels. Without these components, the system would not operate properly or safely.
As the number of solar systems increases, the demand for efficient and reliable BoS equipment is also growing. Ongoing innovations in design, ease of installation, and system integration are making these components more effective and easier to maintain. Their continuous improvement supports the overall performance of solar power systems and plays a key role in the steady growth of the photovoltaic industry.
By Application Analysis
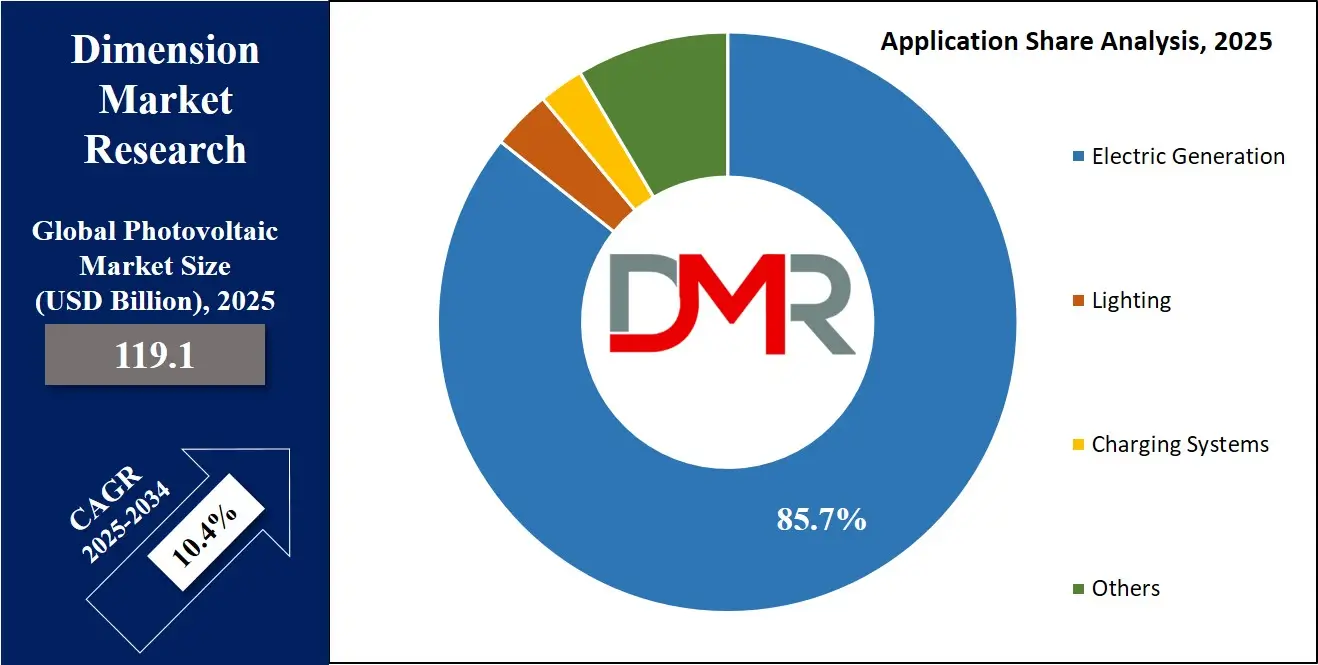
Electricity generation is set to lead the photovoltaic market in 2025, holding a share of 85.7%. Solar panels are extensively used to generate electricity for homes, businesses, and large power plants, playing a crucial role in meeting the world’s growing energy demands with clean and renewable sources. This application is central to the global transition away from fossil fuels, helping to reduce harmful emissions. With significant improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness, solar power systems are now a reliable and scalable solution for energy production in various regions.
Both developed and developing countries are investing in solar farms and rooftop installations to generate electricity and enhance energy security. As technology continues to advance and awareness of climate change rises, electricity generation through solar energy is expanding, positioning solar power as a key element in the future of global electricity supply.
Further, Charging systems are expected to experience significant growth throughout the forecast period, becoming an increasingly important application in the photovoltaic market. Solar-powered charging systems are now commonly used to charge electric vehicles, portable electronics, and backup batteries. These systems help reduce dependence on grid electricity and offer an eco-friendly alternative for powering modern devices.
With the growing use of electric vehicles and the rise in mobile energy needs, solar charging stations are being installed in public spaces, homes, and businesses. They are especially valuable in regions with abundant sunlight and limited grid access. As more individuals seek sustainable energy solutions, solar charging systems are gaining popularity, further contributing to the expansion of the photovoltaic market.
By End User Industry Analysis
Power utilities are projected to lead the photovoltaic market in 2025, holding a share of
58.6%. Utilities are increasingly adopting solar energy as a reliable and clean source of electricity generation. Large-scale solar farms are being developed to supply power to the grid, enabling utilities to meet rising energy demand while reducing carbon emissions. By integrating solar power into the grid, utilities can diversify their energy mix, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and improve energy security. With government incentives and stronger clean energy policies, utilities are expanding their solar projects, making photovoltaic systems a vital part of their strategy for a sustainable energy future.
Further, Industrial facilities are expected to experience significant growth throughout the forecast period, becoming an important end-user sector in the photovoltaic market. Many factories, warehouses, and manufacturing plants are adopting solar power to lower energy costs and reduce their carbon footprint. By installing solar panels on rooftops or in nearby areas, industrial facilities can generate their own clean electricity, which is particularly beneficial for energy-intensive operations.
Solar power also helps businesses comply with environmental regulations and meet sustainability goals. As solar technology becomes more affordable and efficient, the adoption of photovoltaic systems in industrial settings is expected to increase, further contributing to the growth of the solar market.
The Photovoltaic Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Technology
- Crystalline Silicon (c-Si)
- Thin Film
- Others
By Grid Type
By Deployment
- Utility Scale
- Commercial & Industrial
- Residential
By Installation Type
- Ground Mounted
- Rooftop
- Floating Solar
By Component
- Modules
- Inverters
- Balance of System (BoS)
- Mounting Structures & Trackers
By Application
- Electric Generation
- Lighting
- Charging Systems
- Others
By End Use Industry
- Power Utilities
- Commercial Buildings
- Residential Buildings
- Industrial Facilities
- Others
Regional Analysis
Leading Region in the Photovoltaic Market
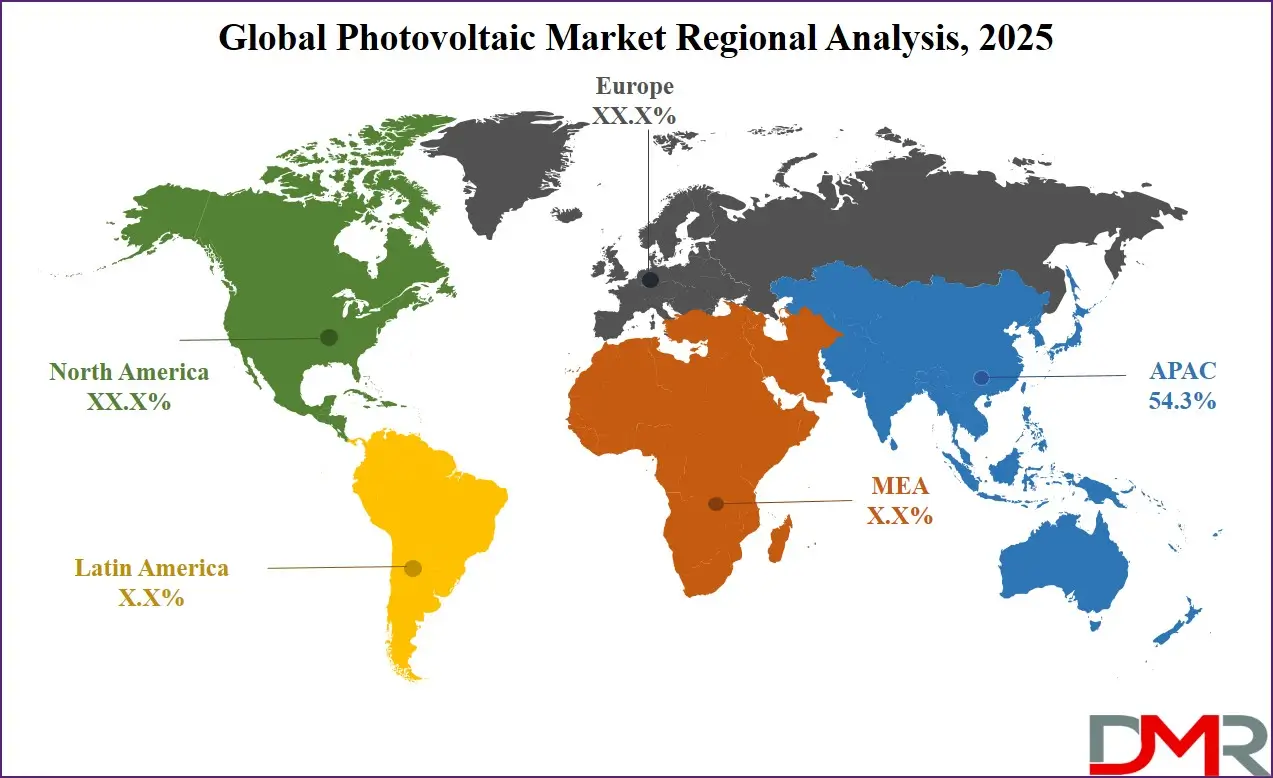
Asia Pacific will be leading in 2025 with a share of
54.3% and will play a major role in the growth of the photovoltaic market. The region benefits from high solar energy potential, a large population, and growing energy needs. Many countries in the Asia Pacific are investing heavily in solar power to reduce dependence on fossil fuels and cut pollution. Governments are supporting solar projects through subsidies, low-interest loans, and clean energy targets. Countries across the region are building large-scale solar farms, encouraging rooftop solar use, and boosting local solar panel manufacturing.
Falling installation costs and better access to technology have also helped more people and businesses adopt photovoltaic systems. The presence of key manufacturing hubs makes it easier and cheaper to produce solar equipment within the region. Asia Pacific’s strong economic development, combined with its focus on renewable energy, is making it a leader in the global solar market and driving the overall growth of photovoltaic use around the world.
Fastest Growing Region in the Photovoltaic Market
With significant growth over the forecast period, Latin America is becoming an important part of the photovoltaic market. The region has strong sunlight throughout the year, making it ideal for solar power generation. Several countries are turning to solar energy to improve electricity access, lower energy costs, and reduce dependence on imported fuels. Supportive government policies, auctions for clean energy, and international investments are helping solar projects grow quickly. Both large solar farms and smaller rooftop systems are being developed. As technology becomes more affordable and more people see the benefits of clean energy, Latin America is steadily increasing its share in the global photovoltaic market.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Competitive Landscape
The photovoltaic market is becoming more competitive as more players enter the industry, from manufacturers to technology developers and installers. Companies are trying to stand out by improving the efficiency of solar panels, lowering production costs, and offering smart energy solutions. There’s also competition in creating panels that work better in different weather conditions and last longer. As demand grows in many countries, especially in sunny regions, businesses are racing to meet that need with better products and faster service. Some focus on large solar farms, while others aim to serve homes and small businesses. Governments supporting clean energy also push the market to grow, encouraging more innovation and competition across the entire solar energy chain.
Some of the prominent players in the Global Photovoltaic are
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Kyocera Corp
- Panasonic Corp
- REC Group
- Suntech Power
- JinkoSolar
- Trina Solar
- LONGi Solar
- Solar Frontier
- Neo Solar Power
- Emphase Energy
- ABB Ltd
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- Adani Solar
- Waaree Energies Ltd
- Total Power Solar Systems
- Vikram Solar
- Delta Electronics
- Huawei Technologies
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In December 2024, The Indian government announced the introduction of an Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) for solar PV cells, effective from 1 June 2026. All solar PV modules used in government-backed schemes, net-metering projects, and open-access renewable energy initiatives must source their solar cells from ALMM List II from June 2026, as the move focuses on bolstering India’s green energy transition by ensuring the use of quality solar PV cells in energy projects. The initiative is part of India’s broader strategy to enhance its solar power sector.
- In November 2024, The Global Solar Council leads the worldwide solar industry in the celebration of achieving 2 TW of installed solar PV capacity. As the deployment of solar energy has exponentially accelerated in recent years, it has carried with it dramatic cost reductions that make solar now the cheapest form of energy available to consumers in many countries across the globe.
- In September 2024, Alpex Solar unveiled its expansion plans to double its photovoltaic solar module capacity to 2.4 GW by FY2025. A greenfield project of 1.2 GW solar PV module capacity will be installed in the company's newly acquired land parcel at Kosi Kotwan, Mathura, in Uttar Pradesh. The company will also explore a foray into solar cell manufacturing in the range of gigawatt capacity.
- In June 2024, First Solar, Inc. unveiled the inauguration of its new facility in Tamil Nadu, India, marking the country's first fully vertically integrated solar manufacturing plant. The facility, situated on six acres with an annual capacity of 3.3 gigawatts (GW), directly employs around 1,000 people. It produces First Solar’s Series 7 photovoltaic (PV) solar modules, developed in the US and optimized for the Indian market. The facility represents an investment of approximately USD 700 million, including USD 500 million in DFC financing.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 119.1 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 289.7 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
10.4% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 18.4 Bn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Technology (Crystalline Silicon (c-Si), Thin Film, and Others), By Grid Type (Grid Connected and Off Grid), By Deployment (Utility Scale, Commercial & Industrial, and Residential), By Installation Type (Ground Mounted, Rooftop, and Floating Solar), By Component (Modules, Inverters, Balance of System (BoS), and Mounting Structures & Trackers), By Application (Electric Generation, Lighting, Charging Systems, and Others), By End Use Industry (Power Utilities, Commercial Buildings, Residential Buildings, Industrial Facilities, and Others) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – US, Canada;
Europe – Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, Rest of Europe;
Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC;
Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America;
Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, Rest of MEA
|
| Prominent Players |
Mitsubishi Electric, Kyocera Corp, Panasonic Corp, REC Group, Suntech Power, JinkoSolar, Trina Solar, LONGi Solar, Solar Frontier, Neo Solar Power, Emphase Energy, ABB Ltd, Siemens AG, Schneider Electric SE, Adani Solar, Waaree Energies Ltd, Total Power Solar Systems, Vikram Solar, Delta Electronics, Huawei Technologies, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user),
Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and
Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to
0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively.
|
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Photovoltaic Market size is expected to reach a value of USD 119.1 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 289.7 billion by the end of 2034.
Asia Pacific is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Photovoltaic Market, with a share of about 54.3% in 2025.
The Photovoltaic Market in the US is expected to reach USD 18.4 billion in 2025.
Some of the major key players in the Global Photovoltaic Market are Mitsubishi Electric, Kyocera Corp, Panasonic Corp, REC Group, and others
The market is growing at a CAGR of 10.4 percent over the forecasted period.