A February 2023 study published by Elsevier Ltd. examined the relationship between COVID-19 cases, vaccination rates, and global antibiotic sales. The study revealed that approximately 75% of COVID-19 patients received antibiotics, significantly contributing to the growing issue of antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
Antibiotic sales, including major classes like cephalosporins, penicillins, macrolides, and tetracyclines, returned to pre-pandemic levels by May 2022. This underscores the need for advanced antimicrobial solutions to address rising AMR challenges, which is driving market demand.
The Pew Charitable Trust reported in December 2020 that 43 promising antimicrobial molecules were under investigation in the U.S. Of these, 15 candidates were in phase 1 clinical trials, 13 in phases 2 and 3, and 2 under review by the FDA.
Notably, 19 candidates targeted gram-negative ESKAPE pathogens, which are critical drivers of AMR. These developments highlight ongoing efforts to innovate and expand the antibiotic pipeline, signaling a positive outlook for the antimicrobial market.
The antibiotics market refers to an industry associated with the production, distribution, income, and intake of antibiotics globally. Key stakeholders in this marketplace vary from multinational pharmaceutical companies to smaller biotech groups, reflecting several panoramas.
The market offers a big product portfolio, including antibiotics like penicillin, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, & others, serving numerous healing functions. Regulatory businesses, which include the FDA & EMA, establish suggestions and oversee safety and efficacy globally.
Antibiotics Market Key Takeaways
- Market size: The global antibiotic market is expected to grow by 27.6 billion, at a CAGR of 4.7 % from 2025 to 2033.
- Market Definition: Antibiotics are a medication used to combat bacterial infections, that come in various forms, such as branded and generic versions.
- Drug class Analysis: By drug class, Penicillin is predicted to dominate the antibiotic market due to its historical significance as it held 28.0% of the market share in 2024.
- Type Analysis: In the context of type, branded antibiotics are predicted to lead this segment as they hold the largest share of this segment in 2024.
- Action mechanism: Based on the action mechanism of antibiotics, cell wall synthesis inhibitors are anticipated to dominate this segment with 53.2 % of the market share in 2024.
- Regional Analysis: Asia-Pacific region is predicted to hold a dominant position in the antibiotics market with 46.0% of the revenue share in 2024.
Antibiotics Market Use Cases
- Chronic Conditions: Antibiotics are used for treating chronic skin conditions like acne as tetracycline derivatives, are used in the treatment of moderate to severe acne which help reduce inflammation and control bacterial growth on the skin.
- Bacterial Infections: The primary function of these antibiotics is to treat bacterial infections like urinary tract infections (UTIs), strep throat, and skin infections caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus.
- Pneumonia: These are important in treating pneumonia, especially when it's caused by bacterial pathogens like Streptococcus pneumonia as they help clear the infection and prevent complications.
- Dental Infections: They also play an important role in treating dental infections which are often caused by bacterial pathogens which are characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums and supporting tissues of the teeth, and can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
Antibiotics Market Dynamic
Drivers
Prevalence of chronic conditionsThe antibiotics market is experiencing significant growth due to a continuous rise in chronic conditions like cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases which require the development of more precise and effective treatment options. They are becoming important in treatment due to their ability to target diseased cells specifically, reducing side effects and improving patient outcomes, driving the market growth.
Technological Innovations in Antibody Development
Advancement in the engineering and manufacturing of antibiotics offers the production of highly potent and specific antibiotics. New technologies like next-generation sequencing and recombinant DNA techniques allow for the creation of monoclonal and bispecific antibiotics with enhanced efficacy and safety profiles.
Restraints
High investment in research antibody and Regulatory Challenge
The production cost of research antibiotics is high which requires time and effort to establish a viable manufacturing process. This process also involves stringent quality and regulatory checks, contributing to the complexity and investment required, restraining the growth of this market.
In addition, the production cost is also increased due to quality control and regulatory compliance, thus smaller research entities and individual researchers can't afford it which constrains market expansion.
Trends
Research and Development
The antibiotic market is shaped through a complicated interplay of factors, including the chronic assignment of antibiotic resistance, using the need for ongoing research and improvement. Stringent regulatory environments, influenced by changing pointers, play a crucial role in the approval and commercialization of antibiotics.
Fostering collaborations among pharmaceutical FirmOngoing studies and development are essential to the market's evolution, fostering collaborations among
pharmaceutical corporations, studies institutions, and authorities’ corporations to deal with antibiotic resistance and beautify remedy alternatives.
Market dynamics are also encouraged via mergers and acquisitions among pharmaceutical corporations, healthcare rules, economic conditions, and public recognition campaigns on responsible antibiotic use.
Opportunities
Personalized Antibiotics MedicineAntibiotics Market is showing tremendous growth opportunities due to a notable shift towards
personalized medicine, as they are tailored to individual patient's characteristics and needs. They are showing growth in different medicinal sectors due to their ability to bind specifically to antigens on cancer cells or pathogens, enabling the development of highly personalized treatments with enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects.
Rising Investment in Antibody Research
Biotech and Pharmaceutical companies are investing resources and money to explore and develop novel antibody treatments for previously untreated conditions. These investment holds the potential to address previously untreatable conditions and also offer promising returns for investors through successful drug development.
Antibiotics Market Research Scope and Analysis
By Drug Class
By drug class, Penicillin persistently dominated the antibiotic market due to its largest market share of 28.0% in 2024 and is expected to show subsequent growth in the forecast period of 2025 to 2033. Penicillin shows a broad spectrum of activity against various bacterial species and is particularly effective against Gram-positive bacteria.
The diverse range of penicillin derivatives, including amoxicillin and ampicillin, enhances their pharmacokinetic properties and resistance to beta-lactamases. With a good safety profile, low price, and good-sized accessibility as a time-honored formula, penicillin stays broadly used, specifically in vulnerable populations like youngsters and pregnant women.
Their validated scientific efficacy, installed through decades of use, and inclusion in remedy guidelines make a contribution to their persevered prominence in scientific practice.
However, the developing difficulty of antibiotic resistance necessitates ongoing studies for brand-spanking new antibiotics and alternative treatment techniques. The desire for antibiotics also relies upon factors along with contamination type, neighborhood resistance styles, and character-affected person traits.
By Type
In the context of type, branded antibiotics are expected to dominate this segment as they hold the highest portion of this segment in 2024 and are anticipated to show subsequent growth in the forthcoming period of 2025 to 2033.
Branded antibiotics dominate the pharmaceutical landscape due to substantial investments in global antibiotic research and development, offering innovative mechanisms of action, and obtaining patent protection that grants exclusivity. These antibiotics often benefit from established brand recognition, a history of success, and rigorous clinical trials, bolstered by regulatory approval.
Educational support programs contribute to proper usage and adherence. The higher prices set for branded antibiotics help pharmaceutical companies recover their investments and stay profitable. They also use market exclusivity tactics, such as adding new uses and combining treatments, to maintain their market position.
However, generic antibiotics play a crucial role by offering cheaper options once the patents expire. This balance between innovation, affordability, and accessibility is key in tackling global healthcare needs and antibiotic resistance issues.
By Action Mechanism
Based on the action mechanism of antibiotics, cell wall synthesis inhibitors are predicted to dominate this segment as they hold 53.2% of the market share in 2024. These inhibitors are a prominent class of antibiotics, leads due to their broad-spectrum activity, essential role in bacterial survival, & clinical effectiveness against various infections. They include well-established antibiotics like penicillin and cephalosporins, which disrupt bacterial cell wall formation, leading to structural instability and cell death.
Their low toxicity to human cells enhances their safety profile for diverse patient populations. The efficacy of cell wall synthesis inhibitors is further sustained by combination therapies and ongoing innovation in research and development, ensuring their relevance and dominance in the market.
While concerns about antibiotic resistance persist, this class has generally demonstrated slower resistance development, and efforts to enhance existing inhibitors and discover new agents continue. However, the evolving landscape focuses on the importance of ongoing surveillance and the exploration of alternative therapeutic approaches in addressing emerging challenges in bacterial infections.
The Antibiotics Market Report is segmented based on the following
By Drug Class
- Penicillin
- Cephalosporin
- Fluoroquinolone
- Macrolides
- Carbapenems
- Aminoglycosides
- Others
By Type
- Branded Antibiotics
- Generic Antibiotics
By Action Mechanism
- Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
- DNA Synthesis Inhibitors
- RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
- Mycolic Acid Inhibitors
- Others
How Does Artificial Intelligence Contribute To Improve Antibiotics Market ?
- Accelerating Drug Discovery – AI rapidly analyzes vast datasets to identify new antibiotic compounds, reducing research time and cost.
- Enhancing Antibiotic Production – AI optimizes fermentation and synthesis processes, increasing production efficiency and reducing waste.
- Improving Diagnostic Accuracy – AI-powered tools enable faster and more precise detection of bacterial infections, ensuring timely treatment.
- Combating Antibiotic Resistance – AI predicts bacterial resistance patterns, helping in the development of more effective antibiotics.
- Optimizing Clinical Trials – AI selects ideal patient groups and predicts drug responses, improving trial efficiency and success rates.
- Enhancing Antibiotic Stewardship – AI provides personalized treatment recommendations to reduce antibiotic misuse and overprescription.
- Monitoring Global Resistance Trends – AI analyzes health data to track emerging resistance threats, aiding in public health strategies.
- Speeding Up Regulatory Approvals – AI streamlines documentation and compliance, reducing approval time for new antibiotics.
Antibiotics Market Regional Analysis
The Asia-Pacific region is predicted to hold a dominant position in the antibiotics market
with 46.0 % of the market share in 2024 and is expected to show subsequent growth in the upcoming period of 2025 to 2033. This dominance is driven by various factors contributing to its significant influence.
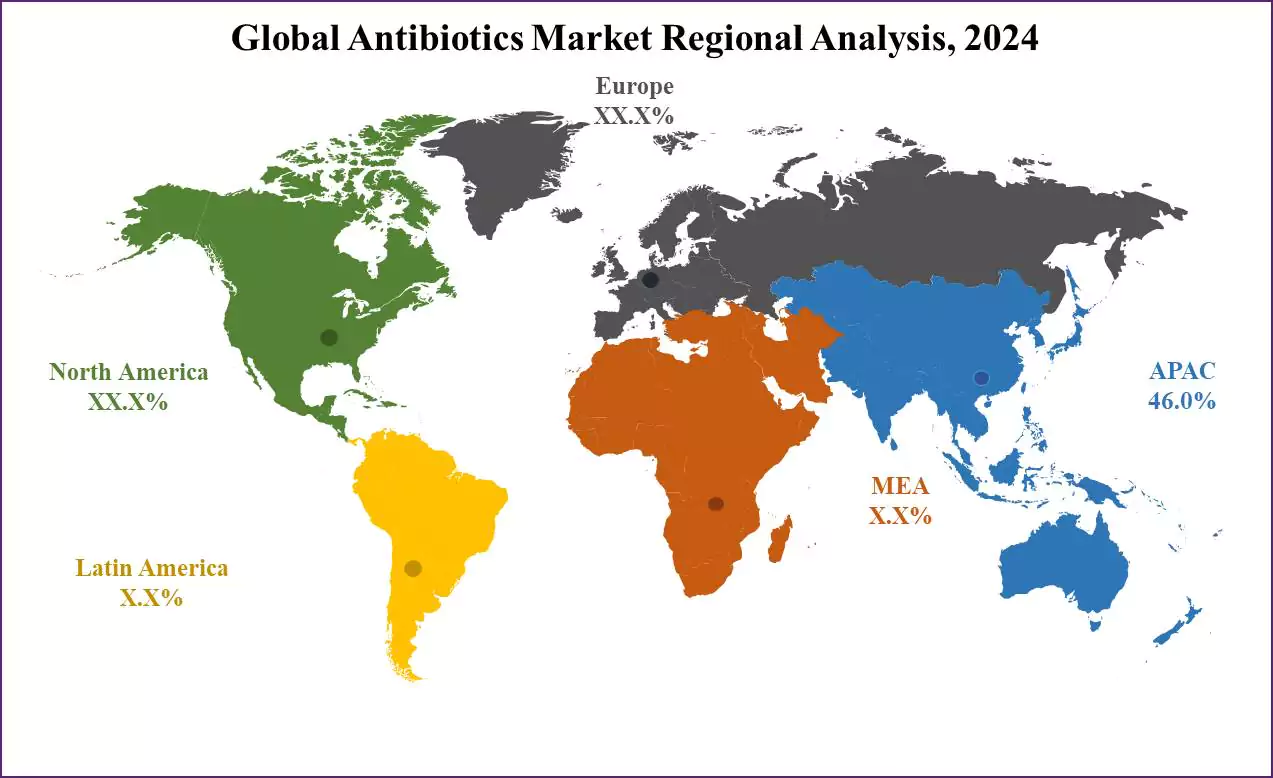
This region's big and various populace studies and the heightened occurrence of infectious diseases necessitate a huge call for antibiotics. Economic growth in numerous international locations in this location has caused extended healthcare spending, in addition to boosting the need for prescription drugs.
The Asia-Pacific pharmaceutical enterprise, specifically in developing countries like China and India, performs an essential position in antibiotic manufacturing, research, and improvement, contributing to innovation. Government initiatives aimed toward healthcare infrastructure improvement and improved public health, coupled with the location's susceptibility to infectious ailments, underscore the essential characteristic of antibiotics.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Antibiotics Market Competitive Landscape
The antibiotics marketplace reveals a dynamic and multifaceted competitive landscape motivated by various factors inclusive of studies and improvement, regulatory dynamics, market consolidation, and worldwide health challenges. Key pharmaceutical gamers inside the worldwide antibiotics market, together with Pfizer, Roche, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and GlaxoSmithKline, dominate the market, often with their diversified portfolios.
Generic competition intensifies after patent expirations, leading to increased competition and capacity fee discounts. Major markets make contributions to innovation, focusing on novel techniques to combat antibiotic resistance.
Ongoing research and improvement tasks are important, with corporations investing in progressive solutions gaining an aggressive edge. The regulatory environment, worldwide collaborations, market consolidation through mergers and acquisitions, tasks addressing antibiotic resistance, and strategic marketplace admission to and pricing techniques are vital components shaping the competitive dynamics. Additionally, responsible antibiotic use is gaining prominence, influencing organizations' practices and marketplace positioning.
Some of the prominent players in the Global Antibiotics Market are
- Abbott Laboratories
- Pfizer Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson Services
- GlaxoSmithKline PLC
- Sanofi
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Novartis AG
- Bayer AG
- Astellas Pharma Inc.
- Others
Antibiotics Market Recent Developments
- In May 2023, The AMR Action Fund added Vedanta Biosciences and Pattern Bioscience to combat antibiotic resistance. Vedanta focuses on a microbiome-directed therapy for Clostridioides difficile infection, receiving $106.5 million for VE303 trials. Pattern Bioscience develops a rapid phenotypic test for pneumonia.
- In March 2023, WHO introduced the Pediatric Drug Optimization (PADO) list, prioritizing age-appropriate antibiotic formulations for children which aims to expedite access through the Global Accelerator for Pediatrics Formulations Network (GAP-f).
- In October 2022, AbbVie announced its acquisition of DJS Antibiotics Ltd, a company specializing in G protein-coupled receptors which is currently undergoing investigational preclinical studies for the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and various other fibrotic disorders.
- In June 2022, The AMR Industry Alliance introduced a global certification for antibiotic manufacturers, developed by BSI, aiming to ensure responsible pharmaceutical manufacturing, combat antimicrobial resistance, and engage major pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer, Roche, and Teva.