Market Overview
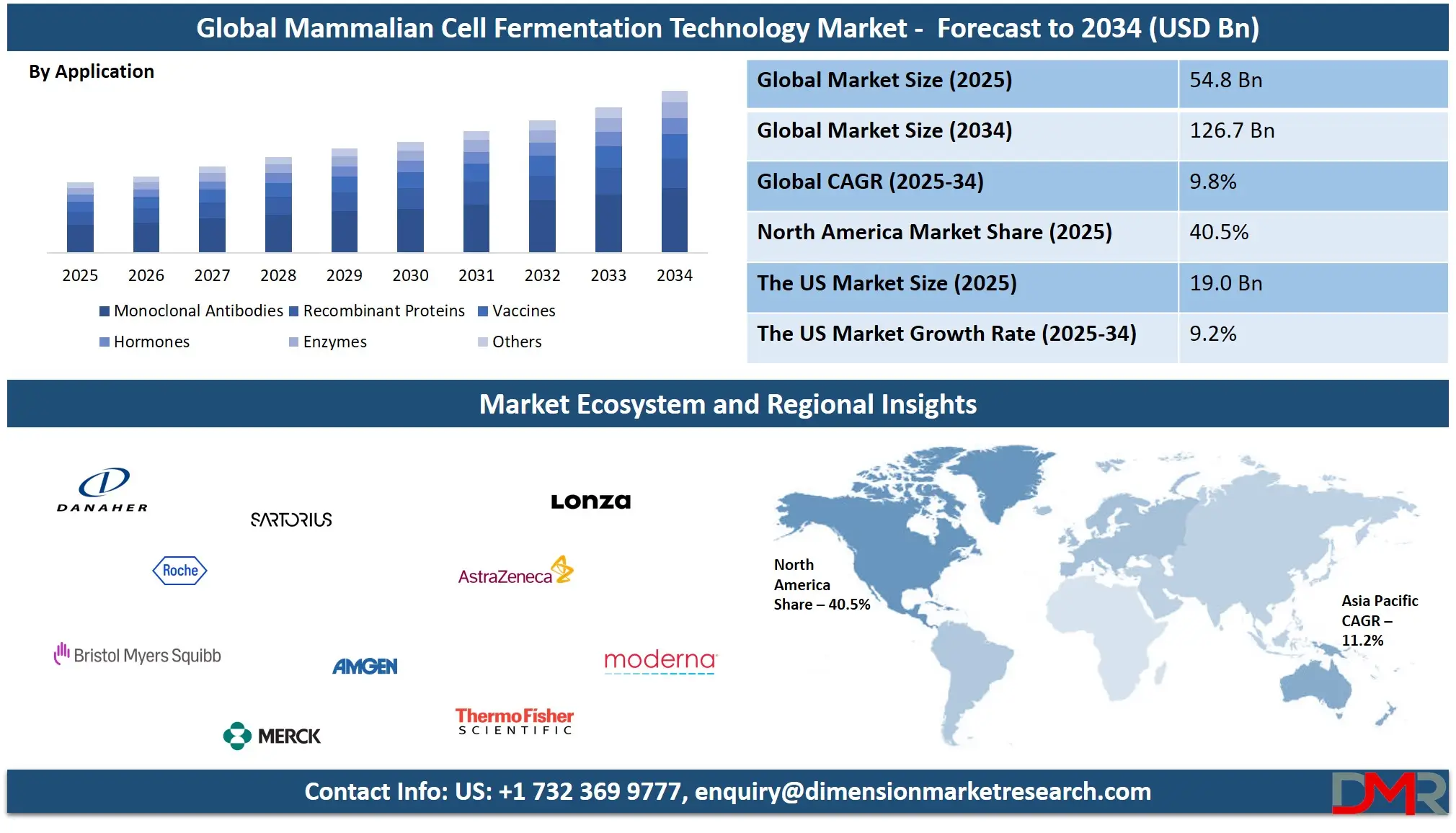
The Global Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market size is projected to reach USD 54.8 billion in 2025 and grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.8% from there until 2034 to reach a value of USD 126.7 billion.
Mammalian cell fermentation technology is a method used in biotechnology to produce complex proteins and other biological substances. These cells, taken from mammals like mice, humans, or hamsters, are grown in controlled environments like bioreactors. Unlike bacteria or yeast, mammalian cells are more suitable for creating human-like proteins because they perform similar chemical modifications. This technology is important in the production of biologic drugs, vaccines, and hormones like insulin and monoclonal antibodies, which are used to treat diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and diabetes.
The demand for mammalian cell fermentation has grown in recent years, mainly due to the rise of biologic medicines. These drugs are often more effective than traditional chemical-based medicines and come with fewer side effects. As more diseases become treatable through targeted therapies, biopharmaceuticals companies are increasing their investment in this area. Furthermore, with a growing number of elderly people and chronic illnesses worldwide, there is a consistent need for advanced treatments, boosting demand for high-quality biologics produced using this technology.
Several key trends are shaping the future of mammalian cell fermentation. One major trend is the development of single-use bioreactors, which make the process more flexible and reduce the risk of contamination. Another trend is the use of automation and artificial intelligence to monitor and control cell growth. These tools help increase production efficiency and product quality. Additionally, researchers are constantly working to develop cell lines that grow faster and produce more proteins, which helps lower manufacturing costs.
Important events in recent years include the rapid development and manufacturing of COVID-19-related therapies and vaccines. Mammalian cell systems played a critical role in producing antibodies and other treatments during the pandemic. Many companies expanded their fermentation capabilities to meet emergency health needs. These efforts not only showed the potential of mammalian cell fermentation but also drove new investments and partnerships in the biotech field.
Another significant insight is the shift toward personalized medicine. Mammalian cell technology supports the creation of customized drugs tailored to individual patients. This approach requires smaller but more frequent production batches, which is different from traditional mass drug production. The technology is well-suited for this because of its flexibility and precision, making it vital in cell therapy and regenerative medicine applications.
The US Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
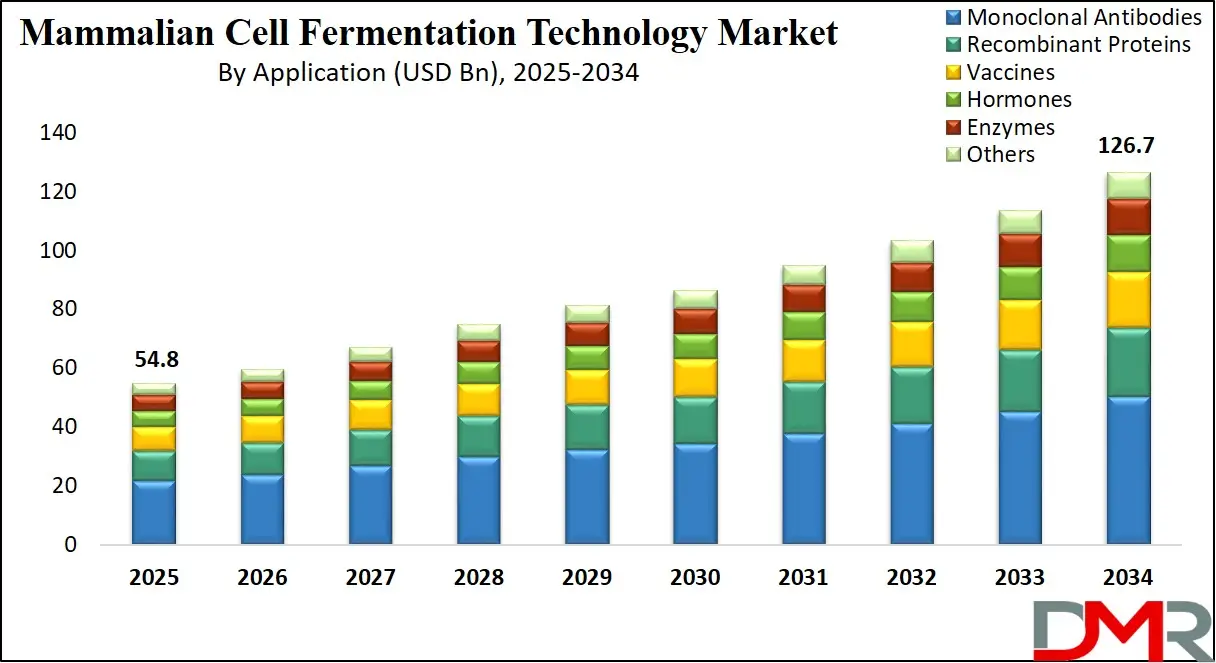
The US Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market size is projected to reach USD 19.0 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 9.2% over its forecast period.
The US plays a leading role in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market due to its advanced biotechnology ecosystem, strong research infrastructure, and high investment in biologics development. It is home to many biopharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and contract manufacturing organizations that specialize in this technology.The US government also supports innovation through funding, tax incentives, and regulatory frameworks that encourage the development of advanced therapies.
With a large patient population and high demand for biologics, the US serves as a key market for commercializing new products. Additionally, the country is a hub for clinical trials and regulatory approvals, making it a central force in shaping global standards and practices in mammalian cell fermentation and biologics manufacturing.
Europe Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
Europe Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market size is projected to reach USD 12.0 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 9.8% over its forecast period.
Europe holds a strong position in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market, supported by its well-established pharmaceutical industry, advanced research institutions, and favorable regulatory environment. Countries like Germany, Switzerland, and the Netherlands are key hubs for biologics manufacturing and innovation. The European Union promotes biotechnology advancements through funding programs and collaborative research initiatives, encouraging the development of high-quality biologic therapies. Europe’s focus on healthcare quality, patient safety, and sustainable manufacturing further drives investment in modern fermentation technologies.
Japan Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
Japan Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market size is projected to reach USD 2.7 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 10.1% over its forecast period.
Japan plays a significant role in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market, driven by its strong pharmaceutical sector, advanced R&D capabilities, and focus on biotechnology innovation. The country is known for its high standards in drug development and quality control, which align well with the precise requirements of mammalian cell-based production. Japanese companies and research institutions actively engage in developing biologics, including monoclonal antibodies and regenerative therapies. Government support for advanced healthcare technologies and collaborations between academia and industry further strengthen Japan’s position. The country also emphasizes automation and efficiency, contributing to process optimization in fermentation. With a growing focus on personalized medicine and aging population needs, Japan continues to be a key contributor to the global advancement of this technology.
Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market: Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market size is expected to grow by USD 67.1 billion, at a CAGR of 9.8%, during the forecasted period of 2026 to 2034.
- By Application: The monoclonal antibodies segment is anticipated to get the majority share of the Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market in 2025.
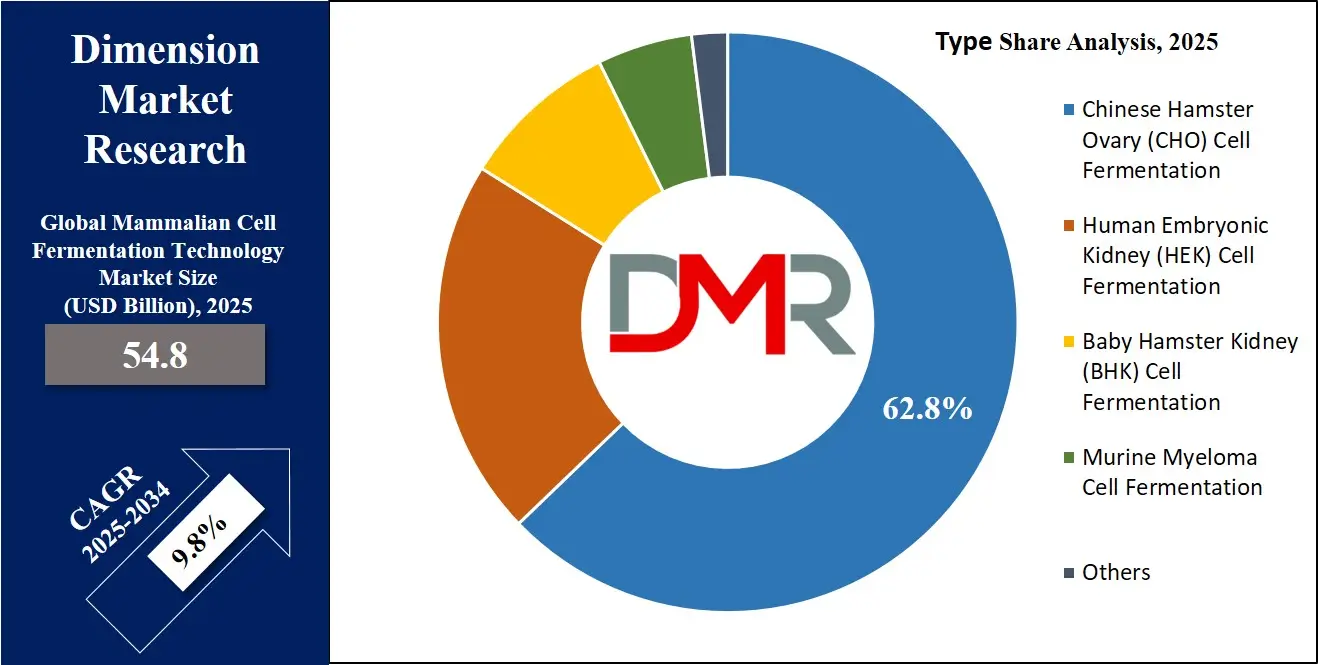
- By Type: The Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Fermentation segment is expected to get the largest revenue share in 2025 in the Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market.
- Regional Insight: North America is expected to hold a 40.5% share of revenue in the Global Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market in 2025.
- Use Cases: Some of the use cases of Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology include vaccine development, gene & cell theraphy, and more.
Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market: Use Cases
- Monoclonal Antibody Production: Mammalian cell fermentation is widely used to produce monoclonal antibodies, which are lab-made proteins that help the immune system fight diseases like cancer and autoimmune disorders. These antibodies need human-like structures that mammalian cells can produce accurately. The technology ensures high purity and effectiveness of these treatments.
- Vaccine Development: Vaccines, especially for complex viruses, often require proteins that resemble those found in the human body. Mammalian cells are ideal for this because they can produce proteins with proper folding and modifications. This method was crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic for the fast development of therapeutic antibodies and vaccines.
- Hormone Manufacturing: Important human hormones like insulin and erythropoietin are made using mammalian cell fermentation. These hormones must be structurally similar to natural human hormones to work properly in the body. Using mammalian cells ensures the right structure and safety of the product.
- Gene and Cell Therapy: The technology supports the creation of viral vectors used to deliver genes in gene therapy. These vectors must be produced in systems that mimic human biology, making mammalian cell fermentation the right choice. It allows precise control and high-quality output required for these advanced therapies.
Market Dynamic
Driving Factors in the Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
Rising Demand for Biologic and Precision Medicines
One of the major growth drivers for the mammalian cell fermentation technology market is the increasing global demand for biologic drugs and precision medicines. Biologics are known for their high efficacy, fewer side effects, and ability to treat chronic and complex conditions like cancer, autoimmune diseases, and rare genetic disorders. As the world shifts toward personalized treatment approaches, the need for biologics that mimic human cellular functions grows stronger. Mammalian cells are the best choice for producing these drugs due to their ability to perform human-like modifications. This demand encourages pharmaceutical and biotech companies to invest more in fermentation platforms. Ongoing innovation in biologics and biosimilars further boosts the need for reliable and scalable fermentation technology. As healthcare needs grow, so does reliance on this technology.
Technological Advancements and Manufacturing Efficiency
Another important growth driver is the continuous advancement in fermentation and bioproduction technologies. The industry is moving toward more efficient, scalable, and cost-effective solutions such as single-use bioreactors, real-time process monitoring, and AI-assisted production systems. These innovations help reduce contamination risks, lower production time, and improve product consistency. Improved cell line engineering is also enabling higher yields of therapeutic proteins with better quality. Such advancements allow faster development and commercialization of biologics, which is especially valuable in urgent situations like pandemics. Companies are also increasingly focusing on sustainability and automation, which aligns well with modern biomanufacturing trends. Altogether, these improvements are making mammalian cell fermentation more attractive and accessible to both large firms and emerging players.
Restraints in the Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
High Production Costs and Infrastructure Requirements
One of the key restraints in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market is the high cost associated with production and infrastructure. Setting up advanced bioreactors, cleanrooms, and quality control systems requires significant investment, which can be a barrier for smaller companies and startups. Additionally, mammalian cells are sensitive and require precise conditions to grow, which increases operational costs. Maintaining sterility and ensuring consistency adds further complexity to the process. Compared to microbial or yeast fermentation, mammalian systems are slower and more expensive. This makes it challenging to scale up quickly or compete on price, especially in emerging markets. As a result, cost remains a major factor limiting wider adoption of the technology across all regions.
Regulatory Challenges and Complex Approval Processes
Another restraint is the strict and often lengthy regulatory approval process for products developed using mammalian cell fermentation. Since these products are typically high-risk biologics, they must meet rigorous safety, quality, and efficacy standards. This involves extensive testing, documentation, and compliance with guidelines set by global authorities like the FDA or EMA. The regulatory environment can be difficult to navigate, especially for companies entering new markets or developing novel therapies. Any delays or failures in approval can result in financial losses and hinder product launch timelines. Moreover, ongoing changes in regulations and the need for frequent audits can increase the burden on manufacturers. These challenges may discourage new entrants and slow innovation in the field.
Opportunities in the Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
Expansion into Emerging Markets and Healthcare Infrastructure Growth
A significant opportunity for the mammalian cell fermentation technology market lies in its expansion into emerging economies. Countries in Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East are investing heavily in healthcare infrastructure and agriculture biotechnology, boosting cross-industry collaboration. With increasing government support and favorable policies, companies can explore cost-effective manufacturing and distribution. Furthermore, rising awareness of chronic diseases and the demand for modern therapies make these markets highly attractive.
Innovation in Personalized and Regenerative Medicine
The growing focus on personalized and regenerative medicine presents another major opportunity for mammalian cell fermentation technology. This technology is essential for producing tailored biologic treatments, such as patient-specific antibodies or gene therapies. As medicine shifts toward customized approaches, demand for small-batch, flexible, and precise manufacturing methods increases. Mammalian cell systems are uniquely suited for this role due to their ability to mimic human cellular processes. Additionally, advancements in stem cell research and tissue engineering depend heavily on mammalian cell fermentation. Companies investing in this space can benefit from being at the forefront of cutting-edge therapies. This trend not only supports innovation but also creates new revenue streams in next-generation healthcare solutions.
Trends in the Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
Growing Adoption of Continuous and Hybrid Fermentation Systems
The mammalian cell fermentation field is shifting from traditional batch production to more dynamic continuous and hybrid systems. Continuous perfusion, where fresh media is added and waste removed while cells remain in the reactor, enables higher cell density and more consistent product quality. Many manufacturers are now experimenting with fed-batch or hybrid models that combine fed-batch and perfusion advantages—extending production time and boosting yield without overcomplicating operations. This push toward enhanced bioprocess intensification reflects a broader trend: improving efficiency, minimizing downtime, and driving cost savings. These next-generation approaches are a key trend shaping the future of biologic manufacturing.
Integration of AI, Automation, and Real‑Time Monitoring
Advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and process analytical technology (PAT) are transforming mammalian cell fermentation. Real‑time monitoring systems now track conditions like pH, oxygen levels, and metabolites, enabling immediate adjustments to maintain ideal growth environments. AI and machine learning algorithms analyze complex datasets from these systems to predict outcomes, optimize media composition, and refine cell line performance. As a result, companies can reduce variability, improve consistency, and speed up process development. This digital shift toward smart bioprocessing is revolutionizing how biologics are produced, making fermentation more precise, reliable, and scalable.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
Artificial Intelligence is significantly transforming the mammalian cell fermentation technology market by improving process efficiency, precision, and scalability. Traditionally, fermentation involving mammalian cells has required constant monitoring and manual adjustments to maintain optimal conditions. With the integration of AI, advanced algorithms can now analyze real-time data from bioreactors to predict outcomes, adjust parameters like pH, oxygen levels, and nutrient supply, and ensure consistent product quality. This not only reduces human error but also shortens development timelines and lowers production costs. AI-driven modeling and simulation further support faster optimization of cell growth conditions, helping companies achieve higher yields and more reliable results in biologics and vaccine production.
Beyond process control, AI is also enhancing innovation and decision-making in research and development. Machine learning can analyze large datasets from experiments to uncover patterns and suggest new formulations or production strategies. This accelerates the development of complex biopharmaceuticals such as monoclonal antibodies and cell-based therapies. AI also plays a role in predictive maintenance of fermentation equipment, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation. In highly regulated environments like pharmaceutical manufacturing, AI improves compliance by enabling automated documentation and traceability. While challenges such as data integration and model validation still exist, the growing use of AI is driving a shift toward smarter, more adaptive, and cost-effective fermentation systems. As a result, AI is not just supporting but reshaping the future of mammalian cell fermentation technology, making it more robust, scalable, and suitable for the demands of modern biotechnology.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Type Analysis
Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell fermentation is expected to be leading in 2025 with a share of 62.8%, playing a key role in driving the mammalian cell fermentation technology market. CHO cells are widely used because they are highly adaptable, easy to grow in suspension, and capable of producing complex proteins with human-like properties. Their proven track record in the development of therapeutic proteins, including monoclonal antibodies and vaccines, makes them a preferred choice for biopharmaceutical companies. These cells also have regulatory acceptance across major global markets, which supports their continued use in clinical and commercial production. As more biologic drugs are developed, the demand for efficient and scalable production systems continues to rise. CHO cell fermentation provides reliability, safety, and consistency, which are essential for large-scale biologics manufacturing. The flexibility of CHO cell systems also supports innovation in personalized medicine and biosimilars, further contributing to their dominance in this growing market.
Baby Hamster Kidney (BHK) cell fermentation is set to see significant growth over the forecast period in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market. BHK cells are known for their strong productivity and have been widely used for the development of vaccines, recombinant proteins, and gene therapy products. Their ability to grow well in suspension cultures and produce high-quality proteins makes them suitable for both research and commercial applications. With increasing demand for specialized biologics and advancements in vaccine development, BHK cell lines are gaining attention as a reliable option for complex protein expression. They also offer good scalability, allowing for efficient transition from lab to large-scale production. As biotech companies continue to explore alternative cell lines for specific applications, BHK cell fermentation is emerging as a valuable platform supporting innovation, especially in viral vector production and next-generation biologics manufacturing.
By Application Analysis
Monoclonal antibodies are set to be leading in 2025 with a share of 39.7%, making them the largest application in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market. These lab-made proteins are designed to target specific cells or substances in the body, making them useful in treating cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious conditions. Mammalian cell systems, especially CHO cells, are ideal for producing monoclonal antibodies because they ensure the right structure and function of these complex proteins. The demand for targeted therapies continues to rise, especially as more personalized medicines enter development. With their proven effectiveness and wide therapeutic use, monoclonal antibodies remain at the center of innovation in biologics. As more of these treatments gain approval worldwide, fermentation platforms are being expanded and optimized to support faster and larger production, reinforcing the essential role of monoclonal antibodies in the continued growth of this technology.
Hormones are playing a highly important role in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market and are set to experience significant growth over the forecast period. These include vital therapeutic proteins like insulin, erythropoietin, and growth hormones, which require human-like modifications for safety and effectiveness. Mammalian cells are well-suited for this purpose because they can produce hormones that closely match natural human forms. The growing number of patients with hormone-related conditions such as diabetes and anemia is increasing the demand for reliable, high-quality hormone therapies. With advancements in cell culture and purification methods, hormone production is becoming more efficient and accessible. The ability to meet global healthcare needs with safe and consistent hormone-based treatments is encouraging more companies to invest in this application. This growing use of mammalian fermentation for hormone production supports long-term market growth and contributes to meeting rising healthcare demands.
By End User Analysis
Biopharmaceutical companies are expected to be leading in 2025 with a share of 55.2%, making them the top end users of mammalian cell fermentation technology. These companies rely heavily on this method to produce complex biologic drugs, including monoclonal antibodies, hormones, and vaccines. The technology supports their need for high-quality, scalable, and safe production systems that meet strict regulatory standards. With the rise in demand for targeted therapies and biosimilars, biopharma firms are investing in advanced fermentation platforms to boost efficiency and reduce time-to-market. In-house capabilities allow these companies to maintain greater control over production and ensure consistent product quality. As biologics become a larger part of the drug pipeline, mammalian cell systems are becoming a central part of operations. This growing reliance on cell-based fermentation helps these companies innovate, expand their product lines, and stay competitive in the fast-moving healthcare landscape.
CMOs & CDMOs are seeing significant growth over the forecast period as key end users in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market. Many biotech and pharmaceutical companies are turning to outsourcing partners to handle complex biologics production. CMOs & CDMOs offer specialized expertise, flexible manufacturing capacity, and access to the latest fermentation technologies, which makes them valuable collaborators. With demand rising for monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and gene therapies, outsourcing has become a cost-effective and efficient solution for scaling up production. These service providers also help speed up clinical development by offering end-to-end support, from process development to large-scale manufacturing. As smaller biotech firms enter the market and larger companies focus on innovation, CMOs & CDMOs play an increasingly vital role in meeting global supply needs while maintaining high quality and compliance standards. Their growth reflects the expanding need for reliable and agile manufacturing partnerships in the biopharma industry.
The Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following:
By Type
- Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) Cell Fermentation
- Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK) Cell Fermentation
- Baby Hamster Kidney (BHK) Cell Fermentation
- Murine Myeloma Cell Fermentation
- Others
By Application
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Recombinant Proteins
- Vaccines
- Hormones
- Enzymes
- Others
By End User
- Biopharmaceutical Companies
- CMOs & CDMOs
- Academic & Research Institutes
Regional Analysis
Leading Region in the Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
North America, leading in 2025 with a share of 40.5%, holds a strong position in the growth of the mammalian cell fermentation technology market. The region benefits from a well-established biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and strong investment in biologics research and development. The United States, in particular, is home to many key players, research institutes, and contract manufacturing organizations that are deeply involved in developing and producing biologic therapies.
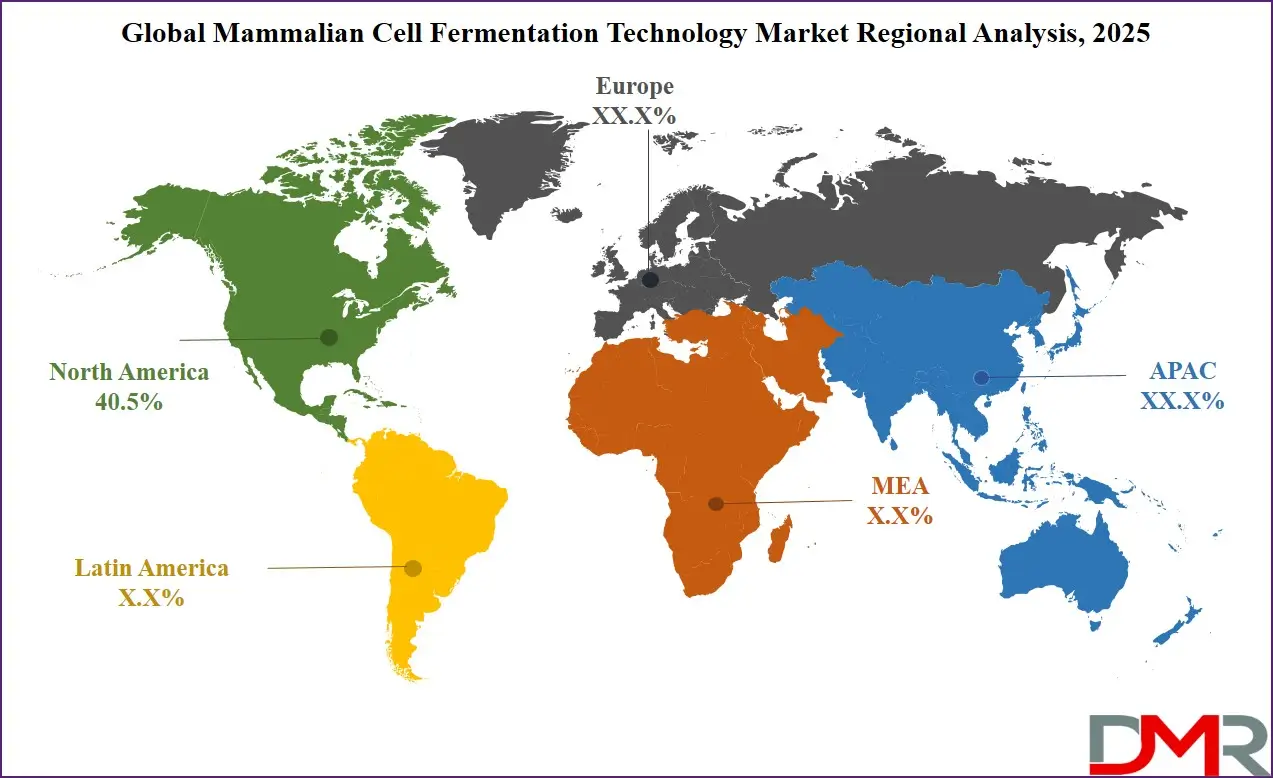
Canada also supports innovation through research grants and public-private partnerships. The presence of skilled professionals, advanced lab facilities, and regulatory frameworks that support fast-track approvals contribute to faster product development. The demand for monoclonal antibodies, gene therapies, and vaccines continues to rise, supporting the adoption of mammalian cell-based systems. With a growing focus on precision medicine, automation, and continuous bioprocessing, North America remains a driving force in shaping the future of this technology. The region’s leadership is expected to continue due to strong demand and constant innovation.
Fastest Growing Region in the Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology Market
Asia Pacific is showing significant growth over the forecast period in the mammalian cell fermentation technology market due to rising investments in biotechnology, increasing demand for biologics, and expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities. Countries like China, India, South Korea, and Australia are strengthening their presence in biopharmaceutical production with supportive government policies and growing research activities. The region is witnessing a rise in chronic diseases, which is boosting the need for advanced therapeutic proteins and monoclonal antibodies. Local companies are also forming partnerships with global players to improve access to technology and expertise. With improved healthcare infrastructure and skilled talent, Asia Pacific is estimated to become a major contributor to global fermentation advancements.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the mammalian cell fermentation technology market is becoming more dynamic as demand for biologic drugs increases. Many companies are focusing on improving cell lines, optimizing fermentation processes, and expanding production capacity to stay ahead. There's also a growing push toward using more efficient and scalable systems, like single-use bioreactors and automated monitoring tools. Startups and smaller firms are entering the market with specialized innovations, while established players are strengthening their positions through partnerships and global expansion. Regulatory approvals and patent protection play a big role in shaping competition. Overall, the market is highly active, with firms racing to offer faster, safer, and more cost-effective ways to produce complex biologic products for growing healthcare needs.
Some of the prominent players in the global Mammalian Cell Fermentation Technology are
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Merck KGaA
- Danaher
- Lonza
- F. Hoffmann La Roche
- Sartorius AG
- AstraZeneca
- Bristol Myers Squibb
- Amgen
- Gilead Sciences
- Moderna
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- GE Healthcare / General Electric
- Samsung Biologics
- WuXi Biologics
- Cytiva
- Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies
- Catalent
- AGC Group / AGC Biologics
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, NIZO and Enzymit have successfully scaled up enzyme production using Enzymit’s proprietary cell-free manufacturing platform, marking a major milestone in alternative biomanufacturing. By combining NIZO’s fermentation and protein expression expertise with Enzymit’s enzyme design capabilities, the partnership offers a streamlined, cell-free solution for producing high-value biomolecules like hyaluronic acid. This method eliminates the need for living cells, reducing complexity and cost. NIZO’s CEO, Nikolaas Vles, highlighted the collaboration as a strong example of advancing innovative biotech toward industrial application.
- In October 2024, WuXi Biologics launched WuXia RidGS™, a high-yield GS-knockout CHO expression platform developed using zinc finger nucleases (ZFN) for targeted gene editing. Built on the WuXia™ platform, WuXia RidGS™ supports antibiotic-free cell line development with strong cell growth, high expression levels exceeding 6 g/L for monoclonal antibodies, and stable performance across various biologics. It delivers consistent product quality, favorable glycosylation, and high purity, making it ideal for mAbs, bispecifics, Fc-fusion proteins, and other recombinant therapeutics.
- In September 2024, Nu-Tek introduced two new Soy Peptone products—HSP-N Soy Peptone for high nitrogen applications and HSP-I Soy Peptone for low carbohydrate needs. Both are manufactured at the Austin Manufacturing Center (AMC) in Austin, Minnesota, a cutting-edge facility dedicated to producing high-quality raw materials for biopharmaceuticals. AMC features advanced quality systems, enhanced traceability, and focused investments in product characterization. These upgrades support Nu-Tek’s commitment to reducing variability and meeting the evolving needs of customers in cell culture media production.
- In August 2024, AGC Biologics and NEC Bio Therapeutics announced a partnership to support the production of NECVAX-NEO1, an oral, bacteria-based DNA vaccine targeting patient-specific tumor neoantigens. This collaboration focuses on advancing personalized cancer therapies by combining the biotechnology expertise of both companies. By working together, they aim to improve the development and manufacturing of tailored treatments, marking a significant step forward in cancer care and highlighting the potential of innovative, patient-focused vaccine technologies.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 54.8 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 126.7 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
9.8 % |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 19.0 Bn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Type (Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) Cell Fermentation, Human Embryonic Kidney (HEK) Cell Fermentation, Baby Hamster Kidney (BHK) Cell Fermentation, Murine Myeloma Cell Fermentation, and Others), By Application (Monoclonal Antibodies, Recombinant Proteins, Vaccines, Hormones, Enzymes, and Others), By End User (Biopharmaceutical Companies, CMOs & CDMOs, and Academic & Research Institutes) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, Rest of Europe; Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Merck KGaA, Danaher, Lonza, F. Hoffmann La Roche, Sartorius AG, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Amgen, Gilead Sciences, Moderna, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, GE Healthcare / General Electric, Samsung Biologics, WuXi Biologics, Cytiva, Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies, Catalent, AGC Group / AGC Biologics, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively. |