Market Overview
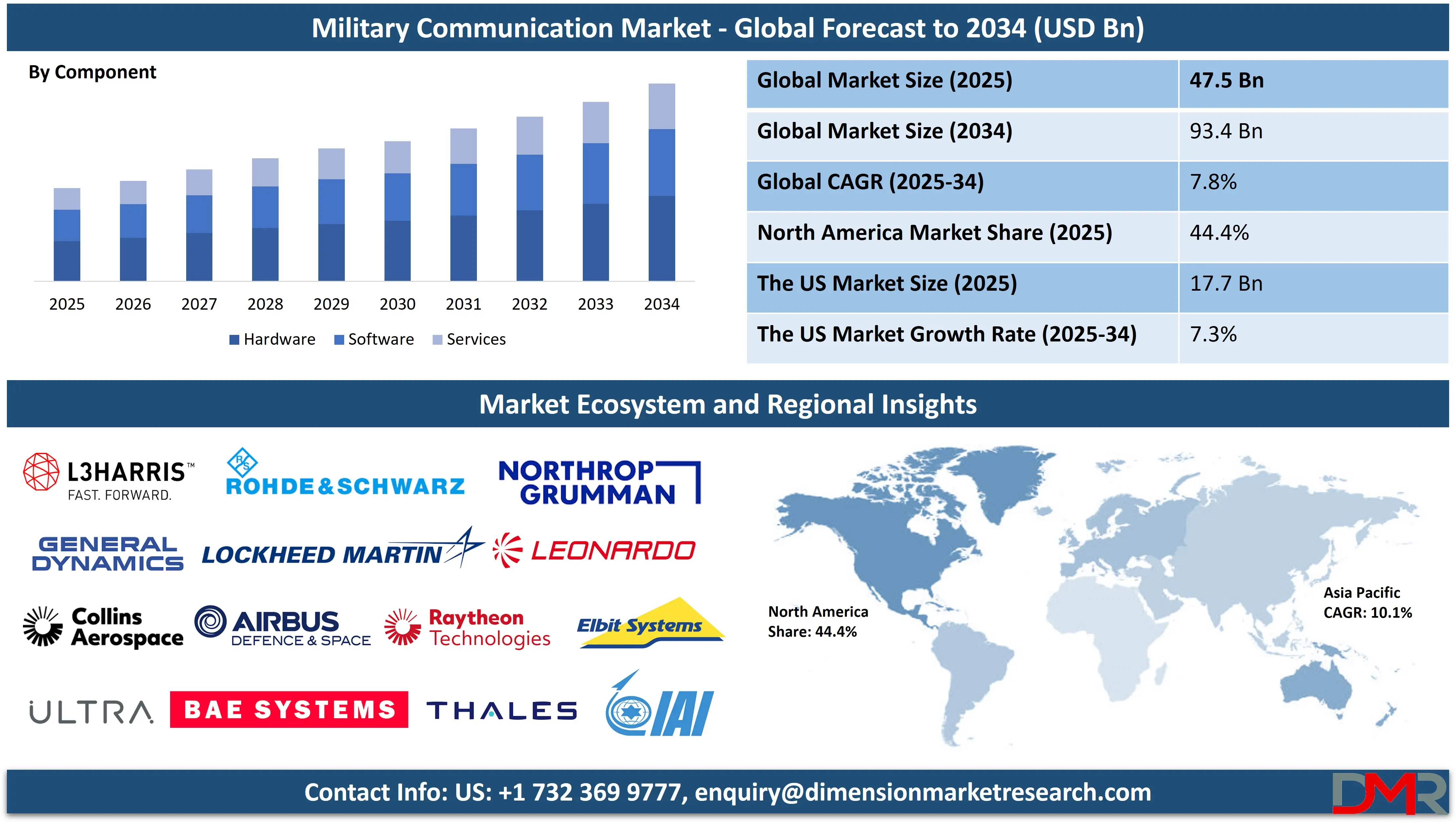
The Global Military Communication Market is projected to reach USD 47.5 billion in 2025 and grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.8% from there until 2034 to reach a value of USD 93.4 billion.
The global military communication market is undergoing a transformative evolution, influenced by rapid digitization of armed forces, increasing defense expenditures, and escalating cross-border conflicts. Modern military operations demand highly secure, interoperable, and real-time communication systems that can sustain dynamic combat environments across land, sea, air, and space domains. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI), 5G, and low-latency satellite constellations is revolutionizing battlefield communication, enabling predictive threat intelligence, autonomous decision-making, and real-time multi-domain command and control (C2).
One of the key trends driving this market is the proliferation of Software-Defined Radios (SDRs) and Network-Centric Warfare (NCW) capabilities. SDRs support frequency agility, multi-band operability, and encrypted data exchange, crucial for joint-force missions and allied operations. Meanwhile, network-centric infrastructures ensure data-driven synchronization of command posts, unmanned systems, and surveillance units, reducing reaction time and increasing operational lethality.
There is a substantial opportunity in the development and deployment of space-based communication assets. The shift from traditional geostationary satellites to low-earth orbit (LEO) constellations, such as those initiated by defense contractors and national space agencies, supports faster connectivity, global coverage, and resilience against anti-satellite threats. Moreover, AI-augmented ISR (intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance) systems that automate battlefield data aggregation and threat pattern recognition are emerging as a central focus for military modernization.
Nevertheless, market growth faces notable restraints. High capital investments, extended procurement cycles, and challenges in integrating legacy communication infrastructure with modern networks limit the pace of transformation, especially in budget-constrained regions. Additionally, military communication systems are increasingly vulnerable to cyber warfare, jamming, and spectrum congestion, requiring constant upgrades in encryption standards and electronic countermeasures.
Looking ahead, the market is poised for robust growth fueled by defense digitalization programs, regional rearmament initiatives, and interoperability frameworks driven by NATO, the Indo-Pacific alliances, and regional coalitions. Countries enhancing their joint operational command systems, like JADC2 in the U.S., ESSOR in Europe, and JICS in Japan, will set the benchmark for global defense communication infrastructure. As conflicts become more data-centric, the demand for secure, real-time, cross-domain communication will be a non-negotiable military imperative, positioning this market at the core of modern warfare innovation.
The US Military Communication Market
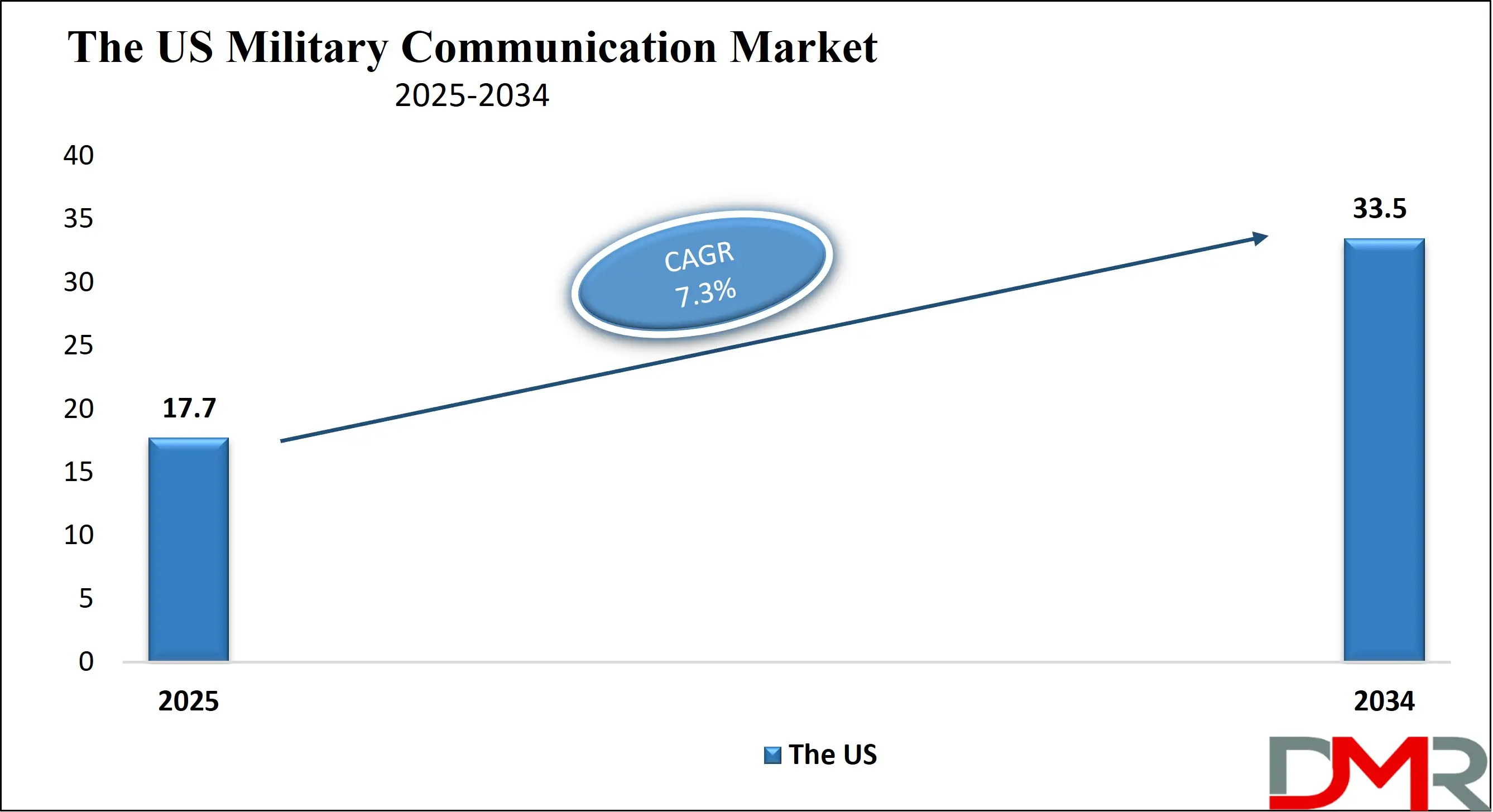
The US Military Communication Market is projected to reach USD 17.7 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 7.3% over its forecast period.
The United States leads the world in military communication capabilities, with unmatched investment, infrastructure, and technological innovation. Driven by its global defense posture and extensive military operations, the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) has consistently prioritized robust, resilient, and interoperable communication systems across all services: Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Space Force. A cornerstone of this approach is the implementation of Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2), aimed at linking every sensor to every shooter using a real-time, secure digital architecture.
According to the U.S. Department of Defense’s budget documents and strategic modernization initiatives, billions have been allocated toward improving battlefield communication systems, ranging from next-generation tactical radios and SATCOM terminals to quantum-resistant encryption and AI-enhanced threat detection. The Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA), under the DoD, manages a vast portion of the military’s cyber infrastructure, supporting secure communications across over 100 countries and 3,000 military installations.
The U.S. Space Force and National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) have expanded military satellite constellations, such as Advanced Extremely High Frequency (AEHF) systems and the upcoming Protected Tactical Enterprise Service (PTES), to enable global, encrypted, and jam-resistant communications. These assets ensure warfighters have continuous access to command and ISR data in even the most remote and contested environments.
Demographically, the U.S. benefits from a diverse and tech-savvy defense workforce. With over 1.3 million active-duty personnel and a significant reserve force, as reported by the U.S. Census Bureau, the country maintains a massive human capital advantage. Extensive training institutions such as the Signal School at Fort Eisenhower (formerly Fort Gordon) train thousands in cybersecurity, electronic warfare, and military communications annually.
Technological advancements are further propelled by government R&D hubs such as DARPA and the NSA, which are investing in next-gen communication paradigms including cognitive radio networks, electromagnetic spectrum maneuvering, and satellite-to-soldier data fusion. The U.S. military’s interoperability with NATO, QUAD, and Five Eyes allies also demands scalable and agile communication systems capable of multilingual data handling and secure coalition-level coordination.
With increasing threats from cyber adversaries and electronic warfare, maintaining dominance in secure, real-time communication remains a non-negotiable strategic priority. This combination of funding, innovation, and talent ensures the U.S. military communication market will remain the global benchmark for years to come.
The Europe Military Communication Market
The Europe Military Communication Market is estimated to be valued at USD 7.1 billion in 2025 and is further anticipated to reach USD 13.0 billion by 2034 at a CAGR of 7.0%.
Europe’s military communication landscape is evolving quickly, catalyzed by regional security challenges, NATO obligations, and EU-driven defense harmonization efforts. Amid rising concerns over hybrid warfare, cyber intrusions, and border tensions, particularly in Eastern Europe and the Baltic, European nations are rapidly upgrading their defense communication capabilities. Programs under the European Defence Fund (EDF) and the Permanent Structured Cooperation (PESCO) are actively fostering collaborative research in secure communication infrastructure.
The European Secure Software-defined Radio (ESSOR) initiative, involving countries like France, Germany, Italy, and Spain, aims to standardize tactical communication platforms to improve interoperability in joint and coalition missions. These efforts are supported by the European Defence Agency (EDA), which reports increasing cross-border defense spending focused on digital networks, tactical data links, and battlefield management systems. With ESSOR entering deployment phases, Europe is set to benefit from harmonized waveform standards and secure coalition-level radio capabilities.
Europe is also making strides in sovereign satellite communication. The IRIS² initiative, supported by the European Commission and ESA, will deliver secure multi-orbit satellite networks for civil and defense applications. This aligns with Europe’s ambition to reduce dependency on non-EU space infrastructure for critical military operations.
Demographically, the region has over 1.4 million active-duty personnel, as reported by Eurostat and EDA data, supported by specialized defense academies and technological universities that provide deep bench strength in engineering, communications, and cybersecurity. Additionally, conscription systems in countries like Finland and Sweden provide a consistent stream of defense-trained individuals familiar with digital communication systems.
However, Europe still faces several challenges. Fragmentation of defense budgets across 27 EU member states leads to uneven adoption of technologies. Legacy systems inherited from the Cold War era complicate integration with modern, software-defined platforms. Furthermore, dependency on U.S.-origin equipment in some NATO members affects sovereignty in defense planning.
Despite these obstacles, the strategic shift toward EU-wide interoperability, spectrum sovereignty, and space-based resilience is driving a new era in European military communication. As geopolitical threats persist and coalition warfare becomes the norm, Europe’s military communication infrastructure will become a critical pillar of regional and global stability.
The Japan Military Communication Market
The Japan Military Communication Market is projected to be valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2025. It is further expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period, holding USD 5.5 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 7.6%.
Japan’s military communication market is gaining unprecedented momentum, backed by sweeping defense reforms and rising security concerns in the Indo-Pacific region. The National Defense Strategy, updated by the Ministry of Defense (MOD), emphasizes enhanced command-and-control architecture, cyber resilience, and multi-domain operational readiness. As Japan shifts from a post-WWII defensive posture toward a proactive deterrence model, secure, rapid communication systems are foundational to its strategic transformation.
A flagship initiative is the development of the Joint Integrated Command System (JICS), a next-generation network designed to integrate the operations of the Ground, Maritime, and Air Self-Defense Forces. The system will offer real-time data fusion, encrypted voice/video exchange, and synchronized situational awareness. According to the MOD, this effort is essential to defend against hypersonic threats, gray-zone warfare, and space-based incursions from regional adversaries.
Japan’s Acquisition, Technology & Logistics Agency (ATLA) is investing in resilient radio waveforms, AI-enabled threat detection, and electromagnetic spectrum control technologies. Through partnerships with national institutes like NICT and GSRC, Japan is developing quantum-safe communications, machine learning-based intrusion prevention systems, and AI-assisted network management tools tailored to high-threat environments.
From a demographic perspective, Japan’s strengths lie in its advanced telecommunications infrastructure and high technical literacy among both civilians and enlisted personnel. According to Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the country boasts one of the most extensive 5G rollouts and broadband penetration rates, enabling swift integration of secure digital platforms into the defense network.
Despite a smaller defense workforce of about 230,000 active SDF personnel, Japan offsets this with highly automated, technology-driven systems and interoperability with U.S. forces under the U.S.-Japan Security Treaty. Joint training operations like Keen Edge and Keen Sword regularly test and refine shared communication protocols and tactical networks.
Japan's strategic position near the Taiwan Strait, East China Sea, and North Korea necessitates robust satellite and undersea communication systems. Recent increases in defense spending targeting 2% of GDP by 2027 are being channeled toward satellite constellations, maritime communication buoys, and cyber protection nodes. These upgrades position Japan as a regional leader in military digital transformation, ensuring rapid information flow and command agility in a contested, multi-domain environment.
Global Military Communication Market: Key Takeaways
- Global Market Size Insights: The Global Military Communication Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 47.5 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 93.4 billion by the end of 2034.
- The Global Market Growth Rate: The market is growing at a CAGR of 7.8 percent over the forecasted period of 2025.
- The US Market Size Insights: The US Military Communication Market is projected to be valued at USD 17.7 billion in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 33.5 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 7.3%.
- Regional Insights: North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Military Communication Market with a share of about 44.4% in 2025.
- Key Players: Some of the major key players in the Global Military Communication Market are BAE Systems, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Thales Group, L3Harris Technologies, and many others.
Global Military Communication Market: Use Cases
- Secure Tactical Radio Networks: Modern infantry units operate in harsh terrains with high threat levels, requiring encrypted VHF/UHF tactical radios with GPS integration and noise-canceling features. These radios enable field commanders to coordinate attacks, request air support, and monitor troop locations in real-time, reducing fratricide and enhancing mission synchronization during night operations and asymmetric warfare conditions.
- Satellite-Based Long-Range Communication (SATCOM): Strategic defense operations leverage satellite communication to link warships, aircraft, and command centers across dispersed geographies. SATCOM ensures real-time high-capacity data transmission for video feeds, telemetry, and logistics, especially in remote theatres like the Arctic or Indo-Pacific maritime zones where terrestrial communication is unfeasible or compromised.
- Cyber-Resilient Defense Networks: Defense communication systems now embed multi-layered cyber protection using blockchain-based authentication, end-to-end encryption, and AI-based anomaly detection. These capabilities protect strategic transmissions from cyber intrusions, ransomware, or spoofing attacks, especially during critical national security operations or electronic warfare missions in adversarial environments.
- Joint Command and Control Systems (C2): Modern command centers utilize integrated communication architecture combining sensor data, battlefield telemetry, and AI-driven dashboards. These platforms enhance decision-making speed and reduce latency between target acquisition and engagement, essential for large-scale joint-force operations involving the army, navy, air force, and allied contingents.
- Unmanned and Autonomous Systems Control: Ground control stations communicate with UAVs, UGVs, and USVs using real-time, jam-resistant data links. This facilitates remote surveillance, reconnaissance, and autonomous targeting. In contested zones like urban conflict environments, such communication ensures minimal human exposure while maintaining persistent situational awareness and precision engagement.
Global Military Communication Market: Stats & Facts
U.S. Department of Defense (DoD)
- The U.S. Department of Defense allocated approximately USD 13.5 billion in FY2024 solely for Command, Control, Communications, Computers, and Intelligence (C4I) development and upgrades, showing the scale and priority of integrated communication in U.S. defense strategies.
- The Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2) initiative is expected to receive over USD 1.4 billion in total funding between FY2023 and FY2025, highlighting the U.S. military’s effort to link all service branches through a secure and agile communication system.
- The DoD maintains and operates more than 100 globally distributed ground stations to support Military Satellite Communication (MILSATCOM), enabling uninterrupted battlefield and inter-service communication across all continents.
- Over 80,000 active-duty personnel and reservists are trained annually in communication, cyber warfare, and signal intelligence, demonstrating the emphasis on building human capital in communication warfare.
U.S. Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA)
- DISA controls a communication backbone comprising over 20,000 miles of fiber optic cable, supporting secure command networks between national and global command centers.
- It provides secure data transmission, messaging, and classified network services to more than 9 million Department of Defense users, including warfighters, analysts, and senior leadership.
- The Global Broadcast Service (GBS), a component of DISA's infrastructure, delivers encrypted video, data, and imagery content at transmission speeds of up to 45 Mbps, facilitating battlefield awareness and tactical updates.
NATO Communications and Information Agency (NCIA)
- NATO channels over USD 1 billion annually into modernizing secure communication systems, software platforms, and cyber resilience across all 30 member states, reflecting the strategic centrality of interoperable communication.
- The agency manages more than 40,000 secure communications connections, which support classified data transfer between member state defense headquarters and allied forces.
- The Federated Mission Networking (FMN) program, designed to enable rapid coalition-building and data sharing, is now deployed in 16 NATO nations, ensuring synchronized battlefield communications during joint missions.
European Defence Agency (EDA)
- Collectively, European nations invested USD 1.8 billion in 2023 on communication and electronic warfare R&D projects under EDA’s collaborative defense programs.
- Software-defined radios (SDRs) have been adopted by over 60% of European land and airborne military platforms, supporting frequency agility and NATO waveform interoperability.
- The ESSOR (European Secure Software-defined Radio) project has established common radio protocols across six EU countries, improving cross-border communication during joint force deployments.
U.S. Army Signal School
- The U.S. Army Signal School at Fort Eisenhower trains more than 18,000 soldiers annually in tactical communications, cybersecurity, and electronic warfare, shaping a new generation of digital warfighters.
- It offers 12 advanced Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) programs, allowing enlisted soldiers to specialize in fields such as satellite communications, network security, and strategic signal planning.
United Kingdom Ministry of Defence (UK MoD)
- The UK Armed Forces utilize over 3,500 Bowman radio systems, which offer encrypted voice and data links for battlefield units operating in harsh or contested environments.
- The Skynet 6 program, the UK’s next-gen satellite initiative, will deliver four new military satellites by 2028, significantly expanding secure SATCOM capacity for British and allied forces globally.
French Ministry of the Armed Forces
- France has fielded more than 5,000 CONTACT software-defined radios, enabling secure, multi-band, high-speed communications across its armed forces.
- The Syracuse IV satellite system provides encrypted coverage over two-thirds of Earth’s surface, ensuring command and intelligence exchange even during overseas missions.
Japan Ministry of Defense (MOD)
- Japan allocated ¥234 billion (approximately USD 1.6 billion) in FY2024 toward military communications, cyber defense, and command system integration as part of its revised national defense plan.
- The Japan Cyber Defense Command currently employs over 1,200 trained specialists responsible for shielding critical communication infrastructure from cyber threats and digital warfare.
- The MOD plans to launch three additional X-band defense satellites by 2027, enhancing real-time communication across Japan’s island chains and maritime operations.
Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD)
- The Indian Army Signal Corps manages more than 2,000 active communication relay nodes, covering high-altitude conflict zones, including the Siachen Glacier and northeastern states.
- India’s Defence Communication Network (DCN) securely links 13 tri-service command centers, enabling encrypted real-time coordination across land, air, and naval assets.
- Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), a state-owned defense contractor, has manufactured over 30,000 secure radio communication devices for use across the Indian armed forces.
German Federal Ministry of Defence (BMVg)
- The Bundeswehr has deployed over 6,000 digital tactical radios compatible with NATO waveforms and operational standards, improving field unit synchronization.
- The KommServer digital platform used at Bundeswehr HQ connects more than 2,500 command-level systems for secure, real-time messaging during crisis scenarios.
Australian Department of Defence
- Australia’s JP 9102 project will establish an independent satellite communication system for defense operations, with Initial Operating Capability targeted by 2027.
- The Australian Defence Force employs over 1,000 Broadband Global Area Network (BGAN) terminals, ensuring broadband-level secure communication for forward-deployed troops.
Canadian Department of National Defence (DND)
- Canada’s Mercury Global program enables secure SATCOM for seven regional defense operations, including NORAD, UN, and NATO missions.
- Funding for tactical radio communication systems has increased by 40% since 2020, aligning Canada’s mobile communication fleet with allied standards.
European Space Agency (ESA)
- The GOVSATCOM initiative aims to provide secure satellite communication access to over 20 EU nations by 2026, strengthening crisis coordination and defense mobility.
- Through the IRIS² initiative, ESA is developing a 170+ satellite constellation to provide encrypted, low-latency communication to European security forces.
U.S. Space Force
- The U.S. Space Force controls a fleet of more than 80 military communication satellites, including Wideband Global SATCOM (WGS) and Advanced Extremely High Frequency (AEHF) platforms.
- The new Protected Tactical SATCOM (PTS) system will enter testing by 2026, delivering resilient, jam-resistant communication capabilities in contested battlespaces.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence in the Global Military Communication Market
- Enhanced Situational Awareness and Decision-Making: AI significantly improves the speed and precision of decision-making on the battlefield. By processing real-time data from satellites, sensors, and field units, AI enables commanders to receive instant threat assessments, identify anomalies, and anticipate enemy movements. This capability reduces human error, enhances battlefield visibility, and allows for timely strategic responses. AI-driven situational awareness tools are now central to modern warfare communication systems, ensuring commanders can act based on reliable and synthesized intelligence.
- Optimization of Tactical Communication Networks: Artificial Intelligence enables military communication networks to become more adaptive, efficient, and resilient. Through intelligent routing, load balancing, and predictive bandwidth management, AI systems help prevent signal congestion and communication breakdowns in high-demand environments. These AI-enhanced networks can self-heal by rerouting traffic in real time, maintaining operational continuity even under cyber threats or physical damage. This is especially crucial during joint operations and multi-domain battlespaces.
- Strengthened Cybersecurity and Threat Detection: AI is revolutionizing military cybersecurity by enabling advanced threat detection and mitigation. Unlike traditional systems, AI models can continuously learn and evolve, detecting unfamiliar malware, phishing attempts, and signal spoofing in real time. It also facilitates predictive cybersecurity, where vulnerabilities are identified and patched proactively. This reduces the risk of data breaches, ensures message integrity, and strengthens encrypted military communication protocols.
- Seamless Integration of Autonomous and Unmanned Systems: The rise of AI-powered drones, unmanned vehicles, and robotic systems has created a need for dynamic communication channels. AI bridges this gap by enabling seamless coordination between autonomous assets and human operators. It ensures synchronized data exchange, route optimization, and command validation across platforms. This results in more cohesive mission execution, better remote control over unmanned units, and reduced latency in high-risk operations.
- Accelerated Interoperability in Multi-Nation Operations: In coalition warfare or joint-force missions, AI facilitates real-time language translation, standardized data exchange, and protocol alignment across different communication infrastructures. Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools help bridge linguistic and procedural differences, ensuring effective coordination among allied forces. AI also supports data fusion from diverse systems, creating a unified operational picture that enhances strategic synchronization and minimizes miscommunication among international military partners.
- Emergence of Cognitive Electronic Warfare Capabilities: AI is redefining electronic warfare by enabling systems to autonomously detect, classify, and respond to electromagnetic threats. These systems can analyze the electromagnetic spectrum in real time, identify enemy jamming efforts, and adjust friendly communication channels accordingly. This cognitive capability provides a critical advantage by ensuring uninterrupted communication under hostile conditions, and it marks a shift from reactive to proactive electronic defense mechanisms in the modern battlespace.
Global Military Communication Market: Market Dynamics
Driving Factors in the Global Military Communication Market
Rising Defense Budgets and Modernization Programs Globally
An upsurge in global defense budgets, particularly in the U.S., China, India, and Europe, is a primary driver for the military communication market. Geopolitical instability, regional conflicts, and power projection requirements are leading to higher investments in communication-centric warfare tools. For instance, the U.S. DoD's annual allocations for C4I systems exceed $13 billion, while countries like Japan and South Korea are enhancing secure communication capabilities as part of next-gen defense reforms.
These budget inflows are accelerating procurement of satellite terminals, secure tactical radios, SDRs, and AI-driven networking platforms. Additionally, many nations are retiring legacy platforms and investing in agile, networked command infrastructure. Digitalization of military operations through multi-layered, encrypted communication channels is now a key criterion for force modernization.
Expanding Use of Satellite Communication (SATCOM) and LEO Networks
SATCOM is becoming the backbone of modern military communication due to its global coverage, scalability, and resilience. The migration from geostationary to low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites offers advantages such as lower latency, faster signal relay, and global connectivity even in GPS-denied or contested regions. Defense agencies are deploying LEO constellations for protected tactical services (PTS), beyond-line-of-sight (BLOS) communication, and persistent ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance).
Moreover, SATCOM ensures secure voice, data, and video transmission across remote combat theatres, naval fleets, and airborne missions. Space programs like U.S. Protected Tactical SATCOM (PTS) and ESA’s IRIS² project exemplify the strategic reliance on satellite-based communication for maintaining military superiority in next-gen warfare environments.
Restraints in the Global Military Communication Market
Integration Challenges with Legacy Infrastructure and High Deployment Costs
Military organizations across the globe face significant hurdles in modernizing communication systems due to existing legacy infrastructure that lacks compatibility with modern platforms. Integrating advanced digital systems like SDRs, AI-based threat detection, and SATCOM terminals into traditional analog frameworks requires expensive overhauls, hardware swaps, and long training cycles. Moreover, defense procurement processes are highly regulated and time-consuming, involving lengthy testing and validation.
The high upfront cost of deploying secure satellite constellations, building encrypted networks, and installing field-based command and control systems often delays deployment. Countries with limited defense budgets may also find it difficult to fund extensive upgrades, further limiting their pace of modernization.
Rising Cybersecurity Threats and Spectrum Congestion
Military communication systems are prime targets for cyber warfare, jamming, spoofing, and spectrum denial attacks. Nation-state actors, hacktivist groups, and cyber mercenaries are increasingly launching sophisticated attacks on communication networks to disrupt command chains or steal classified data. As military operations become increasingly digital, cyber resilience becomes both a strategic necessity and a technical challenge.
Simultaneously, growing spectrum congestion, especially in urban battlefields, makes it difficult to allocate clean frequency bands for secure communication. The requirement for spectrum agility, interference cancellation, and electromagnetic dominance places significant strain on system design, signal integrity, and encryption strength. This complexity limits real-time operational continuity, especially in highly contested environments.
Opportunities in the Global Military Communication Market
Development of Quantum-Resistant and Post-5G Defense Communication
As adversaries enhance cyber capabilities, military institutions are prioritizing quantum-resistant encryption and post-5G secure communication. These technologies present a transformative opportunity for the defense communication sector. Quantum cryptography, including quantum key distribution (QKD), promises unbreakable encryption, especially for satellite-to-ground and shipborne communications. Defense R&D agencies are investing in quantum-proof protocols that can withstand cyber attacks even from quantum computers.
Simultaneously, post-5G networks, including 6G and terahertz communication, will deliver ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), supporting autonomous drones, battlefield robotics, and high-speed ISR data sharing. As military engagements become more digitized, the convergence of 6G and quantum communication represents the next frontier for defense-grade security and efficiency.
Adoption of Mesh Networks and Edge Computing in Combat Zones
The rising use of edge computing and decentralized mesh networks is opening new opportunities for tactical field communication. Mesh networks enable each device (radio, vehicle, drone) to act as a node, ensuring that communication persists even if a link fails or is destroyed. This is crucial in hostile, GPS-denied environments where traditional hierarchical networks can collapse.
Edge computing brings analytics closer to the battlefield, enabling real-time data processing, sensor fusion, and AI inference at the tactical edge without relying on central command servers. This reduces latency, improves operational agility, and allows for rapid decision-making under dynamic threat conditions. Such architectures are increasingly vital for unmanned operations, special forces, and asymmetric warfare.
Trends in the Global Military Communication Market
Multi-Domain Operations and Interoperability Focus
Armed forces worldwide are shifting from single-domain tactics to integrated, multi-domain operations (MDO). Military communication systems now need to enable real-time synchronization across land, air, sea, cyber, and space domains. This trend is driving demand for seamless and interoperable communication platforms that integrate command centers with UAVs, satellites, manned vehicles, and autonomous systems.
Technologies like Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2), Federated Mission Networking (FMN), and ESSOR (European Secure Software Defined Radio) are reshaping defense architecture to provide a shared, real-time operational picture across allied forces. Additionally, the rise of coalition and joint-force operations, such as NATO and QUAD, mandates cross-national communication standards, making interoperability not just strategic but indispensable for rapid response and strategic deterrence.
Integration of AI and Cybersecurity in Tactical Communications
The rise of cyber warfare and digital espionage has led to the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and secure military communication. AI is increasingly embedded into communication systems to automate spectrum management, detect jamming or signal interference, and optimize bandwidth allocation in real time. Moreover, AI-driven encryption, anomaly detection, and machine learning-based network defense are transforming legacy communication systems into intelligent, self-defending ecosystems.
The shift from reactive to predictive security mechanisms ensures enhanced battlefield survivability. Furthermore, AI-enabled chatbots, real-time translation, and auto-routing features are empowering command centers with quicker decision-making tools, particularly in high-pressure environments where time-to-communicate equals time-to-win.
Global Military Communication Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Component Analysis
The hardware segment is expected to lead the Military Communication Market, driven by its indispensable role in establishing and maintaining secure, real-time connectivity across platforms. Hardware includes Military SATCOM systems, tactical radios, encryption devices, antennas, and networking devices, all of which serve as physical enablers of mission-critical communication in conflict zones. With rapid digitalization, there has been a surge in demand for advanced, rugged, and mobile communication hardware that can operate under extreme environments. Tactical edge radios and vehicle-mounted transceivers are widely used by land forces, while airborne and naval platforms rely on high-throughput antennas and multiband encryption units.
Furthermore, with increasing threats from electronic warfare and cyber disruptions, militaries are investing in resilient and frequency-agile devices to secure their voice and data exchange channels. Hardware upgrades also receive a larger portion of defense spending because they involve capital-intensive procurement, installation, and maintenance. For example, the U.S. Department of Defense allocates billions annually for communication equipment modernization programs.
Additionally, countries like India, France, and the UK are expanding their deployment of software-defined radios and SATCOM terminals, reinforcing the hardware segment’s dominance. Unlike software or services, hardware forms the foundational layer of defense infrastructure, making it a strategic asset for command and control superiority.
By Technology Analysis
Satellite Communication (SATCOM) is projected to dominate the military communication market due to its unmatched ability to support beyond-line-of-sight (BLOS) operations, uninterrupted global coverage, and resilience in hostile environments. SATCOM plays a pivotal role in inter-theater command coordination, disaster response, and strategic deterrence by allowing secure, high-bandwidth data exchange between ground, air, naval, and space forces. Modern defense operations increasingly depend on real-time ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance), precision targeting, and remote coordination, all of which require robust SATCOM networks.
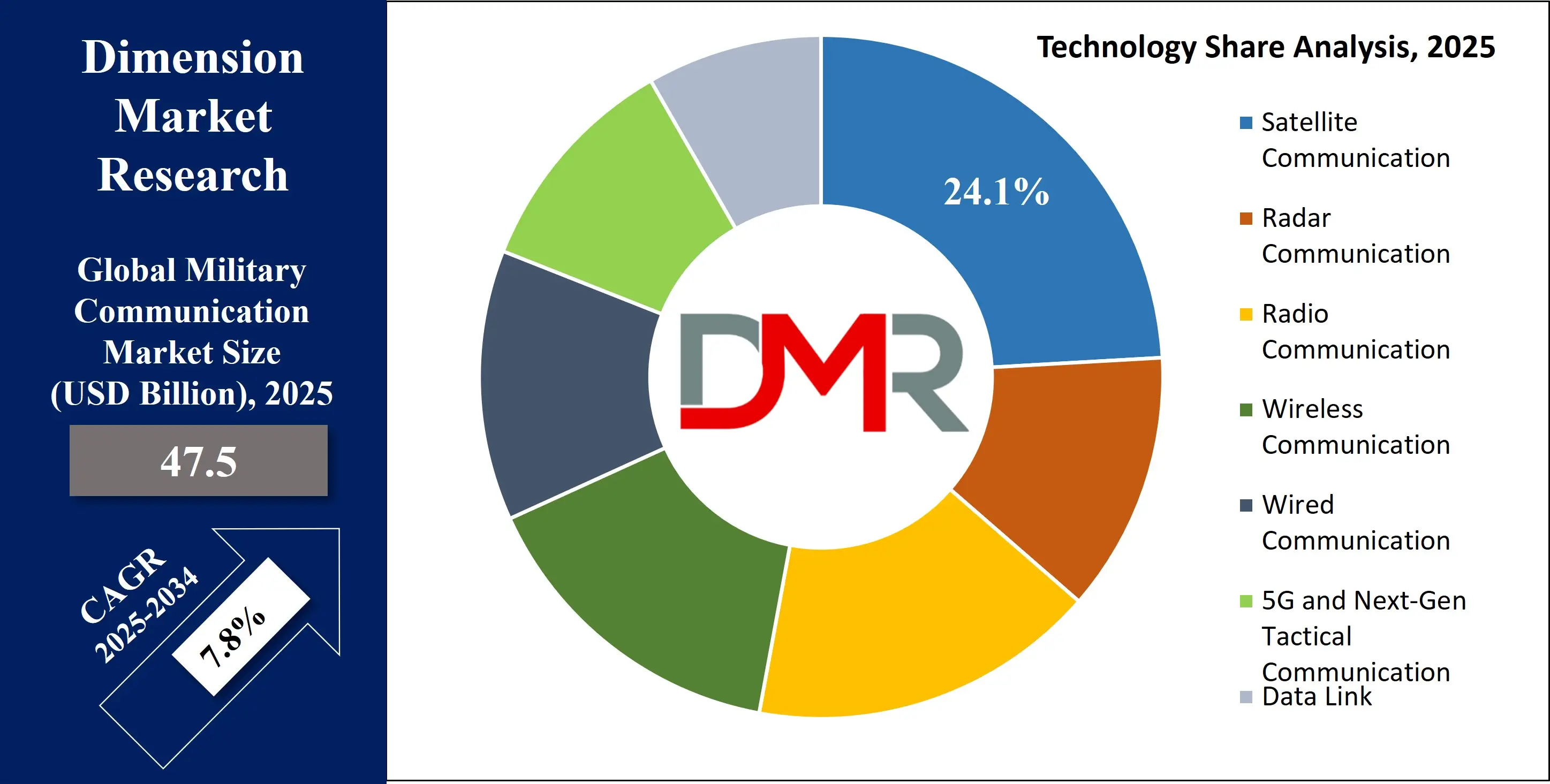
The shift toward low-Earth orbit (LEO) and medium-Earth orbit (MEO) satellite constellations offering lower latency and improved throughput further enhances SATCOM’s effectiveness. Countries such as the United States, Japan, and France are heavily investing in protected tactical SATCOM programs, like the PTS initiative and Syracuse IV, to boost encrypted, jam-resistant communication for their forces. NATO also incorporates SATCOM as a backbone for Federated Mission Networking, supporting coalition interoperability.
In addition to defense satellites, satellite ground control infrastructure, portable terminals, and airborne SATCOM transceivers have seen widespread deployment in multi-domain operations. SATCOM is vital for naval fleets operating in blue water, UAV control beyond radio range, and special forces conducting cross-border surveillance. As warfare moves into space and contested communication landscapes, SATCOM remains an indispensable technology ensuring global military connectivity and mission continuity under all threat conditions.
By Communication Type Analysis
Air-ground communication is poised to represent the most critical and widely deployed communication type in defense operations. It ensures seamless interaction between airborne platforms such as fighter jets, UAVs, and transport aircraft and ground command centers, combat units, or forward-operating bases. This type of communication is vital in missions involving close air support (CAS), precision airstrikes, aerial reconnaissance, and battlefield evacuation.
The growing integration of UAVs and remotely piloted aircraft systems (RPAS) across armed forces has intensified the demand for secure, high-bandwidth, low-latency air-ground communication links. Whether in offensive missions or humanitarian aid deployments, real-time coordination between air assets and troops on the ground determines operational effectiveness and mission safety. Militaries globally are deploying advanced air-ground systems, including line-of-sight (LOS) radio, BLOS satellite uplinks, and data link technologies to improve battlefield responsiveness.
The increasing complexity of air operations combined with multi-national coalition activities requires dynamic spectrum management, encrypted data channels, and AI-based routing to ensure uninterrupted communications. Systems like Link-16, Multifunctional Information Distribution System (MIDS), and Joint Tactical Radio System (JTRS) are commonly used to support this segment. Moreover, the prominence of this segment is underpinned by air dominance doctrines and the strategic shift toward agile air mobility. In both symmetric and asymmetric conflicts, air-ground communication remains the linchpin for time-sensitive targeting, force protection, and synchronized strike execution, thus maintaining its dominance.
By Platform Analysis
Ground platforms are anticipated to dominate the military communication market because of the extensive communication infrastructure deployed across land-based operations. These platforms include armored vehicles, mobile command and control centers, and soldier-worn systems, all of which require integrated communication tools for real-time situational awareness. Land forces form the largest component of any national military and are engaged in diverse missions ranging from peacekeeping to frontline combat. As such, they rely heavily on man-portable radios, vehicle-mounted transceivers, and mobile mesh networks to maintain secure connectivity in both urban and remote environments.
The evolution of network-centric warfare has led to the incorporation of edge computing, AI-driven threat detection, and geospatial communication overlays in ground systems. Commanders now demand seamless communication from the tactical edge to the strategic command level. Moreover, ground units often serve as the central nodes in joint-force operations, interfacing with airborne, naval, and space assets. Countries such as India, China, and the United States are investing in land-centric communication projects, including software-defined radio programs, broadband terrestrial networks, and secure command post connectivity. The scale, diversity, and duration of ground operations combined with the growing digitization of battlefield environments cement ground platforms as the largest and most resource-intensive communication segment. Their requirement for rugged, scalable, and interoperable systems sustains their market leadership.
By Application Analysis
Command and Control (C2) is projected to be the most dominant application in the military communication ecosystem, as it forms the core framework through which all strategic, operational, and tactical decisions are executed. C2 systems allow commanders to plan, direct, coordinate, and control forces and operations using real-time communication channels and data feeds. Modern C2 applications rely on integrated networks that link satellites, command centers, field units, and autonomous systems to provide a unified situational awareness picture.
The increasing complexity of joint and coalition warfare, cyber defense coordination, and rapid response missions necessitates robust C2 frameworks powered by advanced communication technologies. Military doctrines such as the U.S. Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2) or NATO’s FMN directly revolve around strengthening C2 capabilities. These systems are being upgraded with AI analytics, secure cloud integration, and geospatial intelligence to improve decision-making speed and accuracy.
From theater-level coordination to tactical mission execution, C2 serves as the nerve center of any military operation. Additionally, real-time logistics planning, threat assessment, and troop movements depend on secure and continuous C2 communication lines. As countries increasingly adopt data-driven warfare strategies, the demand for resilient, multi-node, and interoperable command and control platforms ensures this application remains the cornerstone of military communication investments.
The Global Military Communication Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Component
- Hardware
- Military SATCOM systems
- Radios
- Encryption devices
- Antennas
- Networking devices
- Software
- Network security software
- Communication system management software
- Encryption & cybersecurity software
- Services
- System integration & installation
- Support & maintenance
- Consulting and training
By Technology
- Satellite Communication
- Radar Communication
- Radio Communication
- Wireless Communication
- Wired Communication
- 5G and Next-Gen Tactical Communication
- Data Link
By Communication Type
- Air-Ground Communication
- Underwater Communication
- Ground-Based Communication
- Shipborne Communication
- Airborne Communication
- SATCOM
By Platform
- Ground
- Armored vehicles
- Soldier systems
- Command and control centers
- Airborne
- Fighter jets
- UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles)
- Transport aircraft
- Naval
- Submarines
- Warships
- Maritime patrol aircraft
- Space
- Military Satellites
- Space-Based Sensors
- Satellite Ground Control Infrastructure
By Application
- Command and Control
- Situational Awareness
- Routine Operations
- Military Training
- Electronic Warfare
- ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance)
- Combat Operations
- Logistics and Coordination
- Other Application
Global Military Communication Market: Regional Analysis
Region with the Largest Revenue Share
North America is expected to dominate the global military communication market with 44.4% of the total revenue by the end of 2025, largely driven by the United States’ unmatched defense infrastructure, budgetary allocations, and technological leadership. The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) maintains the world’s largest defense communication ecosystem, including advanced satellite constellations, cyber-secure tactical radio networks, and Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2) systems. This is further supported by robust military-industrial collaborations with firms such as Lockheed Martin, Raytheon Technologies, Northrop Grumman, and L3Harris Technologies, all of which continuously innovate in secure communication platforms.
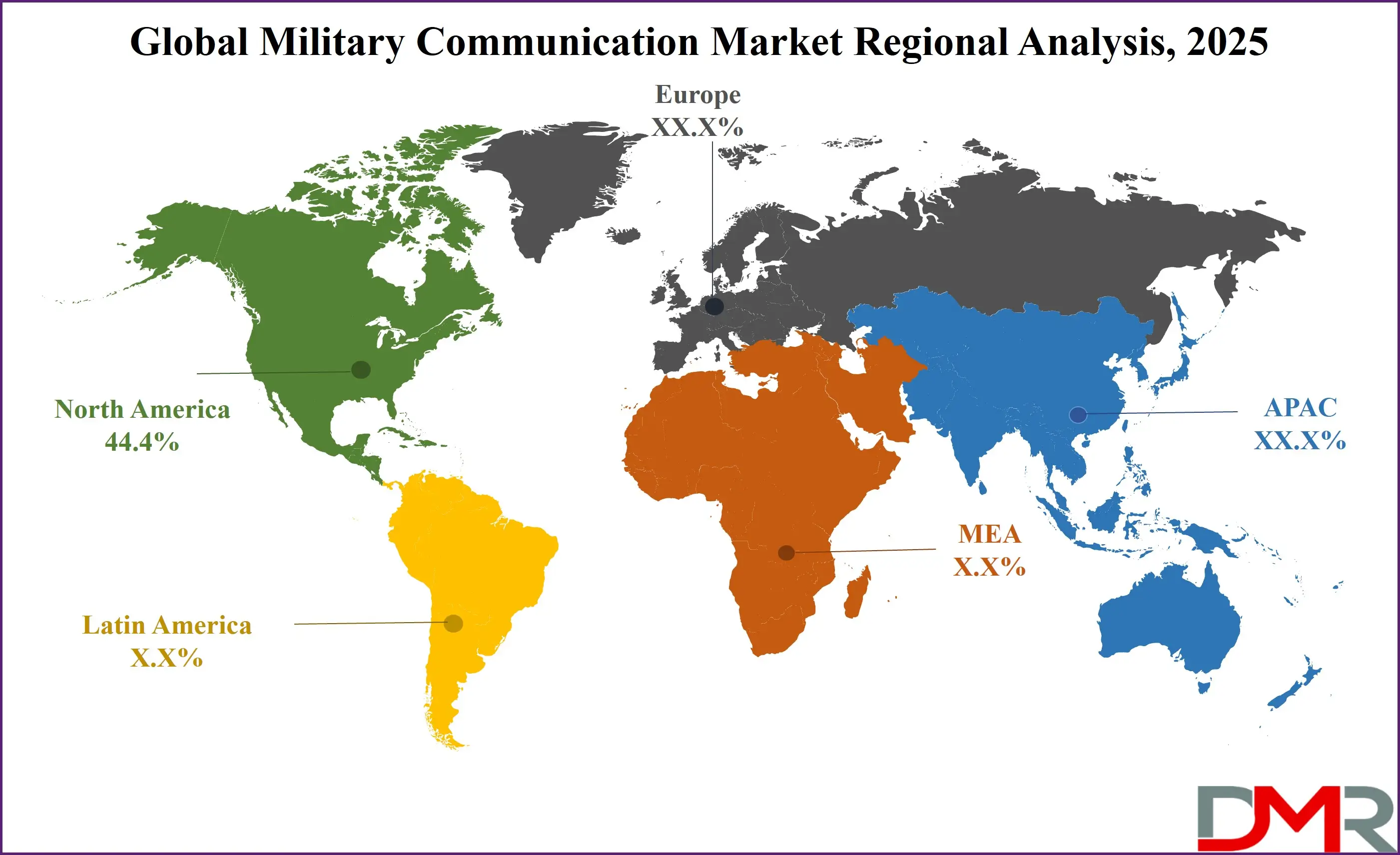
The Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) and U.S. Space Force bolster secure command connectivity across space, land, air, and naval operations. Moreover, the U.S. invests significantly in AI-driven cybersecurity and SATCOM modernization programs, ensuring technological dominance. Canada also contributes to North America’s market strength through programs like Mercury Global for SATCOM and NATO-integrated defense projects. Extensive R&D investments, a sophisticated communication satellite network, and military doctrine based on digitized and network-centric warfare reinforce North America’s leadership. The region's proactive response to cyber warfare threats, together with initiatives like 5G military deployment and resilient mesh networks, further consolidates its top-tier position in the global defense communication landscape.
Region with the Highest CAGR
Asia Pacific is witnessing the highest CAGR in the military communication market due to increasing geopolitical tensions, large-scale defense modernization, and rapidly expanding regional defense budgets. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are significantly boosting investments in military-grade communication systems to strengthen command, control, and surveillance capabilities. China has embarked on next-generation battlefield digitization and launched integrated satellite networks for military use, reinforcing its aim for joint-force operational readiness. India’s Defence Communication Network (DCN) and software-defined radio (SDR) deployments across tri-services showcase aggressive modernization to bridge legacy gaps. Japan’s Ministry of Defense has also prioritized resilient satellite communication networks and cyber-secure tactical communication to respond to growing threats in the Indo-Pacific. The region’s emphasis on indigenous development and defense self-reliance, such as India’s “Make in India” initiative and South Korea’s military R&D programs, is catalyzing innovation. Additionally, border security, regional maritime disputes, and increasing participation in multilateral defense exercises are driving the need for interoperable, encrypted communication systems. The growing adoption of 5G for tactical edge communication, smart soldier systems, and AI-based ISR tools is accelerating Asia Pacific's momentum. These developments position the region as a high-growth hub for military communication technologies, surpassing traditional growth rates.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Global Military Communication Market: Competitive Landscape
The global military communication market is highly competitive, with dominance spread across North American and European defense contractors, alongside a growing presence from Asia-based defense electronics firms. Leading players such as Lockheed Martin Corporation, Raytheon Technologies, Northrop Grumman, and BAE Systems offer comprehensive communication suites, from SATCOM terminals and tactical radios to secure networking solutions and AI-powered battlefield management tools. These firms collaborate closely with defense departments and space agencies to develop and deploy state-of-the-art technologies aligned with emerging doctrines like JADC2 and FMN. European companies such as Thales Group, Leonardo S.p.A., Saab AB, and HENSOLDT AG are also actively engaged in providing software-defined radios, encrypted communication systems, and tactical edge solutions, often integrated within NATO frameworks. Moreover, rising players like Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) and ASELSAN A.Ş. are gaining ground through government-funded modernization programs and regional partnerships. Companies are investing in LEO satellite constellations, cyber-hardened communication platforms, and real-time ISR networking tools to stay competitive. Strategic initiatives such as mergers, long-term defense contracts, R&D alliances, and product diversification continue to shape the landscape. Technological leadership, secure system reliability, and interoperability with allied forces remain key competitive parameters in this evolving defense communication arena.
Some of the prominent players in the Global Military Communication Market are:
- BAE Systems
- Raytheon Technologies Corporation
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Thales Group
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- General Dynamics Corporation
- Leonardo S.p.A.
- Airbus Defence and Space
- Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co KG
- Elbit Systems Ltd.
- Collins Aerospace
- Saab AB
- Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI)
- Cubic Corporation
- HENSOLDT AG
- ASELSAN A.Ş.
- Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
- Ultra Electronics Holdings plc
- ViaSat Inc.
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments in the Global Military Communication Market
- June 2024: L3Harris secured a $500M U.S. DoD contract to integrate AI-driven encryption into tactical radios, enhancing cybersecurity for frontline troops in contested environments.
- May 2024: Thales and Leonardo formed a NATO-focused JV to develop next-gen SATCOM with anti-jamming capabilities, strengthening alliance interoperability in electronic warfare scenarios.
- April 2024: BAE Systems' new SDR system enables seamless cross-platform communication for joint forces, supporting multi-domain operations with advanced frequency-hopping technology.
- March 2024: RTX's $1.2B acquisition of Kongsberg’s comms division expands Arctic warfare capabilities, including cold-weather hardened tactical networking solutions.
- February 2024: Saab will supply India with advanced Tactical Data Links for its fighter jets, enabling real-time data sharing across air defense networks.
- January 2024: Elbit’s AI-powered C4ISR upgrade enhances Asia-Pacific militaries’ battlefield awareness through predictive analytics and secure mesh networking.
- December 2023: Northrop Grumman and Lockheed Martin collaborate on a hybrid satellite-terrestrial network for the Space Force, ensuring resilient communications in GPS-denied environments.
- November 2023: Rheinmetall acquires HENSOLDT’s radio division, boosting its European market share in secure military communications for armored vehicles.
- October 2023: General Dynamics unveils ultra-secure mesh networking at AUSA 2023, enabling dismounted squads to maintain connectivity in urban warfare.
- September 2023: Boeing and Inmarsat enhance MILSATCOM for airborne platforms, integrating high-throughput Ka-band solutions for global ISR missions.
- August 2023: Rafael wins an Israeli MoD contract for quantum-secured comms, protecting critical defense networks from future decryption threats.
- July 2023: BAE and Honeywell demonstrate anti-jam waveforms at Eurosatory, ensuring reliable communications in high-electronic-warfare threat zones.
- June 2023: ASELSAN’s new MANET radio enables self-forming tactical networks for the Turkish Armed Forces, improving mobility in rugged terrains.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 47.5 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 93.4 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
7.8% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 17.7 Bn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Component (Hardware, Software, Services), By Technology (Satellite Communication, Radar Communication, Radio Communication, Wireless Communication, Wired Communication, 5G and Next-Gen Tactical Communication, Data Link), By Communication Type (Air-Ground Communication, Underwater Communication, Ground-Based Communication, Shipborne Communication, Airborne Communication, SATCOM), By Platform (Ground, Airborne, Naval, Space), By Application (Command and Control, Situational Awareness, Routine Operations, Military Training, Electronic Warfare, ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance), Combat Operations, Logistics and Coordination, Other Application) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, Rest of Europe; Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
BAE Systems, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Thales Group, L3Harris Technologies, Inc., General Dynamics Corporation, Leonardo S.p.A., Airbus Defence and Space, Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co KG, Elbit Systems Ltd., Collins Aerospace, Saab AB, Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), Cubic Corporation, HENSOLDT AG, ASELSAN A.Ş., Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Ultra Electronics Holdings plc, ViaSat Inc., and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Military Communication Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 47.5 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 93.4 billion by the end of 2034.
The market is growing at a CAGR of 7.8 percent over the forecasted period of 2025.
The US Military Communication Market is projected to be valued at USD 17.7 billion in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 33.5 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 7.3%.
North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Military Communication Market, with a share of about 44.4% in 2025.
Some of the major key players in the Global Military Communication Market are BAE Systems, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Thales Group, L3Harris Technologies, and many others.