Market Overview
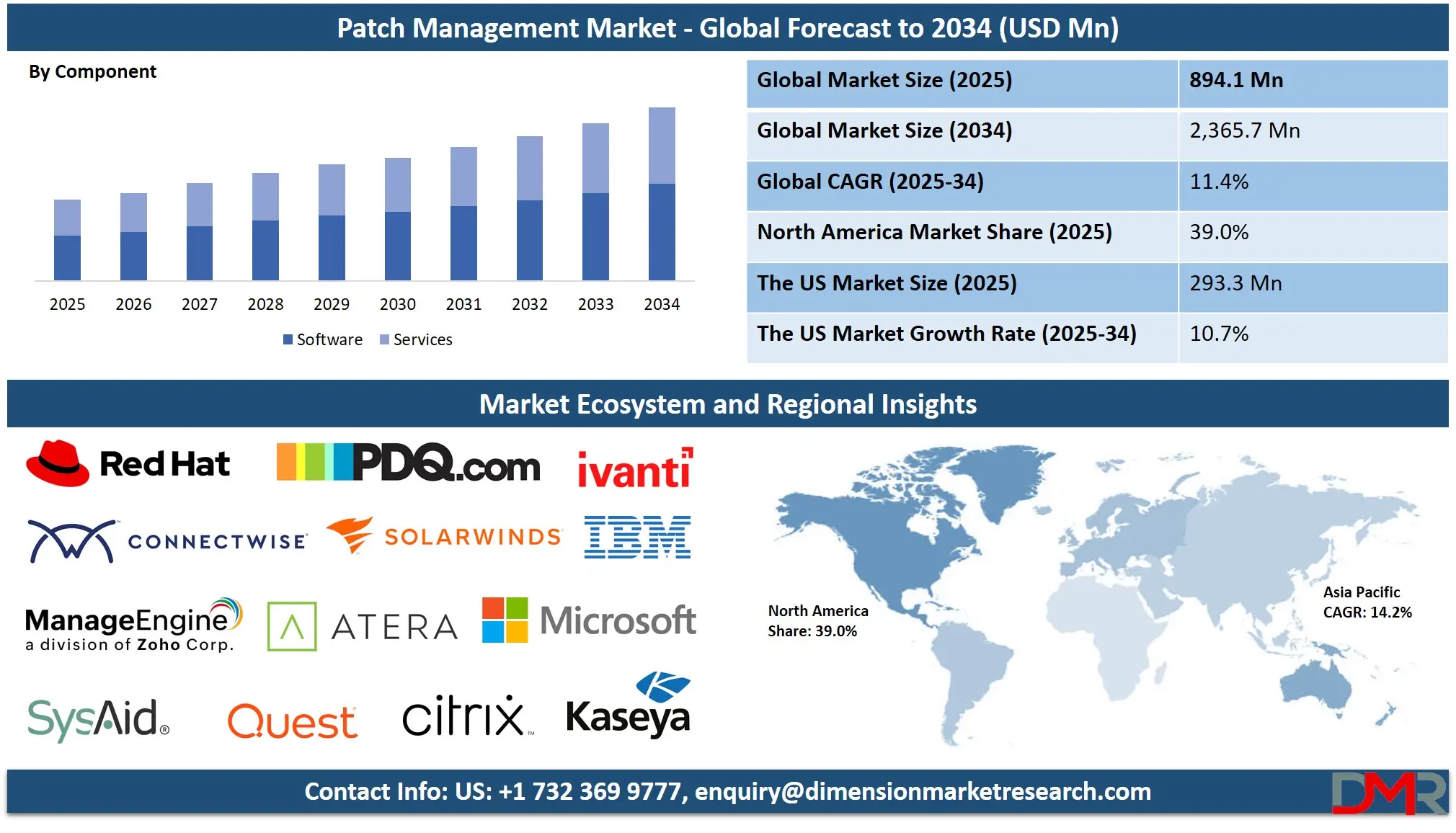
The Global Patch Management Market is projected to reach USD 894.1 million in 2025 and grow at a CAGR of 11.4% from 2025 to 2034, reaching a value of USD 2,365.7 million.
The global patch management market is experiencing significant growth due to rising cybersecurity threats, rapid digital transformation, and increased remote working environments. Organizations are prioritizing real-time patching solutions to prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited by threat actors. Automation tools and centralized patch deployment systems are streamlining IT operations while reducing manual intervention, making them a critical component of endpoint security strategies.
he increasing adoption of cloud infrastructure, IoT devices, and hybrid systems has expanded the potential attack surface, making patch management essential for risk mitigation. According to industry patterns, enterprises are focusing more on compliance with security frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST, and GDPR, which necessitate regular patch updates.
A notable trend in the market is the shift toward predictive patching using artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms. These tools proactively identify system weaknesses and automate prioritization based on threat severity. Vendors are integrating patching capabilities with vulnerability scanners and SIEM tools to enable unified endpoint management. In sectors like finance and healthcare, real-time patch compliance is becoming mandatory due to regulatory audits and the rising demand for vulnerability management solutions.
Key opportunities lie in underserved SME segments, where low awareness and limited IT budgets have traditionally hindered patch adoption. With the rise in low-cost SaaS solutions, managed security services, and support from Cybersecurity Consulting Services, small businesses are now investing in robust patch frameworks. Additionally, the demand for mobile device patching and cross-platform compatibility is opening new avenues for innovation.
Restraints include complexities in legacy systems, fragmented IT ecosystems, and patch testing failures that may cause service disruptions. Despite these challenges, the market is poised for strong expansion due to ongoing digitization, zero-trust architectures, and evolving threat landscapes demanding consistent patch updates.
The US Patch Management Market
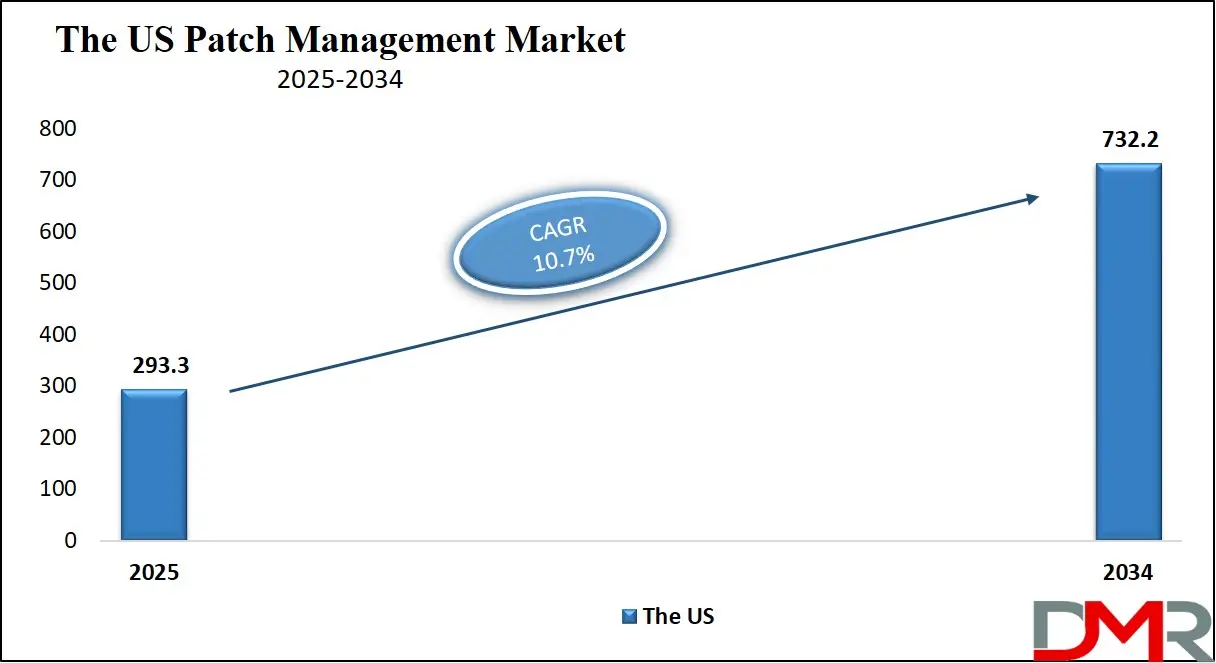
The US Patch Management Market is projected to reach USD 293.3 million in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 10.7% over its forecast period.
The U.S. patch management market is expanding rapidly, underpinned by a strong digital economy, federal cybersecurity mandates, and widespread cloud adoption. According to the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), vulnerabilities stemming from unpatched software are among the most exploited by threat actors, prompting urgent patch enforcement across federal, state, and private entities. In response, Binding Operational Directives like BOD 22-01 mandate federal agencies to identify and patch known exploited vulnerabilities (KEVs) on a strict timeline.
Public sector IT infrastructure, including transportation, utilities, and emergency response systems, increasingly relies on secure patching practices aligned with NIST SP 800-40 guidelines. Additionally, Executive Orders on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity require federal departments to standardize their patch protocols as part of a broader zero-trust architecture.
The U.S. demographic advantage lies in its skilled cybersecurity workforce. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, over 168,000 information security analysts are employed nationwide, supporting enterprise-scale patch management operations. High broadband penetration and a mature cloud services ecosystem allow for real-time patch orchestration across distributed endpoints and mobile devices.
In the private sector, Fortune 500 companies are integrating patching into DevSecOps pipelines to enhance software agility and security posture. Compliance with SOX, HIPAA, and GLBA drives sector-specific adoption. Additionally, U.S.-based universities and innovation hubs foster continuous R&D in automated vulnerability remediation and AI-based patch prioritization.
Challenges persist in legacy-heavy industries like healthcare and manufacturing. However, the push for cyber insurance, digital sovereignty, and government incentives continues to accelerate the adoption of advanced patch management solutions.
The Europe Patch Management Market
The Europe Patch Management Market is estimated to be valued at USD 134.1 million in 2025 and is further anticipated to reach USD 316.2 million by 2034 at a CAGR of 10.0%.
Europe's patch management market is evolving in response to rising cyberattack frequency, stringent data protection frameworks, and digital transformation across industries. The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) has identified timely patching as a critical control to counteract ransomware, phishing, and supply chain threats that have grown since the onset of hybrid work. Regulatory frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the NIS2 Directive mandate strict security controls, including regular vulnerability remediation and endpoint monitoring.
In the financial sector, the introduction of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) mandates patch oversight as part of IT risk management, driving demand for automated tools with built-in reporting features. National agencies like Germany’s BSI and France’s ANSSI offer localized patching recommendations tailored to critical sectors such as healthcare, energy, and government.
Demographically, the European Union benefits from a highly educated tech workforce and advanced internet infrastructure. Eurostat reports increasing cloud adoption among SMEs and large enterprises, which supports centralized and remote patching. Countries like the Netherlands, Estonia, and Finland lead in digital readiness, creating a favorable landscape for cloud-native patch management solutions.
Cross-border IT operations pose unique challenges in language support, time-zone coordination, and compliance mapping. Nevertheless, open-source adoption, government-subsidized cybersecurity programs, and EU-wide funding under the Digital Europe Programme are enabling broader SME participation.
Sustainability and digital sovereignty are also shaping buying decisions, with European buyers favoring local cloud providers that offer compliant patch orchestration. With AI-enabled automation and policy harmonization, the regional market is expected to maintain strong growth momentum, supported by secure Data Center Power infrastructure that underpins digital resilience.
The Japan Patch Management Market
The Japan Patch Management Market is projected to be valued at USD 53.6 million in 2025. It is further expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period, holding USD 138.4 million in 2034 at a CAGR of 11.0%.
Japan’s patch management market is advancing as cyber resilience becomes a national priority amid rapid digital infrastructure expansion. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), under its Cybersecurity Management Guidelines, underscores patch management as a fundamental IT hygiene practice. The Basic Act on Cybersecurity, implemented by the National Center of Incident Readiness and Strategy for Cybersecurity (NISC), promotes patching across critical sectors, including finance, manufacturing, and public services.
Japanese enterprises, particularly in smart manufacturing and precision engineering, are integrating patch management into their operational technology (OT) environments. Smart factories deploying SCADA and MES systems are now subject to vulnerability assessments aligned with international standards like IEC 62443, with patching tools tailored to non-disruptive update cycles.
Japan’s demographic strength includes a technically skilled workforce and one of the world’s highest internet penetration rates. According to the Statistics Bureau of Japan, over 99% of businesses are small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), creating a large addressable market for cost-effective, cloud-hosted patching solutions. These SMEs are now adopting patching via managed service providers due to limited in-house cybersecurity teams.
Major events like Expo 2025 in Osaka and increasing investments in smart city projects have spurred the government to issue national guidelines for vulnerability disclosure and patch response timelines. Challenges include aging infrastructure in the public sector, vendor lock-in, and complex multi-language systems in multinational corporations.
Nonetheless, partnerships between academia, industry consortia, and ministries are fostering a strong cybersecurity ecosystem. As Japan accelerates toward Society 5.0, demand for automated, multilingual, and AI-based patching platforms is projected to rise steadily.
Global Patch Management Market: Key Takeaways
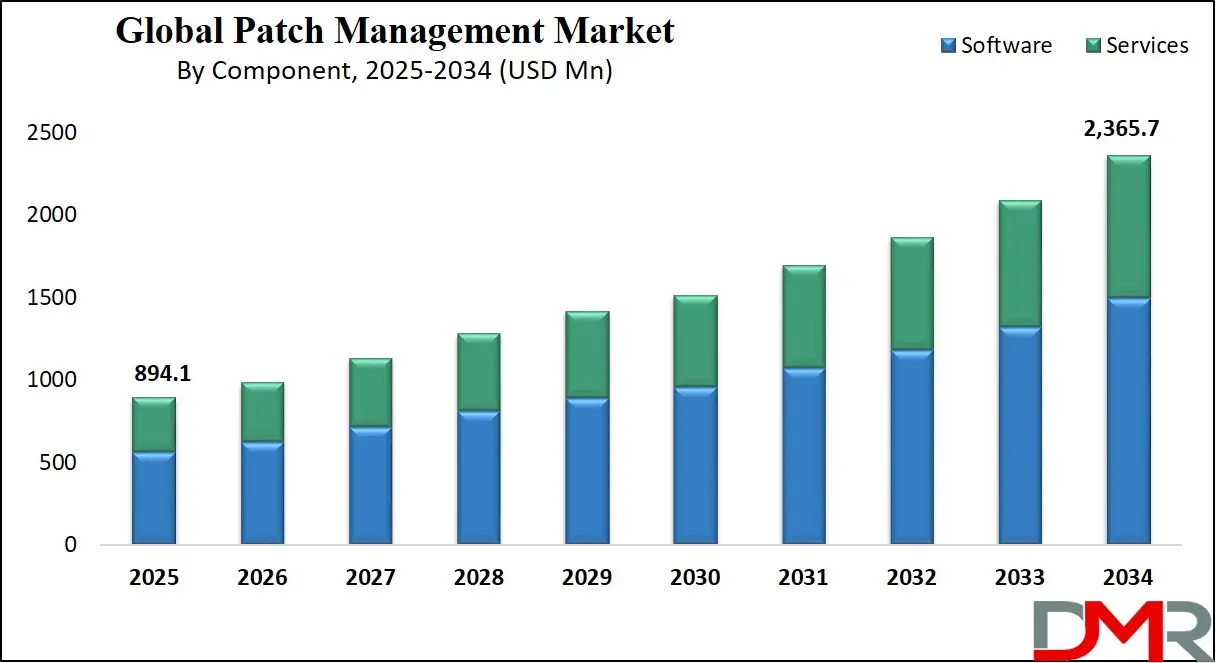
- Global Market Size Insights: The Global Patch Management Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 894.1 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2,365.7 million by the end of 2034.
- The Global Market Growth Rate: The market is growing at a CAGR of 11.4 percent over the forecasted period of 2025.
- The US Market Size Insights: The US Patch Management Market is projected to be valued at USD 293.3 million in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 732.2 million in 2034 at a CAGR of 10.7%.
- Regional Insights: North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Patch Management Market with a share of about 39.0% in 2025.
- Key Players: Some of the major key players in the Global Patch Management Market are Microsoft Corporation, IBM Corporation, Ivanti Inc., SolarWinds Corporation, ManageEngine (Zoho Corporation), Micro Focus International plc (OpenText), BMC Software Inc., and many others.
Global Patch Management Market: Use Cases
- Healthcare Compliance: Hospitals and healthcare networks use automated patching tools to maintain HIPAA, HITECH, and HL7 compliance. Timely security patches on Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, diagnostic platforms, and medical IoT devices reduce vulnerabilities that can be exploited in ransomware or patient data breach scenarios, ensuring operational uptime and data integrity.
- Banking & Financial Systems: Banks deploy automated patch management for ATM firmware, online banking applications, and internal transaction servers. Patching ensures compliance with PCI DSS and FFIEC guidelines, preventing injection attacks, phishing, and fraud. Timely updates help maintain consumer trust, reduce exposure during audits, and support anti-money laundering software integrity.
- Government IT Infrastructure: Federal and state-level governments use patch orchestration platforms to meet mandates from cybersecurity frameworks like FISMA and NIST. Patching legacy software in sensitive areas like public safety networks, tax systems, and electoral technologies ensures uptime, data confidentiality, and resistance to nation-state cyber attacks or hacktivist disruptions.
- Retail & eCommerce Platforms: Retailers use patching tools to secure Point-of-Sale (POS) systems, CRM platforms, and inventory control software. This protects against payment card breaches and data theft in high-volume transactional environments. Automated patching also ensures compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and helps reduce the scope of regular security audits.
- Manufacturing & Industrial Systems: Industrial enterprises patch Operational Technology (OT) systems, including SCADA, PLCs, and smart sensors, to maintain secure production lines. Patch tools protect against cyber-physical attacks and ensure continuity of just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing models. Integration with ICS/OT monitoring tools enables real-time visibility into vulnerabilities in factory automation systems.
Global Patch Management Market: Stats & Facts
CISA, NSA, FBI (United States Federal Cybersecurity Agencies)
- In 2023, U.S. federal agencies reported that 11 of the 15 most-exploited vulnerabilities were zero-day flaws, meaning the vulnerabilities had no available patches at the time of exploitation.
- According to the NSA and CISA, the median time taken by organizations to patch Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEVs) was approximately 174 days, while non-KEVs took a median of 621 days, showing a significant delay in addressing vulnerabilities.
- Over 35% of U.S.-based organizations had at least one system affected by a KEV in 2023, exposing them to ransomware and targeted breaches.
- Vulnerabilities associated with ransomware were patched 2.5 times faster than those not directly linked to ransomware campaigns, reflecting growing awareness but also reactive behavior rather than proactive protection.
CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog
- As of June 2024, the CISA KEV Catalog had documented 1,378 actively exploited vulnerabilities across commonly used enterprise, cloud, and industrial systems.
- Federal Binding Operational Directives now require these vulnerabilities to be patched within a specific time frame, particularly within 21 days for high-severity exploits.
ENISA – European Union Agency for Cybersecurity
- Between June 2023 and July 2024, ENISA analyzed 11,079 cybersecurity incidents across Europe, a majority of which stemmed from the exploitation of unpatched systems and misconfigurations.
- Among those incidents, 19% targeted public administration, 11% targeted the transportation sector, and 9% impacted financial institutions.
- 46% of finance-related cyber incidents involved credit institutions such as banks and insurance companies.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks in Europe saw 58% targeting banks, while 21% were aimed at public financial services like tax authorities and central banks.
- In the healthcare sector, 54% of recorded cyberattacks were ransomware-based, while **46% were focused on stealing sensitive patient or research data.
- Of the healthcare breaches, 61% were caused by vulnerabilities in third-party software and hardware components, underlining the importance of patching external vendor tools.
NJBIA – New Jersey Business & Industry Association (USA)
- Reports indicated that cyberattacks exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities nearly tripled in 2023, accounting for 14% of all breaches, up from less than 5% the previous year.
- Additionally, 68% of all breaches in New Jersey businesses were rooted in human error, often due to a lack of awareness about timely software updates or patch installation.
Armis and Ponemon Institute Collaboration
- Research from Armis and the Ponemon Institute found that approximately 60% of all data breaches globally were directly attributed to unpatched or poorly patched software systems, affecting both enterprise and critical infrastructure.
CVE Database and Security Vulnerability Records
- The global Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) system reported over 240,000 unique vulnerabilities by the end of November 2024, growing by thousands each month.
- Zero-day exploits vulnerabilities discovered and exploited before patches are available typically remain viable for attackers for an average of 6.9 years if undetected.
- For vulnerabilities discovered by third parties, the average lifespan before discovery is shorter, lasting around 1.4 years.
- It takes an average of 22 days to develop a working zero-day exploit once a vulnerability is identified.
- There are an estimated 400 to 1,500 independent developers operating on exploit markets, with annual earnings between USD 5,500 and USD 20,800, depending on skill and specialization.
MOVEit Software Data Breach (2023 Incident Reference)
- One of the most critical breaches in recent years was the MOVEit Transfer software attack, which exploited an unpatched vulnerability and led to the compromise of more than 2,700 organizations globally.
- This single vulnerability exposure affected approximately 93.3 million individuals, including private data such as Social Security Numbers, medical records, and financial details.
- More than 80% of the affected entities were based in the United States, emphasizing the risk of delayed patch application even in developed economies.
CISA Ransomware Vulnerability Alert
- In early 2025, CISA added vulnerability CVE-2024-57727, found in remote monitoring software, to its KEV catalog after evidence of active exploitation in ransomware attacks.
- This reflects the growing threat of attackers targeting remote access and administrative tools with known security flaws left unpatched in IT environments.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence in the Global Patch Management Market
- Predictive Vulnerability Assessment: AI enables proactive identification of vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Machine learning models analyze historical vulnerability data, CVE disclosures, threat intelligence feeds, and attack patterns to predict which systems are most likely to be targeted. This allows security teams to prioritize high-risk assets for immediate patching, thereby reducing the attack surface and potential breach points. For example, platforms like IBM BigFix and Ivanti Neurons use AI-powered risk-based prioritization to prevent patch fatigue and alert overload.
- Intelligent Patch Prioritization & Automation: AI helps automate the ranking of available patches based on severity, exploitability, asset criticality, and business impact. This automation eliminates human guesswork, minimizes delays, and ensures that security patches are deployed in a timely and efficient manner. Natural language processing (NLP) is used to interpret patch notes and identify relevance across diverse IT environments. Tools like Automox and Microsoft Defender utilize AI for real-time patch scoring and auto-remediation.
- Real-Time Threat Correlation & Contextual Decision-Making: AI algorithms analyze data from EDR, SIEM, and threat intelligence platforms to correlate active threats with unpatched vulnerabilities. This enables context-aware patch decisions, allowing IT teams to focus on patches that defend against current threat campaigns instead of applying all updates blindly. AI-driven patch engines can scan up to 5,000+ CVEs/hour, ensuring instant identification of exploitable flaws.
- Enhanced Patch Management in Hybrid and Cloud Environments: In cloud and hybrid setups, AI helps optimize patching schedules and identify under-patched assets distributed across on-premise and multi-cloud environments. AI agents support dynamic asset discovery, risk profiling, and compliance tracking, reducing gaps due to misconfiguration or visibility issues. Cloud-native tools like ManageEngine and Syxsense apply AI to detect asset drift and automate zero-touch patching.
- Adaptive Learning and Feedback Loops: AI-powered systems learn from patch failures, reboots, and rollback events, enabling more reliable future deployments. These feedback loops enhance predictive analytics and refine patch recommendations over time, especially in complex environments like healthcare, telecom, or manufacturing. This self-improving model reduces the risk of system downtime and operational disruption from faulty patches.
- AI for Compliance and Governance: AI supports compliance by automating policy enforcement, maintaining patch audit logs, and generating real-time dashboards for governance. This is critical for aligning with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, NIS2, and CISA directives that mandate vulnerability management and remediation documentation. AI ensures continuous compliance readiness and reduces manual reporting burdens.
Global Patch Management Market: Market Dynamic
Driving Factors in the Global Patch Management Market
Increasing Cyber Threats and Ransomware Attacks
The rising frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks, especially ransomware, are significantly driving the patch management market forward. Ransomware groups exploit unpatched vulnerabilities as a primary entry point, often targeting publicly known flaws that remain unaddressed for months. High-profile attacks, such as those involving WannaCry, Petya, and MOVEit, exploited well-documented CVEs with available patches. These incidents have underscored the business-critical importance of proactive patching. Government agencies such as CISA and NIST have issued numerous directives and frameworks mandating the timely remediation of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEVs) within set timeframes.
Organizations now face financial, legal, and reputational consequences if breaches occur due to patch neglect. The proliferation of hybrid work, cloud environments, and connected OT devices has expanded attack surfaces, amplifying the risk. In response, organizations are increasing investments in automated patch orchestration tools, vulnerability scanners, and endpoint detection and response systems. As cyber insurance premiums rise and coverage becomes conditional on cybersecurity hygiene, including patch compliance, the market for patch management platforms is expected to grow significantly over the coming years.
Regulatory Compliance and Governance Requirements
Compliance with global data protection and cybersecurity regulations is a critical growth catalyst in the patch management market. Laws such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the U.S. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) mandate stringent cybersecurity controls, including the rapid remediation of known vulnerabilities. Enterprises are now required to maintain records of patch deployment cycles, audit trails, and evidence of remediation efforts as part of compliance audits. Failure to implement timely updates can result in severe fines, operational sanctions, or litigation.
For instance, under GDPR, data breaches due to unpatched software could lead to penalties amounting to 4% of annual global revenue. Additionally, frameworks like ISO/IEC 27001 and NIST SP 800-40 explicitly recommend periodic patch evaluations and prioritization based on asset criticality. Governments are also pushing regulations that require critical infrastructure entities to comply with baseline patching standards. As the cybersecurity threat landscape evolves, compliance demands will continue to increase in complexity and scope, pushing organizations toward more comprehensive, automated, and audit-friendly patch management solutions.
Restraints in the Global Patch Management Market
Legacy Systems and Compatibility Challenges
One of the most formidable barriers to patch management adoption is the prevalence of legacy systems across critical industries. Organizations in manufacturing, healthcare, aviation, and government often rely on legacy hardware and software platforms that are either out of vendor support or highly customized.
These systems are vital to operations and cannot be easily replaced due to cost, compliance dependencies, or integration complexity. Applying patches in these environments carries a high risk of system failure, application breakdown, or data corruption. As a result, many IT teams adopt a “do not touch” policy, leaving such environments vulnerable for extended periods.
Even where patches exist, the testing cycles for legacy systems are lengthy, requiring simulation of hundreds of interdependencies before approval. Furthermore, older systems may not support modern patch delivery protocols, making automation impossible. Organizations are also constrained by a shortage of legacy IT experts who can manage these updates manually. This incompatibility and inertia hinder the adoption of modern patching tools, leaving critical infrastructure exposed. Until viable modernization strategies or compatible patch orchestration layers are developed, this challenge will continue to limit the full scalability of the patch management market.
Fragmented IT Environments and Change Resistance
The complexity of modern enterprise IT environments spread across public clouds, private data centers, remote endpoints, and diverse operating systems presents a serious challenge to centralized patch management.
Different departments within a single organization may run different tech stacks, each with unique patch cycles, third-party dependencies, and business-critical uptime windows. This fragmentation complicates coordination, often resulting in missed patches, inconsistent policies, and vulnerability blind spots. Additionally, organizational resistance to change significantly impedes patch management practices.
Many business units fear patch-related downtimes, particularly during critical operations, and request exemptions or delays. DevOps teams may avoid patches to preserve deployment stability. Even within security teams, competing priorities lead to patch deferral or inadequate risk assessment. Such human and structural resistance undermines automation, extends vulnerability exposure, and erodes compliance readiness.
Overcoming these challenges requires strong executive mandates, a comprehensive asset inventory, and investment in change management protocols. Without these structural reforms, even the best patch management tools face limited effectiveness in fragmented environments.
Opportunities in the Global Patch Management Market
Expansion into Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
While patch management has traditionally been a domain of large enterprises, the rising digital maturity of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) is unlocking a significant growth opportunity for vendors in this space. SMEs are increasingly becoming targets for cyberattacks due to their relatively weaker security postures and inadequate IT staffing.
Despite limited budgets, the transition to cloud-based infrastructure, reliance on third-party vendors, and the rise of remote workforces have compelled SMEs to adopt basic cybersecurity hygiene practices, starting with patch management. The emergence of lightweight, cloud-native patch management tools has dramatically reduced entry barriers. These tools require minimal infrastructure, are priced on flexible subscription models, and often come bundled with endpoint protection services.
In parallel, Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) are extending patch management as part of their offerings to SMEs, providing on-demand remediation without the need for in-house expertise. Government-backed initiatives in several countries are offering cybersecurity grants, free vulnerability assessments, and awareness programs specifically tailored to small businesses. This combination of economic models, regulatory nudges, and threat-driven urgency is positioning SMEs as a fertile market segment for growth. As digital ecosystems evolve, SME compliance is also being scrutinized due to supply chain risks, further accelerating patch management adoption in this sector.
Mobile Device and IoT Patch Management
The exponential growth of mobile devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure presents vast opportunities for patch management solutions tailored to non-traditional endpoints. In sectors like healthcare, logistics, agriculture, and energy, thousands of distributed IoT nodes and mobile terminals are performing mission-critical operations, yet often lack consistent update mechanisms.
These systems, if left unpatched, can become entry points for sophisticated cyberattacks, including lateral movement within enterprise networks. Traditional patching platforms are often inadequate for these environments due to differences in architecture, real-time processing constraints, and limited compute capabilities of embedded systems.
This gap creates a major opportunity for vendors developing Over-the-Air (OTA) patching solutions, lightweight agents, and remote firmware update protocols that can work across 5G, LPWAN, and satellite-based communication networks. With the global rollout of smart cities, Industry 4.0, and connected healthcare infrastructure, IoT patch management is no longer optional; it’s essential. Governments and industry consortia are also beginning to issue specific mandates for securing embedded and mobile systems. As organizations strive to reduce their attack surface and ensure end-to-end visibility across digital assets, integrated patch management solutions that span desktop, mobile, and IoT ecosystems will be in high demand.
Trends in the Global Patch Management Market
AI-Driven Patch Prioritization and Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing patch management by transforming how vulnerabilities are identified, ranked, and remediated. Traditionally, IT teams were overwhelmed with manually sorting through thousands of patches, many of which were low risk or irrelevant to critical operations.
AI-powered platforms now automate this process by dynamically prioritizing patches based on exploitability, asset sensitivity, business impact, and historical incident trends. Machine learning algorithms can ingest data from sources like the National Vulnerability Database (NVD), CISA’s KEV catalog, and endpoint telemetry to assess threats in real time.
These platforms simulate patch deployment in virtual environments, flagging potential conflicts before rollouts. Moreover, AI ensures minimal disruption to users by recommending optimal patch windows and rollback mechanisms.
Organizations integrating AI-based patching systems report faster response times, improved security postures, and compliance with regulatory frameworks such as ISO 27001 and NIST SP 800-53. As threat actors increasingly use automation for attacks, defensive systems must do the same, making AI-driven patching not just a convenience but a necessity.
Integration with Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) Platforms
The increasing convergence of patch management with Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) platforms is a growing trend shaping enterprise IT security. Modern workplaces include a wide range of endpoints laptops, desktops, mobile devices, servers, and IoT devices, across varied operating systems and networks. Managing patches for each of these separately results in inefficiency, non-compliance, and security blind spots. UEM platforms provide a unified interface to manage, monitor, and secure all endpoints under a single policy framework.
By embedding patch management directly into UEM tools, organizations achieve consistent security postures, reduce operational overhead, and simplify audit compliance. These integrations offer real-time visibility into device health, automate patch rollouts, and support granular segmentation of patching rules based on geography, department, or device type.
This approach aligns with the rise of hybrid work, where IT teams must manage devices remotely across multiple time zones and network environments. As enterprises seek to consolidate security tools, integrated UEM and patch platforms are increasingly favored for their scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Global Patch Management Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Component Analysis
Software-based patch management platforms are projected to dominate this segment due to their comprehensive, scalable, and automated capabilities that meet the evolving needs of modern cybersecurity frameworks. These tools streamline the full lifecycle of patch activities from scanning and prioritization to deployment, rollback, and reporting across diverse IT environments. With the increasing number of zero-day vulnerabilities and ransomware threats, the ability to quickly deploy security patches across endpoints and servers is essential.
Software platforms like ManageEngine, Ivanti, Microsoft SCCM, Automox, and others offer cloud-native solutions with AI-based patch recommendation engines, patch health monitoring, vulnerability scoring, and seamless OS/application integrations. These capabilities are critical in ensuring consistent patching practices across hybrid environments, including physical, virtual, and cloud assets.
Additionally, enterprises are shifting toward continuous compliance models, requiring audit-ready documentation and real-time dashboard features natively available in software platforms. Such platforms often support integration with ITSM tools like ServiceNow, vulnerability management tools like Qualys and Tenable, and asset inventory systems, which enhances their enterprise appeal. Meanwhile, while services remain important (e.g., managed patching by MSSPs), they tend to be reactive, labor-intensive, and not as scalable.
Services are often sought by organizations lacking in-house IT teams, but software solutions provide long-term value, automation, cost efficiency, and better visibility. As cyber threats grow in volume and sophistication, the need for high-frequency patching, intelligent prioritization, and autonomous workflows makes software the indispensable foundation of modern patch management strategies.
By Organization Size Analysis
Large enterprises are poised to dominate this segment due to their complex IT ecosystems, stringent regulatory obligations, and expansive digital footprints, which demand advanced and automated patch management solutions. These organizations typically operate across multiple geographies, manage thousands of endpoints, and run mission-critical applications on diverse operating systems and platforms.
The sheer scale and heterogeneity of their environments make manual patching infeasible. For instance, a global bank may manage over 100,000 devices, each with unique configurations and compliance requirements necessitating robust patch management automation, centralized control, and detailed audit logs.
Moreover, large enterprises are high-value targets for ransomware gangs and nation-state actors. As a result, they face heightened risk exposure and require continuous, policy-driven vulnerability remediation. To address this, large enterprises deploy enterprise-grade solutions such as Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager, ServiceNow Patch Management, and BigFix.
These tools allow seamless integration with SIEM systems, Active Directory, vulnerability scanners, and cloud management platforms. Also, these firms typically fall under multiple data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, CMMC), which mandate timely security patching. They must also report patch status during audits and risk assessments.
Large organizations are also better positioned to adopt DevSecOps methodologies, integrating patching directly into CI/CD pipelines. This is especially vital for technology, finance, and healthcare sectors. Additionally, most large firms are covered under cyber insurance policies, which require patching of known vulnerabilities as a precondition. Overall, due to the scale of operations, risk profile, and governance expectations, large enterprises will continue to lead the demand for structured, integrated patch management systems.
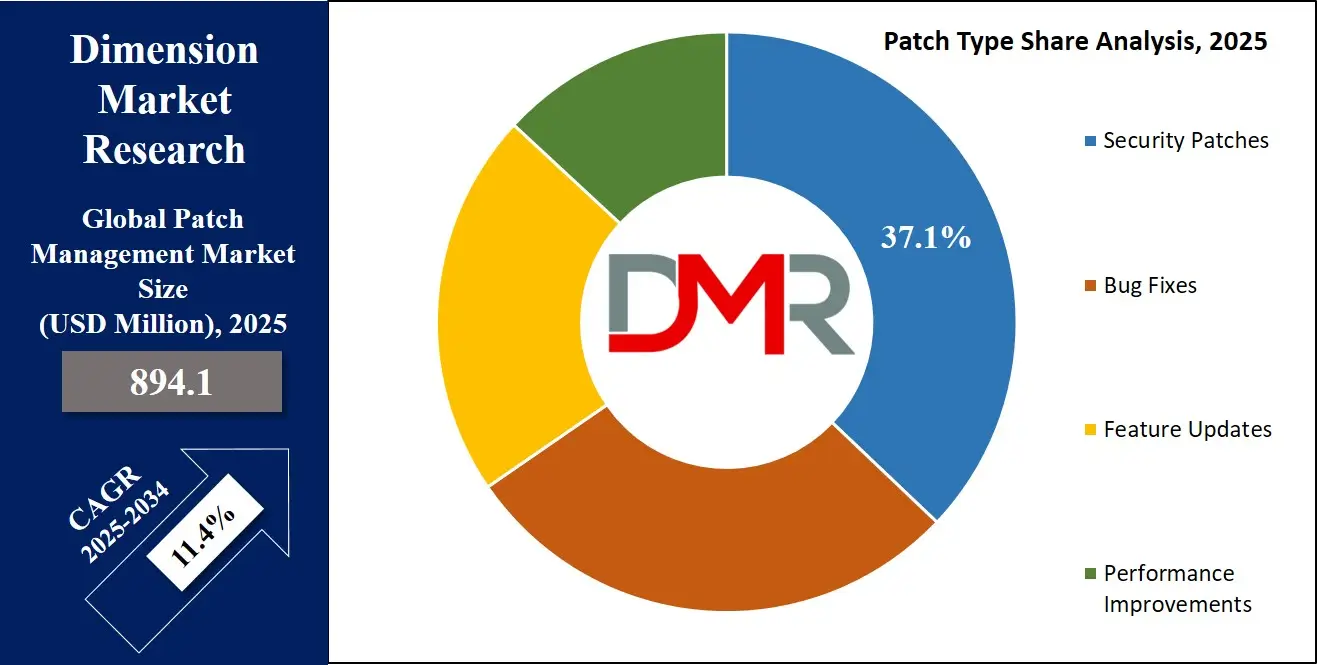
By Patch Type Analysis
Security patches are anticipated to lead the patch type segment due to their critical role in preventing active cyber threats, reducing vulnerability exposure, and maintaining compliance with global data protection regulations.
These patches are designed specifically to close known security flaws that, if left unaddressed, can be exploited by threat actors to deploy ransomware, access sensitive data, or disable critical infrastructure. In contrast to bug fixes or performance enhancements, security patches carry immediate risk mitigation value, making them a top priority in IT operations.
In the wake of increasingly high-profile cyberattacks from the Log4j vulnerability to the MOVEit software breach, organizations are more aware of the consequences of delayed security patching. Government agencies such as CISA and ENISA have released vulnerability catalogs and mandates, requiring timely patch application for known exploited vulnerabilities (KEVs).
For example, CISA’s Binding Operational Directive 22-01 enforces patching of high-risk security vulnerabilities across U.S. federal agencies within defined deadlines. Private enterprises are aligning with similar standards to avoid legal liabilities and reputational damage.
Moreover, insurers and regulators are increasing scrutiny on patch hygiene, especially for security vulnerabilities, when assessing cyber risk profiles. Failure to apply critical security patches has been cited as a root cause in numerous breach investigations.
As a result, security patches are now subject to automated workflows that ensure faster rollout, pre-deployment testing, and real-time reporting. Given the rapid growth in zero-day vulnerabilities and the public disclosure of CVEs, organizations view security patches as a foundational cybersecurity control, solidifying their dominance in this category.
By Deployment Analysis
Cloud-based patch management solutions are expected to dominate the deployment segment, propelled by widespread adoption of remote work models, multi-cloud infrastructure, and agile DevOps workflows. Unlike traditional on-premise tools that require in-house servers, rigid configurations, and complex maintenance cycles, cloud-native platforms are agile, scalable, and rapidly deployable.
They offer centralized visibility over distributed IT assets, enabling real-time patch status monitoring, vulnerability alerts, and automated policy enforcement across remote devices and cloud workloads.
With hybrid and remote teams becoming standard across industries, IT security teams need to patch systems regardless of physical location or network.
Cloud patching platforms such as Automox, ManageEngine Cloud, and NinjaOne allow seamless patch deployment to geographically dispersed endpoints over the internet, without the need for VPNs or local servers. This functionality is vital for modern BYOD environments and global enterprises with decentralized infrastructure. Moreover, cloud platforms integrate easily with existing ITSM, MDM, and threat detection tools, improving orchestration and response times.
Additionally, cloud platforms offer better uptime, vendor-managed updates, and faster access to zero-day patch information. Organizations also benefit from lower total cost of ownership, elastic resource scaling, and built-in disaster recovery.
Regulatory frameworks like ISO 27017 and CSA STAR provide cloud security governance models, reinforcing trust in these platforms. As enterprises accelerate cloud migration and adopt agile, containerized environments, cloud-native patch management systems offer the flexibility and speed required to maintain cyber hygiene, making them the clear preference in modern IT ecosystems.
By Operating System Analysis
Windows is anticipated to dominate the operating system segment of the patch management market due to its pervasive presence in enterprise computing. Most corporate desktops, servers, and administrative applications globally still operate on the Windows OS.
According to various IT audits, over 75% of business endpoints run Windows, making it the primary focus for patch management operations. Microsoft’s monthly "Patch Tuesday" schedule releases critical security updates and bug fixes for Windows and associated services, emphasizing the volume and regularity of patches required to maintain system integrity.
Moreover, Windows environments are frequent targets for cybercriminals due to their widespread use and extensive documentation. Threat actors often exploit vulnerabilities listed in Microsoft's CVEs to deploy ransomware, remote access Trojans, or privilege escalation tools. Enterprises cannot afford to delay patching in such environments without risking compliance violations or operational disruptions. Regulatory standards like CIS Benchmarks, HIPAA, and PCI DSS all emphasize timely patching, especially on Windows platforms.
Microsoft has also improved its enterprise patching tools, offering Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), Endpoint Manager (Intune), and Microsoft Defender integration, which streamline deployment and compliance reporting.
Additionally, Windows-based patching integrates seamlessly with AD and Group Policy, making it easier for IT teams to deploy policies organization-wide. Because of its critical role in core business operations, continuous exposure to cyber threats, and structured patch release cycle, Windows remains the dominant OS segment in patch management strategies across industries.
By End User Industry Analysis
The IT & Telecom sector is expected to lead patch management adoption due to its complex, interconnected, and high-risk digital infrastructure. Telecom service providers, internet backbone operators, and IT service companies are the backbone of global digital communication, handling vast volumes of sensitive data and managing critical network infrastructure. Any disruption due to vulnerabilities or exploits can have cascading effects on businesses, consumers, and even national security. Therefore, patch management is non-negotiable for business continuity and regulatory compliance in this sector.
These organizations run heterogeneous systems ranging from legacy switches and routers to cloud-native platforms and 5G networks, requiring meticulous patching schedules. The sector is often classified as Critical Information Infrastructure (CII) by governments, placing it under mandatory cybersecurity regulations like the U.S. FCC rules, the NIS2 Directive in Europe, and the IT Act in India. Compliance with these regulations involves strict reporting of patch status, incident response plans, and vulnerability management frameworks.
Additionally, IT firms offering managed services or cloud platforms to third-party clients must demonstrate strong security postures to retain contracts and avoid liability. As providers of essential services and infrastructure, IT & Telecom players face a higher frequency of targeted attacks, making real-time, automated patch management platforms essential. The rapid rollout of 5G, edge computing, and AI services also expands the attack surface, reinforcing the need for proactive patching strategies. Due to operational complexity, industry regulations, and high risk of disruption, IT & Telecom continues to be the most dominant end-user industry in the patch management market.
The Global Patch Management Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Component
By Organization Size
- Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Large Enterprises
By Patch Type
- Security Patches
- Bug Fixes
- Feature Updates
- Performance Improvements
By Deployment
By Operating System
- Windows
- Linux
- Mac OS
- Others
By End User Industry
- IT & Telecom
- BFSI
- Retail
- Government
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Others
Global Patch Management Market: Regional Analysis
Region with the Largest Revenue Share
North America is anticipated to dominate the global patch management market as it holds 39.0% of the total market revenue by the end of 2024, due to its advanced IT infrastructure, high cybersecurity maturity, and strict regulatory landscape. The U.S. government and federal bodies like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) mandate timely patching as part of the national cybersecurity strategy.
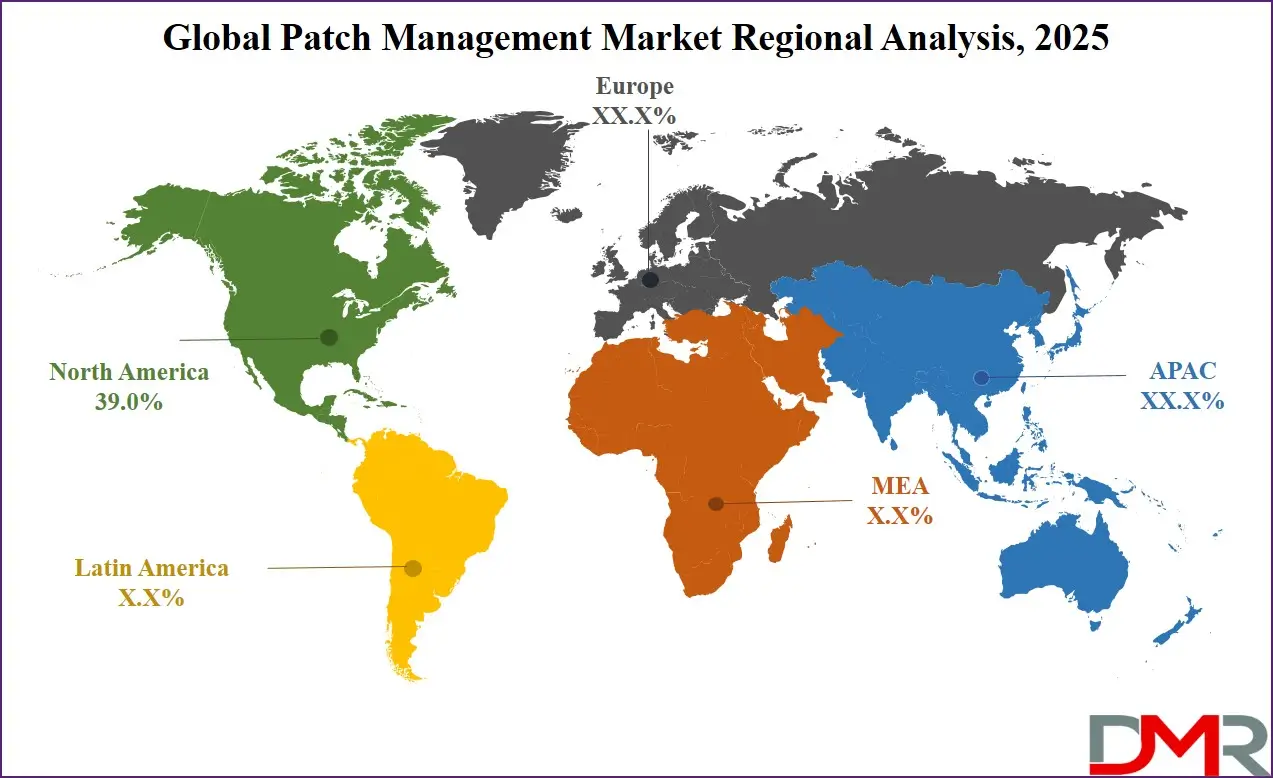
The region is home to several Fortune 500 companies, tech giants, cloud service providers, and critical infrastructure sectors (e.g., healthcare, finance, telecom), all of which require real-time, automated patch management for risk mitigation and compliance.
Organizations in the region are also early adopters of AI-powered patch orchestration tools, Zero Trust architecture, and DevSecOps practices that integrate patching into CI/CD pipelines. Additionally, the presence of leading solution vendors such as Microsoft, Ivanti, Qualys, and ServiceNow strengthens the regional ecosystem by offering enterprise-grade patch tools.
The growing cyberattack volume, ransomware threats, and third-party risk have also fueled demand for unified endpoint management (UEM) platforms with integrated patch features. Moreover, cyber insurance underwriters in the U.S. now assess patching frequency as a key risk metric, pushing organizations to adopt automated and auditable patch workflows. These factors collectively reinforce North America's market leadership in the patch management domain.
Region with the Highest CAGR
Asia Pacific is projected to witness the highest CAGR in the patch management market due to rapid digital transformation, expanding enterprise IT footprints, and increasing cybersecurity regulations. Countries like India, China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia are aggressively investing in digital infrastructure, cloud adoption, and national cyber defense programs. With the rise of smart cities, 5G networks, and Industrial IoT deployments, the region's digital attack surface is expanding, creating a critical need for proactive patching across endpoints, servers, and OT devices.
Governments in Asia Pacific are introducing stricter data protection laws, such as India’s Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act and China’s Cybersecurity Law, which mandate regular vulnerability assessments and remediation. Additionally, rising cyberattacks on financial institutions, public sector databases, and healthcare networks have made security patching a strategic priority.
SMEs in Southeast Asia are also adopting cloud-based patch tools due to their affordability and minimal infrastructure requirements. Japan, South Korea, and Singapore are promoting AI integration in cybersecurity, further accelerating intelligent patch automation.
Moreover, increased funding in cybersecurity training, MSSP adoption, and threat intelligence sharing alliances (like Japan’s JC3 and India’s CERT-IN) are improving awareness and readiness. This mix of economic modernization and regulatory enforcement is fueling the region’s rapid growth in patch management solutions.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Global Patch Management Market: Competitive Landscape
The global patch management market is moderately fragmented, with a mix of established software giants, cybersecurity specialists, and emerging SaaS vendors competing on automation, scalability, and integration capabilities. Leading players include Microsoft Corporation, Ivanti, Qualys Inc., ManageEngine (Zoho Corporation), SolarWinds, Automox, ServiceNow, Micro Focus, and HCL BigFix. These companies offer a range of on-premise and cloud-native platforms that integrate with asset inventory systems, vulnerability scanners, and endpoint protection tools.
Competition is intensifying as vendors invest heavily in AI-driven patch prioritization, real-time risk scoring, and zero-touch deployment to differentiate their offerings. Companies like Automox and Syxsense are gaining traction by targeting mid-sized enterprises with lightweight, cloud-native solutions, while established firms like Microsoft and Ivanti continue to dominate large enterprise and public sector contracts.
Strategic partnerships are also shaping the competitive landscape. For instance, integration with ITSM platforms like ServiceNow or security solutions like CrowdStrike enables vendors to offer more unified cybersecurity stacks. The growing demand for MSP-ready solutions has also prompted vendors to build multi-tenant platforms. As cybersecurity compliance tightens globally, the competition will increasingly center around automation, analytics, and seamless integration across hybrid IT environments.
Some of the prominent players in the Global Patch Management Market are
- Microsoft Corporation
- IBM Corporation
- Ivanti
- Broadcom Inc. (Symantec)
- SolarWinds Corporation
- ManageEngine (Zoho Corporation)
- Micro Focus (OpenText)
- BMC Software
- Qualys, Inc.
- Automox Inc.
- ConnectWise
- GFI Software
- LANDesk Software (Now part of Ivanti)
- Red Hat, Inc.
- SysAid Technologies
- Quest Software
- Atera Networks
- PDQ.com
- Kaseya Limited
- Citrix Systems, Inc.
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments in the Global Patch Management Market
June 2025
- NSF-backed Secure Software Supply Chain Summit: The Secure Software Supply Chain Center (S3C2) hosted a key summit emphasizing the role of patch management in strengthening software supply chains. Attendees from federal cybersecurity agencies, infrastructure sectors, and cloud vendors discussed how unpatched open-source components pose critical risks in the AI era.
April 2025
- VMware Invests USD 500 Million in AI-Driven Patch Management: VMware announced a USD 500 million initiative focused on enhancing its patch orchestration capabilities with AI/ML to support predictive remediation, intelligent prioritization, and cloud-native deployment across global enterprise networks.
December 2024
- IBM Upgrades BigFix with Predictive Analytics: IBM enhanced its BigFix solution by integrating machine learning models for threat pattern recognition. The update enables forecasting of future vulnerability vectors and improves exploit prevention accuracy across over 600,000 managed servers globally.
October 2024
- Microsoft SCCM Receives Integrated Vulnerability Scanning: Microsoft upgraded its System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) with native vulnerability scanning capabilities across Windows, Linux, and hybrid systems. The update supports remediation across over 1.2 million endpoints using automation-based patch deployment rules.
September 2024
- Absolute Security Acquires Syxsense: Absolute Security completed the acquisition of Syxsense Inc., integrating Syxsense’s cloud-native automated patching and vulnerability remediation solutions into its cyber resilience platform to strengthen endpoint protection capabilities.
July 2024
- ManageEngine Launches Agentless Patching: ManageEngine introduced agentless patching features across its Endpoint Central suite. The capability enables remote patching of over 220,000 endpoints while reducing bandwidth usage by 30%, ideal for decentralized and hybrid workforce environments.
May 2024
- Automox Deploys AI Risk-Scoring Engine: Automox released a real-time risk-scoring engine leveraging AI to assess over 5,000 CVEs per hour. The platform accelerates patch deployment cycles and reduces average remediation windows by nearly 50%, particularly for actively exploited vulnerabilities.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 894.1 Mn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 2,365.7 Mn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
11.4% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 293.3 Mn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Component (Software, Services), By Organization Size (Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Large Enterprises), By Patch Type (Security Patches, Bug Fixes, Feature Updates, Performance Improvements), By Deployment (Cloud, On-Premises), By Operating System (Windows, Linux, Mac OS, Others), By End User Industry (IT & Telecom, BFSI, Retail, Government, Healthcare, Manufacturing, Others) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, Rest of Europe; Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
Microsoft Corporation, IBM Corporation, Ivanti Inc., Broadcom Inc. (Symantec), SolarWinds Corporation, ManageEngine (Zoho Corporation), Micro Focus International plc (OpenText), BMC Software Inc., Qualys Inc., Automox Inc., ConnectWise LLC, GFI Software Ltd., LANDesk Software Inc. (part of Ivanti), Red Hat Inc., SysAid Technologies Ltd., Quest Software Inc., Atera Networks Ltd., PDQ.com Corporation, Kaseya Limited, Citrix Systems Inc., and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Patch Management Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 894.1 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2,365.7 million by the end of 2034.
The market is growing at a CAGR of 11.4 percent over the forecasted period of 2025.
The US Patch Management Market is projected to be valued at USD 293.3 million in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 732.2 million in 2034 at a CAGR of 10.7%.
North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Patch Management Market with a share of about 39.0% in 2025.
Some of the major key players in the Global Patch Management Market are Microsoft Corporation, IBM Corporation, Ivanti Inc., Broadcom Inc. (Symantec), SolarWinds Corporation, ManageEngine (Zoho Corporation), Micro Focus International plc (OpenText), BMC Software Inc., and many others.