Market Overview
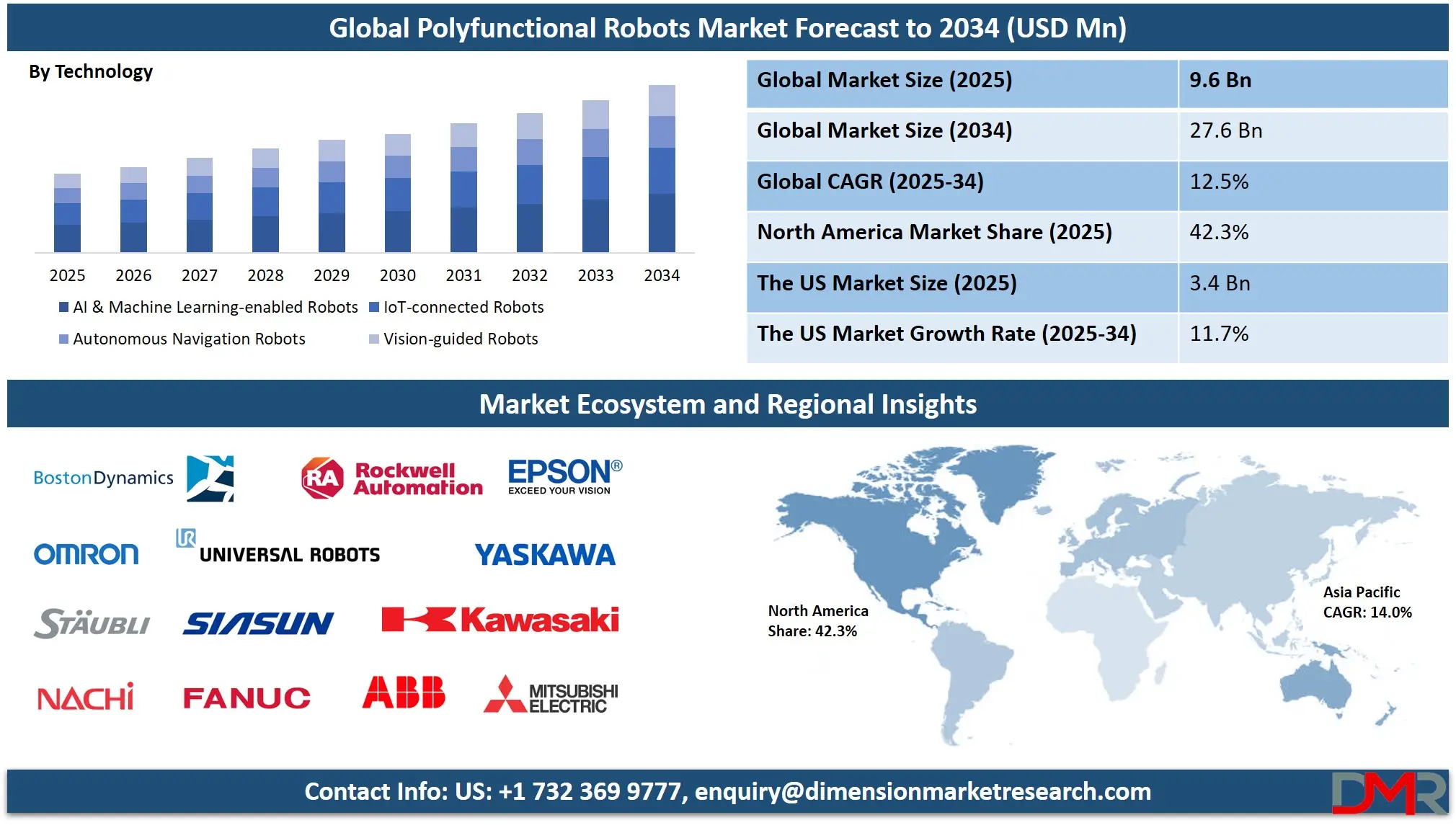
The Global Polyfunctional Robots Market is projected to reach USD 9.6 billion in 2025 and grow at a compound annual growth rate of 12.5% from there until 2034 to reach a value of USD 27.6 billion.
The global polyfunctional robots market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technologies. These robots, capable of performing multiple tasks across various industries, are becoming integral in sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and agriculture. The integration of AI enables robots to adapt to dynamic environments, enhancing their utility and efficiency.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Opportunities abound in emerging economies where labor shortages and the push for automation are prevalent. In healthcare, for instance, robots assist in surgeries and patient care, addressing the increasing demand for medical services. In agriculture, robotic systems are employed for planting, harvesting, and monitoring crop health, improving productivity and sustainability. The logistics sector benefits from robots in warehousing and delivery services, optimizing operations and reducing costs.
However, the market faces restraints such as high initial investment costs and the need for skilled personnel to operate and maintain these sophisticated systems. Small and medium-sized enterprises may find it challenging to adopt such technologies due to financial constraints. Additionally, concerns over job displacement and ethical considerations regarding human-robot interactions pose challenges to widespread acceptance.
Despite these challenges, the growth prospects remain robust. Continuous research and development efforts are leading to more affordable and user-friendly robotic solutions. Government initiatives and funding in various countries support the adoption of robotics, aiming to enhance productivity and address labor shortages. As technology advances and costs decrease, the adoption of polyfunctional robots is expected to become more widespread, transforming industries and contributing to economic growth.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
The US Polyfunctional Robots Market
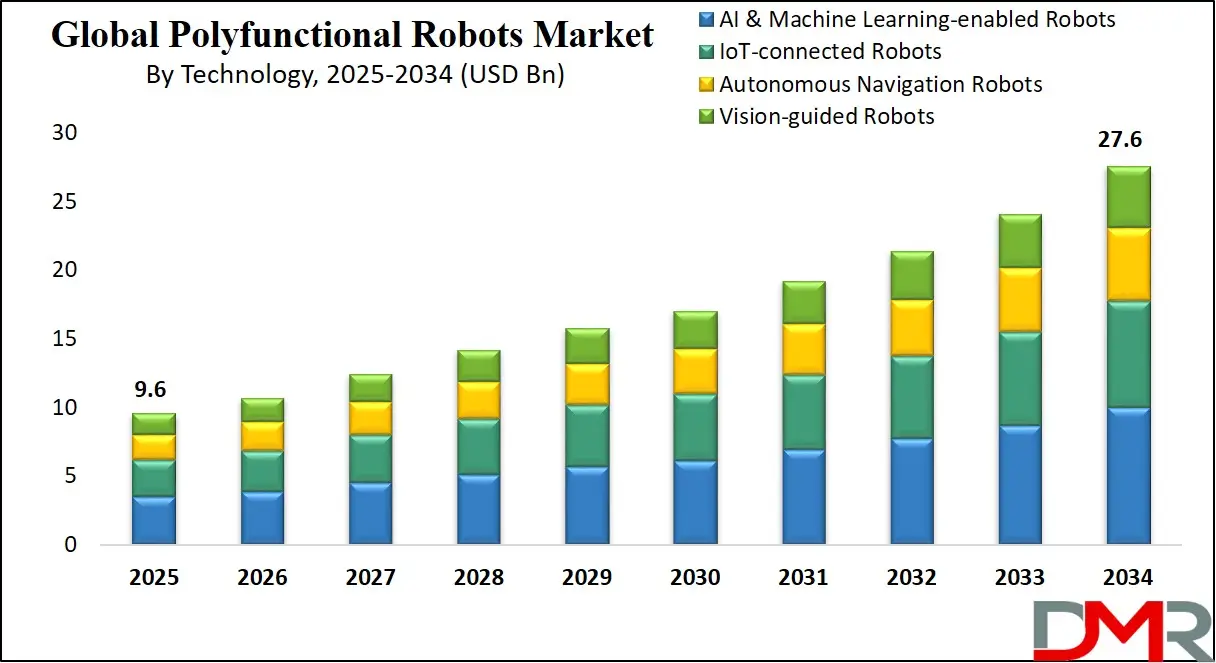
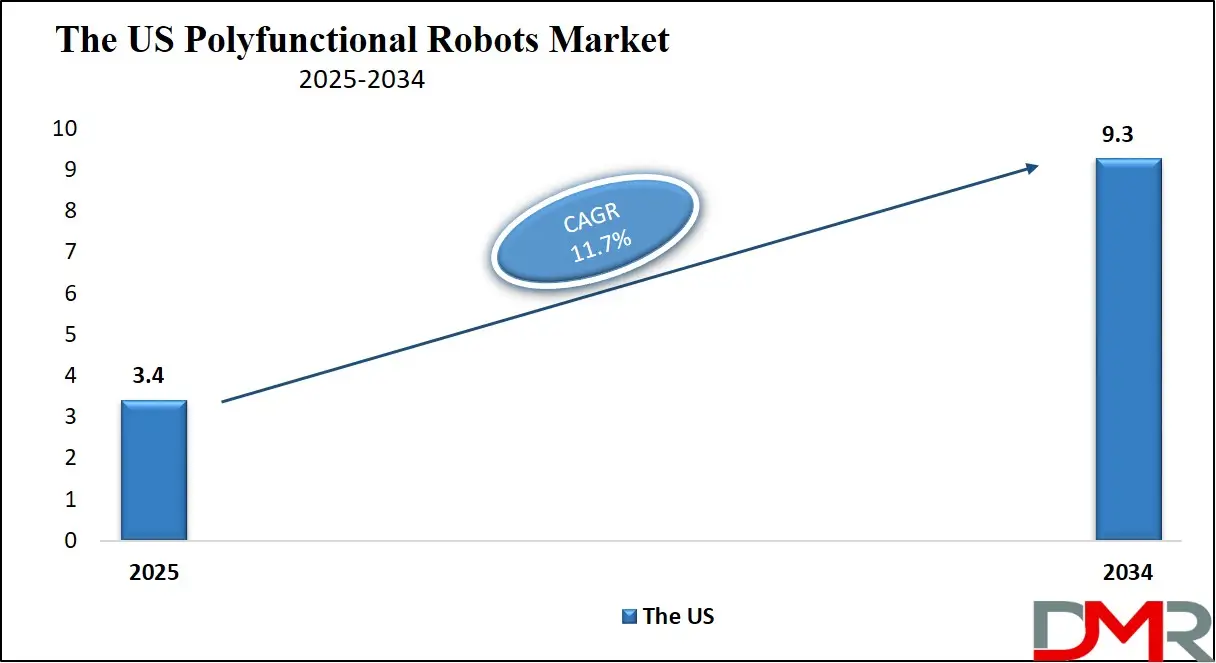
The US Polyfunctional Robots Market is projected to reach USD 3.4 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 11.7% over its forecast period.
The United States maintains a strong foothold in the polyfunctional robots market owing to its advanced R&D ecosystem, industrial digitalization, and favorable demographics for automation. as per the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, sectors like logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare face ongoing labor shortages. Coupled with an aging population, a median age over 38 years, this demographic shift is accelerating automation across the board. Robots are bridging skill gaps while maintaining high productivity.
Government-backed initiatives like the National Robotics Initiative (NRI) and the Advanced Robotics for Manufacturing (ARM) Institute support innovation in multifunctional robotics. These programs foster academia-industry collaboration to develop next-generation robotic platforms suitable for adaptive use in small and large enterprises alike. Tax incentives and infrastructure grants are further driving robotic integration in precision farming, medical support systems, and smart warehouses.
The U.S. also benefits from a highly skilled workforce trained in robotics, AI, and mechatronics. Educational institutions such as MIT, Carnegie Mellon, and Georgia Tech contribute significantly to robotic system innovation and deployment. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Department of Defense (DoD) are also among major public sector consumers of advanced robotics for agricultural automation and logistics streamlining, respectively.
Urban centers like Boston, Pittsburgh, and San Francisco are emerging as robotics innovation clusters. With a synergy of robotics startups, established tech firms, and accessible venture capital, the U.S. polyfunctional robot market is poised for sustained growth. Demand for robots that are task-flexible, mobile, and collaborative will continue to rise, reshaping workforce dynamics across critical sectors.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
The Europe Polyfunctional Robots Market
The Europe Polyfunctional Robots Market is estimated to be valued at USD 1.44 billion in 2025 and is further anticipated to reach USD 3.13 billion by 2034 at a CAGR of 9.0%.
Europe stands as a mature and strategically positioned market for polyfunctional robots, driven by a strong emphasis on industrial automation, sustainability goals, and labor efficiency. Countries like Germany, France, Italy, and Sweden are at the forefront of robotic adoption, particularly in manufacturing, automotive, and healthcare sectors. According to Eurostat, the EU labor force is gradually aging, with over 20% aged 65 and above, signaling a demographic trend that supports automation.
Germany’s industrial base, known for its high-precision engineering, is heavily investing in multipurpose robotic platforms for use in modular assembly lines and collaborative human-robot environments. In France and Italy, robots are increasingly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and surgical healthcare. The European Commission supports this trend via Horizon Europe funding and Digital Europe programmes, encouraging the integration of intelligent robotics in SMEs and startups.
Moreover, Europe’s regulatory framework, such as GDPR and ISO standards, ensures ethical and secure robot deployment. This boosts consumer and industrial trust in autonomous systems. Urban infrastructure projects across the EU are increasingly relying on robotics for smart construction, energy grid maintenance, and public service optimization.
Europe’s universities and technical institutes have world-class robotics research programs that feed talent into the region’s expanding robotic industry. Furthermore, cultural acceptance of automation and collaborative robots (cobots) makes it easier for companies to deploy polyfunctional robots in mixed human-robot workplaces. With sustainability, labor efficiency, and digitization as policy priorities, Europe is expected to remain a powerhouse in the polyfunctional robotics ecosystem in the years ahead.
The Japan Polyfunctional Robots Market
The Japan Polyfunctional Robots Market is projected to be valued at USD 38.0 million in 2025. It is further expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period, holding USD 1.06 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 12.0%.
Japan remains one of the most technologically advanced and robot-friendly nations globally, making it a key market for polyfunctional robots. With one of the fastest aging populations, nearly 29% of citizens are over 65, according to Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the demand for multifunctional automation is accelerating. Robotics is actively used to alleviate labor shortages in sectors ranging from elder care to logistics and precision agriculture.
The Japanese government’s “Society 5.0” initiative aims to merge cyber and physical systems, placing intelligent robotics at the heart of national development. Through public funding, policy incentives, and R&D support, multifunctional robots are being integrated into hospitals, smart factories, and rural agricultural zones. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) promotes adoption through innovation subsidies and robotics infrastructure investments.
Japanese manufacturers like FANUC, Yaskawa, and Kawasaki Heavy Industries lead in the design and global export of versatile robotic systems. These robots are designed not only for industrial use but also for human-interactive environments. In Tokyo and Osaka, service robots in hotels, airports, and malls are already part of everyday consumer interactions.
Japan’s cultural affinity toward technology acceptance plays a crucial role in enabling wider robotic integration. The education system emphasizes science, engineering, and AI skills, producing a future-ready workforce. Additionally, Japan’s disaster-prone geography encourages the use of robots in disaster response, infrastructure inspection, and utility repair. With innovation, demographic urgency, and cultural synergy all aligned, Japan is set to maintain leadership in the development and deployment of polyfunctional robotic systems.
Global Polyfunctional Robots Market: Key Takeaways
- Global Market Size Insights: The Global Polyfunctional Robots Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 9.6 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 27.6 billion by the end of 2034.
- The US Market Size Insights: The US Polyfunctional Robots Market is projected to be valued at USD 3.4 billion in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 9.3 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 11.7%.
- Regional Insights: North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market with a share of about 42.3% in 2025.
- Key Players: Some of the major key players in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market are ABB, FANUC, KUKA, Yaskawa, Mitsubishi Electric, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Denso, Nachi-Fujikoshi, Stäubli, Universal Robots, Comau, Omron, Epson Robots, Schunk, Festo, and many others.
- Global Market Growth Rate: The market is growing at a CAGR of 12.5 percent over the forecasted period of 2025.
Global Polyfunctional Robots Market: Use Cases
- Automotive Manufacturing: Polyfunctional robots in automotive plants perform simultaneous tasks like welding, component assembly, and inspection. They adapt in real time to production changes, improving output speed and reducing defects. These robots contribute to lean manufacturing by minimizing downtime and optimizing workflow across multiple vehicle models and product lines.
- Surgical and Medical Robotics: In modern hospitals, multi-purpose robots support surgeons during complex operations, sterilize equipment, and deliver medication. These systems enhance precision in minimally invasive surgeries while reducing human fatigue. With integrated AI, they adapt to patient-specific anatomy, assisting in diagnostics, post-operative care, and even robotic rehabilitation routines.
- Warehouse and Distribution Centers: Polyfunctional robots automate inventory picking, package sorting, and stock replenishment in large logistics hubs. They collaborate with human workers using sensor-based navigation and machine learning to improve last-mile delivery efficiency. These robots reduce operational errors and accelerate fulfillment rates for e-commerce and omnichannel retailing.
- Smart Agriculture Operations: Advanced agricultural robots carry out tasks such as soil analysis, crop spraying, seeding, and weed removal simultaneously. With embedded vision systems and GPS tracking, they monitor field health in real time, enabling data-driven decisions. These robots enhance crop yields, reduce manual labor dependency, and promote precision farming.
- Hospitality and Customer Service: Robots in the hospitality industry manage check-ins, room service, concierge tasks, and multilingual guest interactions. Equipped with facial recognition and natural language processing, they offer personalized experiences. By integrating with hotel management software, these robots reduce staff load and deliver round-the-clock service consistency.
Global Polyfunctional Robots Market: Stats & Facts
International Federation of Robotics (IFR)
- As of 2023, approximately 4.28 million operational industrial robots are functioning across global industries. This includes robots for assembly, welding, packaging, and handling tasks.
- The automotive sector remains the dominant consumer of industrial robots, accounting for nearly 30% of all global installations due to increasing automation in vehicle production lines.
- In 2018, China led the world in robot adoption, with over 154,000 industrial robots installed, highlighting the country’s ongoing manufacturing transformation.
- The United States recorded a shipment of 35,880 industrial robots in 2018, reflecting a 7% year-over-year growth, emphasizing growing interest in intelligent automation.
Stanford University Research on Robotics
- In 2021, China installed more than 268,000 industrial robots, the highest annual installation count worldwide, underscoring its manufacturing modernization.
- Japan was the second-largest installer with 47,200 units, followed by the United States with 35,000, South Korea with 31,100, and Germany with 23,800, illustrating strong adoption in developed economies.
- The United States leads the professional service robotics segment with 225 companies manufacturing robotic solutions for defense, healthcare, and logistics purposes.
National Science Foundation (NSF)
- According to NSF, only 28% of robotics professionals in the U.S. are women, reflecting a significant gender gap in STEM and the need for increased inclusivity in tech education and hiring pipelines.
U.S. Department of Defense (DoD)
- The U.S. Department of Defense allocated approximately $7.5 billion toward robotics and unmanned systems development in 2021, funding land, air, and sea-based robotic platforms used for surveillance, logistics, and combat support.
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- NASA increased its robotics R&D budget to $3 billion in 2024, with a focus on developing autonomous systems for Mars rovers, lunar landers, and AI-driven space maintenance technologies.
Pew Research Center
- In a national U.S. survey, 65% of respondents expressed optimism that robotics would significantly enhance quality of life in the next decade, supporting public confidence in assistive and smart robotic systems.
Food Robotics Association
- The robotics segment in food manufacturing is rapidly expanding, projected to reach $10 billion in value by 2025, driven by the need for precision cooking, hygienic handling, and labor cost reduction.
AARP Research on Elder Care Robotics
- Robotics aimed at elder care, such as companion bots, autonomous wheelchairs, and assistive medical systems, is forecast to grow into a $30 billion global market by 2026, helping countries manage aging populations.
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
- Robots used in disaster recovery and emergency search operations have shown a 90% success rate in locating survivors and assessing hazardous areas, offering vital support during floods, earthquakes, and fires.
EdTech Magazine Educational Insights
- Schools and colleges that incorporated robotics into their STEM curriculum reported a 40% increase in student engagement, suggesting robotics as a key driver for practical, interactive education across all levels.
Global Polyfunctional Robots Market: Market Dynamics
Driving Factors in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market
Labor Shortages and Rising Demand for Operational Efficiency
A major growth driver for the polyfunctional robots market is the global shortage of skilled labor and the rising need to optimize operational efficiency across industries. Aging populations, particularly in countries like Japan, Germany, and Italy, are resulting in a shrinking workforce. In parallel, younger generations are increasingly seeking knowledge-based or remote work, creating a talent gap in sectors that require physical labor, such as manufacturing, logistics, and construction. This demographic shift is compelling companies to automate multi-task operations with robots that can work tirelessly across shifts, maintain consistent quality, and adapt to variable workloads. In sectors like e-commerce fulfillment, polyfunctional robots that can sort, pick, pack, and move goods autonomously are helping firms meet surge demands without compromising accuracy.
Moreover, in precision-driven industries like semiconductor manufacturing or pharmaceuticals, multifunctional robots provide the repeatability and fine motor control that human workers often lack under pressure. The need for energy efficiency, reduction in overhead costs, and maximization of throughput further reinforces the rationale for robotic integration. Governments are also supporting automation as a strategic response to labor market pressures, offering subsidies and tax benefits to businesses investing in robotic technologies. As labor constraints tighten globally, the demand for intelligent, versatile, and scalable robotic solutions is poised to grow exponentially.
Government Initiatives and National Automation Roadmaps
Government-led initiatives and national automation strategies are significantly driving the adoption of polyfunctional robotic technologies. Across Asia, Europe, and North America, national policies are being crafted to support industrial digitization through public funding, regulatory reforms, and academic-industry collaboration. For example, Japan's “Society 5.0” strategy envisions a super-smart society where intelligent robotics and IoT form the foundation of economic development. Similarly, Germany's “Industrie 4.0” promotes smart factory ecosystems with modular robotics playing a central role. In the United States, initiatives like the Advanced Robotics for Manufacturing (ARM) Institute aim to democratize access to robotic automation by offering shared R&D infrastructure and workforce upskilling programs.
These policies not only incentivize businesses to invest in automation but also build national capabilities in AI, mechatronics, and robotics software development. Furthermore, these strategies are often accompanied by grants and pilot projects for integrating robotics into public services, including healthcare, elderly care, transportation, and emergency response. The EU has also included robotics in its Horizon Europe funding framework, encouraging cross-border research collaboration and ethical deployment of multifunctional robots. These structured roadmaps are helping reduce entry barriers, ensuring technology diffusion beyond large corporations to SMEs and public institutions. As policy-backed automation becomes integral to national competitiveness and digital sovereignty, polyfunctional robotics will see increased mainstream adoption.
Restraints in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market
High Cost of Integration and Technical Complexity
Despite the technological appeal, the high cost of deployment and complexity involved in integrating polyfunctional robots remain a major restraint for many organizations. The purchase of industrial-grade robots with AI and vision systems can run into hundreds of thousands of dollars, excluding software customization, staff training, and infrastructure upgrades. Moreover, multifunctional robots require tailored integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, factory execution software, or hospital information systems, which can be both time-consuming and capital-intensive. Small and medium-sized enterprises often lack in-house expertise in robotics engineering or automation strategy, which adds to the cost burden. The return on investment (ROI) may also not be immediate, especially when robots are used for low-throughput or highly variable tasks.
Furthermore, industries with legacy systems or analog operations face compatibility challenges. Even in large enterprises, transitioning from single-purpose automation to polyfunctional robotic ecosystems demands extensive planning, pilot testing, and change management. The lack of industry-specific plug-and-play robotic solutions exacerbates these issues. Until costs decline and integration becomes more seamless through interoperable APIs, adaptive interfaces, and modular hardware, many potential adopters may delay or avoid investing in polyfunctional robotic platforms.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Ethical Challenges
The regulatory landscape surrounding multifunctional robots is still evolving and presents a complex barrier to broader adoption. Most countries lack comprehensive standards for the safety, liability, and interoperability of polyfunctional robotic systems, especially those operating in shared human environments. For example, robots used in healthcare or public spaces must comply with strict data privacy and safety norms, yet many jurisdictions do not have robotic-specific regulations to address AI-based decision-making or sensor-based data collection. Additionally, the ethical use of robots, such as ensuring non-discriminatory behavior in service roles or preventing over-reliance on robotic care for vulnerable populations, remains a concern. In some regions, the use of autonomous robots in surveillance or defense raises human rights debates and legal scrutiny.
The absence of harmonized international frameworks also complicates cross-border trade and the deployment of robotic systems. Developers and manufacturers often face delays and uncertainty while navigating multiple certification and compliance processes. Moreover, public apprehension and labor union resistance can impede deployment, especially in sectors perceived as vulnerable to automation-related job displacement. Unless governments and global bodies create clear, enforceable, and adaptive robotic governance structures, regulatory ambiguity will continue to inhibit the speed and scale of polyfunctional robot implementation.
Opportunities in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market
Expansion into Service Robotics and Human-Centric Applications
The future of polyfunctional robots lies not just in industrial automation but in their expansion into human-centric services and consumer applications. While industrial robots have long dominated sectors like automotive and electronics, multifunctional service robots are gaining ground in healthcare, hospitality, retail, and home assistance. These robots are being designed to perform varied roles from patient monitoring, medication delivery, and elderly care to concierge services in hotels and autonomous checkout in stores. The growing demand for labor in high-touch, repetitive service roles, coupled with hygiene concerns in a post-pandemic world, is creating fertile ground for service robotics. As populations age globally, eldercare robots capable of lifting, assisting, and monitoring individuals are becoming increasingly critical. Additionally, AI-enhanced emotional intelligence is enabling these robots to engage in basic conversations, recognize human emotions, and personalize interactions.
As voice interfaces and natural language processing improve, multifunctional robots can assist differently abled individuals with household tasks, improving quality of life and independence. With greater affordability and modularity, such robots are also entering middle-income homes and public service areas. This expansion into non-industrial domains represents a massive untapped market, offering manufacturers and developers an opportunity to diversify beyond traditional applications and redefine the scope of robotic versatility in daily life.
Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) and Subscription-Based Deployment Models
One of the most transformative opportunities in the polyfunctional robots market is the emergence of the Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, which allows businesses to access robotic systems via subscription rather than through capital-intensive purchases. This model reduces financial barriers, especially for startups, SMEs, and public institutions that cannot afford upfront investment in advanced robotics. With RaaS, users pay for robot performance or usage time, and the provider handles maintenance, upgrades, and technical support. This approach makes robotic deployment agile, scalable, and less risky. The RaaS model is particularly gaining traction in logistics, retail, and healthcare, where operational demands fluctuate and technological adaptability is crucial. For instance, hospitals can deploy disinfection robots during disease outbreaks without long-term investment.
Similarly, retailers can use robotic stock managers during peak seasons. Additionally, RaaS platforms often come with data analytics dashboards, allowing users to optimize workflows and make data-driven decisions. The rise of cloud robotics, where control, storage, and intelligence are managed remotely, further enhances the feasibility of this model. Companies offering modular, polyfunctional robots that can be reprogrammed for various tasks under the same subscription have a competitive edge. As this pay-as-you-go structure aligns with enterprise digital transformation trends, RaaS will emerge as a major catalyst in accelerating the global adoption of multifunctional robotic platforms.
Trends in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market
Integration of AI and Edge Computing into Robotic Intelligence
A key trend in the polyfunctional robots market is the growing fusion of artificial intelligence (AI) with edge computing capabilities. Robots are no longer limited to performing static, pre-programmed tasks; instead, they are becoming cognitive systems capable of contextual awareness and real-time decision-making. Edge computing enables these robots to process massive volumes of data locally, minimizing latency, reducing reliance on cloud connectivity, and improving response times. For example, AI-powered vision systems now allow robots to identify objects, interpret human gestures, and assess environmental risks within milliseconds. This transformation is especially valuable in sectors like healthcare and defense, where speed and contextual understanding are critical.
Manufacturers are embedding GPUs and AI accelerators within robot control units to make them self-adaptive across various roles, from precision welding to autonomous delivery. This evolution is turning robots into multi-role assets that can learn from past interactions and continuously improve their performance. As machine learning models become lighter and more power-efficient, AI-infused edge robotics is expected to reshape industries, making robots flexible collaborators instead of rigid tools. The convergence of AI, computer vision, and edge inference is not only increasing robot autonomy but also enabling deployment in environments previously considered too complex for automation, such as construction sites, agricultural fields, and emergency zones.
Rise of Human-Robot Collaboration (Cobotics) in Mixed Environments
Another prominent trend in the polyfunctional robots market is the accelerated adoption of collaborative robots (cobots) across manufacturing, warehousing, and service industries. Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate within caged environments, cobots are designed to safely work alongside human operators without physical barriers. These robots are equipped with advanced sensors, real-time obstacle avoidance systems, and force-limiting actuators, allowing them to perform tasks that involve direct physical interaction with people. The emphasis is shifting from full automation to hybrid workspaces where robots enhance human capabilities rather than replace them.
This trend is particularly relevant for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that lack the scale or capital for large-scale automation but still seek productivity improvements. Cobots are increasingly being used in applications like precision assembly, quality inspection, machine tending, and even customer service in retail. Additionally, the integration of voice recognition, gesture control, and AI-based behavior prediction is making cobots more intuitive to use, reducing the need for expert programming. This human-centric robotic design is not only making workplaces safer and more efficient but is also expanding the reach of automation into sectors like education, hospitality, and eldercare. As regulatory frameworks evolve to accommodate collaborative robotics, this trend is set to become foundational in the next wave of industrial and service automation.
Global Polyfunctional Robots Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Type Analysis
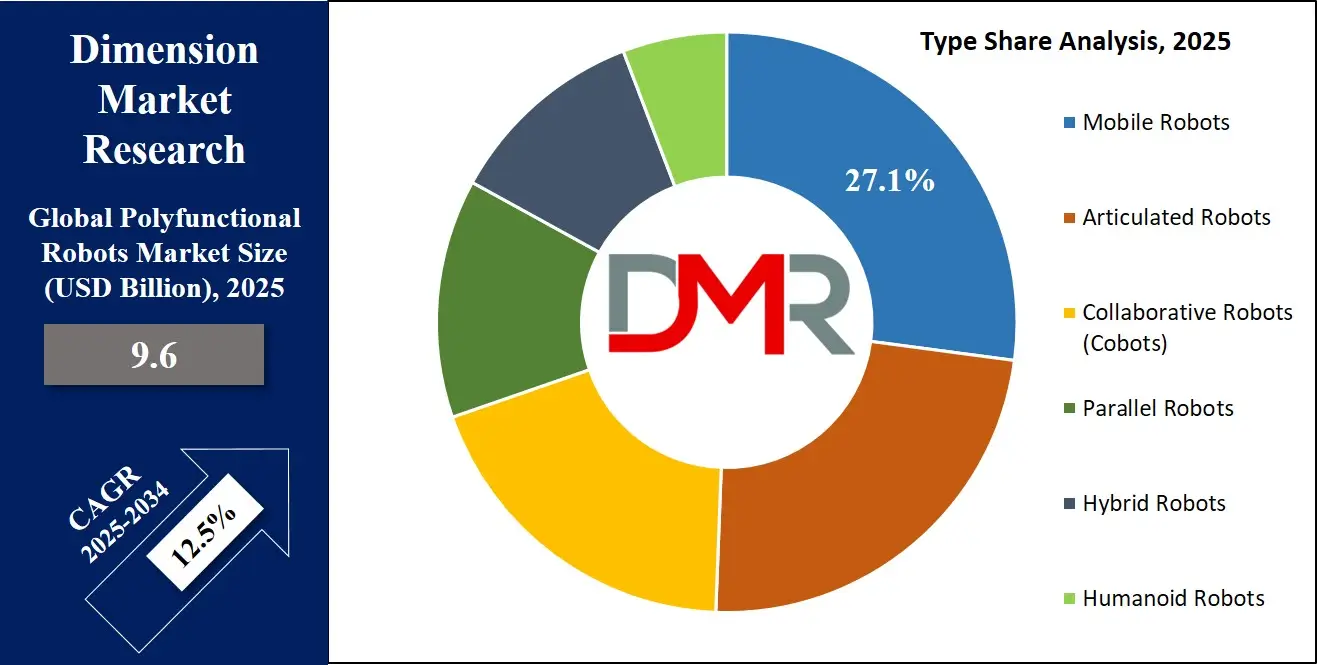
Mobile robots are projected to dominate the polyfunctional robots market due to their inherent versatility, autonomous mobility, and adaptability across dynamic environments. These robots are engineered to navigate physical space independently, enabling their deployment in large-scale warehouses, hospitals, construction sites, and agricultural fields where fixed-location robotics falls short. Their ability to operate untethered from static workstations allows organizations to automate repetitive, labor-intensive logistics and inspection tasks, boosting operational efficiency and flexibility.
In industries such as e-commerce, last-mile delivery, and manufacturing, mobile robots are used for real-time material handling, order picking, and intra-logistics without the need for human intervention. Advanced features such as simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), computer vision, and obstacle avoidance empower them to operate in human-populated environments safely. Additionally, mobile platforms can be outfitted with interchangeable payloads ranging from robotic arms to sensors, making them multi-role units adaptable for different workflows.
The growing demand for robotics in urban infrastructure, smart cities, and healthcare logistics further accelerates mobile robot adoption. For instance, autonomous disinfection robots in hospitals and surveillance units in airports and malls demonstrate their multifaceted applications. With continued advancements in wireless connectivity, battery technology, and AI-based route optimization, mobile robots offer a scalable and cost-effective alternative to fixed automation. Their ability to perform tasks across vast and unpredictable terrains while maintaining real-time coordination with centralized systems makes them indispensable in modern, flexible automation strategies, securing their dominance in the polyfunctional robots market.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
By Technology Analysis
AI and Machine Learning-enabled robots are expected to dominate the technology segment of the polyfunctional robots market due to their transformative ability to adapt, learn, and optimize performance in real time. Unlike rule-based or pre-programmed robots that perform fixed sequences, AI-driven systems dynamically respond to variables such as object changes, environmental noise, and user behavior. This makes them highly effective in unstructured and semi-structured environments where predictability is limited, such as manufacturing lines, disaster response zones, or hospital wards.
Machine learning empowers robots to identify objects, interpret sensory inputs, and enhance decision-making over time, significantly improving task accuracy and efficiency. In manufacturing, AI-enhanced robots can detect product defects autonomously; in healthcare, they can analyze patient behaviors for personalized care; in logistics, they can optimize pathfinding based on traffic and bottlenecks. AI also enables predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by analyzing internal system data and forecasting failures before they occur.
Additionally, AI integration supports natural language processing, facial recognition, and gesture tracking, making human-robot collaboration more intuitive. This is crucial for service robots, collaborative arms (cobots), and humanoid assistants. With ongoing advancements in edge AI, robots can now process complex algorithms locally, reducing latency and enhancing real-time responsiveness. These capabilities are not just performance boosters, they redefine the scope of robotic functionality.
As industries push toward smart automation and contextual adaptability, AI-powered robots become indispensable for scaling operations, improving safety, and ensuring higher return on investment. Their self-learning capabilities make them future-proof assets, securing their leadership position in the evolving polyfunctional robotic landscape.
By Application Analysis
Manufacturing is poised to dominate the application segment of the polyfunctional robots market due to its longstanding integration with automation, large-scale operational needs, and demand for precision, scalability, and productivity. The sector was the earliest and most consistent adopter of robotic systems, initially using them for welding, painting, and assembly. However, the advent of polyfunctional robots has transformed traditional automation into a dynamic, intelligent ecosystem capable of multitasking and decision-making in real time.
Manufacturers now deploy robots that not only assemble but also inspect, sort, package, and transport goods autonomously, reducing cycle times and error rates. These robots operate 24/7, ensuring continuity in production lines and mitigating the impact of labor shortages. The ability to reprogram polyfunctional robots for different tasks adds flexibility, particularly valuable in industries like automotive and electronics, where product variants are frequent and speed-to-market is critical.
Moreover, the incorporation of AI, vision systems, and force sensors has expanded robotic utility in delicate and complex assembly operations. Predictive maintenance algorithms also ensure reduced downtime and better machine utilization. The integration of cobots further enhances productivity by enabling seamless human-machine collaboration, especially in tasks requiring dexterity and cognitive input.
Governments and industries are heavily investing in “smart factory” initiatives, where IoT-enabled robots form the digital backbone of Industry 4.0. These trends, combined with cost reduction, rising competition, and the need for customization, are compelling manufacturers to upgrade to polyfunctional robotic systems. As the linchpin of global supply chains, the manufacturing sector continues to drive demand, innovation, and large-scale deployment of multifunctional robots.
The Global Polyfunctional Robots Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following:
By Type
- Mobile Robots
- Articulated Robots
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
- Parallel Robots
- Hybrid Robots
- Humanoid Robots
By Technology
- AI & Machine Learning-enabled Robots
- IoT-connected Robots
- Autonomous Navigation Robots
- Vision-guided Robots
By Application
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Heavy Machinery
- Surgical Robots
- Rehabilitation Robots
- E-Commerce
- Supply Chain Automation
- Harvesting
- Seeding
- Drones
- Service Robots
- Cleaning Robots
- Inspection In Oil & Gas
- Power Plants
- 3D Printing
- Bricklaying Robots
Global Polyfunctional Robots Market: Regional Analysis
Region with the Largest Revenue Share
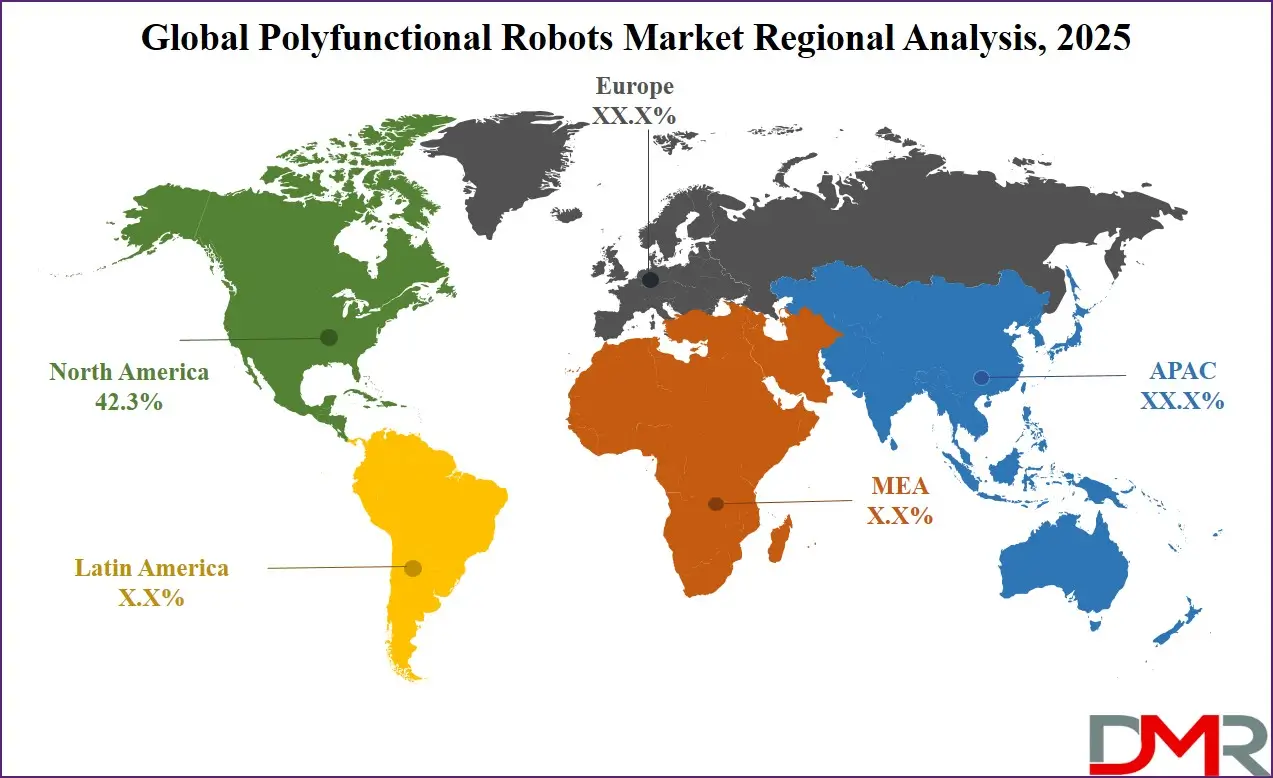
North America is expected to lead the polyfunctional robots market as it holds 42.3% of the total market revenue by the end of 2025, due to its robust industrial automation infrastructure, strong innovation ecosystem, and consistent investments in advanced robotics across critical sectors. The U.S. boasts a highly developed manufacturing base that aggressively integrates AI-powered and collaborative robotic systems for precision machining, logistics, and quality control. Additionally, the presence of leading robotics companies such as Boston Dynamics, iRobot, and Teradyne drives the commercialization of cutting-edge polyfunctional robotic platforms tailored to diverse applications, including defense, healthcare, and warehousing.
The region’s dominance is further supported by federal funding initiatives, such as the Advanced Robotics for Manufacturing (ARM) Institute and National Robotics Initiative (NRI), which promote public-private R&D collaboration. Moreover, the widespread use of mobile and AI-enabled robots in e-commerce fulfillment centers, especially by tech giants like Amazon, exemplifies practical adoption at scale. High labor costs and aging workforce challenges across Canada and the U.S. also push industries toward robotics adoption to maintain competitiveness. With a mature regulatory environment, high digital readiness, and extensive use of automation in both private and public sectors, North America remains the most influential contributor to global polyfunctional robot revenues.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Region with the Highest CAGR
Asia Pacific is projected to register the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the polyfunctional robots market, driven by rapid industrialization, strong government support, and aggressive automation efforts, especially in countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India. China, the world’s largest manufacturing hub, is accelerating its robotics adoption through its “Made in China 2025” plan, aiming to localize advanced robot production and reduce dependence on foreign automation technologies.
Japan and South Korea, with their aging populations and shrinking labor pools, are embracing multifunctional robots in healthcare, agriculture, and domestic applications. Japan’s “Society 5.0” vision further fosters AI and robotics integration into everyday life. In Southeast Asia and India, rising wages and skill shortages are prompting small and mid-sized enterprises to adopt modular robotic solutions. The region’s booming e-commerce and electronics sectors, coupled with ongoing smart city and infrastructure projects, also provide fertile ground for mobile and AI-enabled robotic systems. This multi-industry demand and supportive policy environment position Asia Pacific as the fastest-growing region for polyfunctional robots.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Global Polyfunctional Robots Market: Competitive Landscape
The polyfunctional robots market is characterized by intense innovation and a growing number of global and regional players focusing on cross-industry applications, modularity, and intelligence. Key companies such as ABB, FANUC, KUKA, Yaskawa Electric, and Mitsubishi Electric dominate the industrial robotics space with extensive portfolios of articulated, mobile, and collaborative robots integrated with advanced vision systems and AI algorithms. These firms continuously invest in R&D to enhance robot flexibility, autonomy, and multi-tasking capabilities, targeting high-growth sectors like electronics, automotive, and healthcare.
In the service and mobile robotics domain, companies such as Boston Dynamics, iRobot, and Mobile Industrial Robots (MiR) lead with innovations in humanoid robots, logistics automation, and autonomous navigation platforms. Startups and mid-tier players like Locus Robotics, Fetch Robotics, and PAL Robotics are rapidly gaining traction by offering Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) models and modular systems that enable fast deployment and scalability.
Strategic partnerships, acquisitions, and regional expansions are common tactics, allowing companies to access new verticals and geographies. Moreover, increased collaboration between robotics firms and cloud providers (like AWS and Microsoft Azure) is accelerating the shift toward cloud-connected, AI-optimized robots. The competitive landscape is evolving swiftly, with players racing to offer versatile, intelligent, and cost-efficient robotic solutions.
Some of the prominent players in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market are:
- ABB Ltd.
- FANUC Corporation
- KUKA AG
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Denso Corporation
- Nachi-Fujikoshi Corp.
- Stäubli International AG
- Universal Robots A/S
- Comau S.p.A.
- Omron Corporation
- Epson Robots
- Schunk GmbH & Co. KG
- Festo AG & Co. KG
- Harmonic Drive Systems Inc.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Boston Dynamics
- Doosan Robotics
- Siasun Robot & Automation Co., Ltd
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market
November 2024
- Robotics and Automation Innovation Lab Launch: Tata Elxsi, DENSO, and AAtek inaugurated the Robotics and Automation Innovation Lab in Frankfurt. The alliance aims to advance robotics automation across healthcare sectors by leveraging Tata Elxsi's med-tech expertise, DENSO's robotic technology, and AAtek's integration capabilities.
April 2024
- Collaborative Robotics Funding: Collaborative Robotics secured USD 100 million in Series B funding to develop AI-driven collaborative robots (cobots) for industries such as manufacturing and healthcare. The investment aims to enhance AI capabilities and expand cobot deployment, addressing labor shortages and improving supply chain efficiency.
February 2024
- ABB and METTLER TOLEDO Collaboration: ABB Robotics partnered with METTLER TOLEDO to integrate ABB's robots with METTLER TOLEDO's LabX software. This collaboration enhances lab automation, improves workflow precision, and supports data integration in pharmaceutical, food, and academic laboratories.
November 2023
- TECHMAN ROBOT's TM AI Cobot TM25S Launch: TECHMAN ROBOT INC. introduced the TM AI Cobot TM25S at iREX 2023. It features a 25kg payload capacity and integrates with NVIDIA's Isaac Sim platform, reducing programming time by 70% and cycle times by 20% on production lines.
June 2023
- Universal Robots and SICK AG Collaboration: Universal Robots and SICK AG developed a new safety system for collaborative applications. This solution uses safety-certified 3D time-of-flight cameras to ensure safe human-robot interaction and quick deployment in industrial settings.
March 2023
- LG Uplus and Bigwave Robotics Partnership: LG Uplus signed an MoU with Bigwave Robotics to enhance robot automation platforms. The partnership focuses on expanding smart factory capabilities and AI integration within industrial robot deployments.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 9.6 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 27.6 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
12.5% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 3.4 Bn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Type (Mobile Robots, Articulated Robots, Collaborative Robots (Cobots), Parallel Robots, Hybrid Robots, Humanoid Robots), By Technology (AI & Machine Learning-enabled Robots, IoT-connected Robots, Autonomous Navigation Robots, Vision-guided Robots), By Application (Manufacturing, Healthcare, Logistics & Warehousing, Agriculture, Aerospace & Defense, Retail & Hospitality, Energy & Utilities, Construction) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – US, Canada;
Europe – Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, Rest of Europe;
Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC;
Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America;
Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, Rest of MEA
|
| Prominent Players |
ABB, FANUC, KUKA, Yaskawa, Mitsubishi Electric, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Denso, Nachi-Fujikoshi, Stäubli, Universal Robots, Comau, Omron, Epson Robots, Schunk, Festo, Harmonic Drive, Rockwell Automation, Boston Dynamics, Doosan Robotics, Siasun Robot & Automation, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user),
Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and
Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to
0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively.
|
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market?
▾ The Global Polyfunctional Robots Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 9.6 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 27.6 billion by the end of 2034.
What is the size of the US Polyfunctional Robots Market?
▾ The US Polyfunctional Robots Market is projected to be valued at USD 3.4 billion in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 9.3 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 11.7%.
Which region accounted for the largest Global Polyfunctional Robots Market?
▾ North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market, with a share of about 42.3% in 2025.
Who are the key players in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market?
▾ Some of the major key players in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market are ABB, FANUC, KUKA, Yaskawa, Mitsubishi Electric, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Denso, Nachi-Fujikoshi, Stäubli, Universal Robots, Comau, Omron, Epson Robots, Schunk, Festo, and many others.
What is the growth rate in the Global Polyfunctional Robots Market in 2025?
▾ The market is growing at a CAGR of 12.5 percent over the forecasted period of 2025.