Market Overview
The
South Korea Warehouse Automation Market size is expected to reach a
value of USD 4,137.8 million in 2024, and it is further anticipated to reach a market
value of USD 14,024.2 million by 2033 at a
CAGR of 14.5%.
The growth of the South Korean warehouse automation market has been rapid, owing to increasingly widespread applications of advanced technologies applied in industries. Expansion of this market is growing as companies pursue efficient warehouses, less dependency on labor, and supply chain operations. Geographically, South Korea is a regional logistics hub, and this has rendered it an ideal market wherein one can strategically set up automation investments that target both domestic and international trade.
This growing demand is especially evident in retail, e-commerce, and manufacturing sectors, where the race for speed regarding order fulfillment and improving inventory accuracy is critical. Warehouse automation in South Korea incorporates a variety of technologies, such as automated storage and retrieval systems, collaborative mobile robots, robotics, conveyor systems, and warehouse management systems (WMS).
These technologies empower optimization in warehouse operations for better picking accuracy, reduction of human errors, and overall productivity. The labor shortage in the South Korean Market specifically, in logistics a crucial factor driving the adoption of automation solutions as businesses look to mitigate rising labor costs and challenges presented by a limited workforce.
The leading companies in this industry include Hyundai Movex, Locus Robotics Korea, SFA Corporation, and Hik Robotics, among others, representing a wide array of automation solutions to meet diverse business needs in South Korea. The market prospect is excellent because very solid growth can be expected over the next few years, whereby companies are sure to turn to further automation technologies to increase their competitive advantage.
Key Takeaways
- Market Value: The South Korean warehouse automation market size is estimated to have a value of USD 4,137.8 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 14,024.2 million by the end of 2033.
- By Component Segment Analysis: Hardware is anticipated to lead the components segment of this market as it will hold 43.7% of the market share in 2024.
- By Automation Level Segment Analysis: Warehouse system automation is expected to lead the automation level segment in this market with the highest market share in 2024
- By Application Segment Analysis: Retail and e-commerce are projected to be the dominant application segments in this market as they hold 39.0% of market share in 2024.
- Key Players: Some of the major key players in the South Korea warehouse automation market are CJ Logistics, Hanjin Transportation, LG CNS, Korea Express, Hanjin Shipping, STX Logistics, Hyundai Glovis, and many others.
- Growth Rate: The market is growing at a CAGR of 14.5 percent over the forecasted period.
Use Cases
- E-commerce Fulfillment Centers: In South Korea, automated systems, such as robotics and conveyor systems, support people in managing a high order volume with speed and accuracy, efficiently running fulfillment operations.
- Cold Storage and Perishable Goods: Due to the growing demand for online food delivery, along with cold storage facilities, automated warehouse technologies such as automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) provide the perfect conditions for perishable items to maintain the three key benefits of accuracy, speed, and spoilage prevention.
- 3PL Warehousing: Third-party logistics (3PL) providers in South Korea are investing more in automation technologies so as to extend their value proposition. On the list are WMS systems, together with collaborative mobile robots, which will be used to optimize order accuracy, productivity, and other key performance indicators for a dedicated client operation.
- Automotive Manufacturing Supply Chains: The automotive sector will benefit by automating warehouses and ensuring inventory management, thereby making the parts just-in-time available at production, reducing a lot of downtime, hence enhancing efficiency.
Market Dynamic
Trends
AI and Robotics IntegrationArtificial intelligence and robotics play an increasingly large role in being the catalyst for change in South Korea's Warehouse Automation Market. These smart systems replace human labor, optimizing all other operations of the warehouse by increasing their precision, speed, and flexibility. It is collaborative robots or cobots that have come into demand, allowing human workers to work with machines and thereby enhancing efficiency regarding processes such as picking, sorting, and packing.
Moreover, AI-driven automation systems help reduce downtime by predicting maintenance needs, consequently improving productivity and allowing seamless operations in the warehouse. With more South Korean businesses focusing on digital transformation, the integration of AI and robotics will keep dominating warehouse innovation.
Rise of E-commerce Fulfillment Centers
An explosive growth in e-commerce in South Korea is changing the face of warehousing. Full-fledged automation characterizes Fulfillment Centers these days, as they were designed to handle a high volume, rapid turnover of orders courtesy of e-commerce, to meet the increasing consumer demand for fast delivery. Technologies such as AS/RS, conveyor belts, and mobile robots have become a part of such warehouses, as boost accuracy and reduce the processing times of an order.
This was further accelerated by the growth of online food delivery services and omnichannel retail, paving the way for technology-enabled warehouses to spread all over the country. This trend will most likely continue to be driven by e-commerce growth in the next few years.
Growth Drivers
Labor Shortages
The main driving forces for the rapid diffusion of warehouse automation technologies in the South Korean economy largely emanate from the current labor shortage, primarily in supply chain logistics and warehousing businesses. The South Korean workforce is dwindling due to an aging population and dwindling interest in low-skilled manual labor jobs, hence the need for firms to resort to automated ways of bridging this gap.
In addition, it includes robotics, conveyor systems, and automated guided vehicles that reduce dependence on human labor and enable the business to sustain levels of productivity during the shortage. Secondly, automation systems are crucial in improving accuracy and efficiency in warehouse operations, thereby compensating for the shortage of skilled workers.
Government Support and Initiatives
The South Korean government has decided that warehouse automation is crucial for the development of the country's global competitiveness. Thus, the government has provided favorable conditions in its policies, reformed regulatory environments, and offered tax incentives to stimulate the use of automation technologies. Consequently, all these measures attract investments in warehouse automation among local small and medium-sized enterprises that are keen on scaling up operations.
Government-backed programs also try to develop skilled labor in the field of robotics and automation, hence ensuring that a sustainable workforce is available to operate and maintain these systems. Such support accelerates growth in the South Korean warehouse automation market.
Growth Opportunities
Cold Storage Automation
With increasing demand for online grocery shopping and food delivery services, South Korea also saw its need for efficient cold storage logistics grow. Regarding cold storage warehouses, investments in automation technologies have increasingly been made to control the temperature at all times, enhance storage, and minimize the chances of spoiled goods. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), temperature-sensitive robotics, and AI-powered inventory management systems are now critical in cold storage operations.
This has been one of the most significant growth areas for warehouse automation providers as businesses compete in an atmosphere of increased demand for cold chain logistics.
AI and Machine Learning Adoption
AI and machine learning are unlocking newer growth avenues in the South Korean warehouse automation market. These allow for advanced predictive analytics that enables better demand forecasting, optimization of inventory levels, and waste reduction. Machine learning algorithms analyze patterns in warehouse operations and allow better decision-making processes that will help businesses smoothen their workflows.
The increasing use of AI in WMS allows businesses to handle multi-channel supply chains that are increasingly complex. As more and more companies from South Korea consider these newer technologies, the demand for deploying AI and machine learning-based automation solutions will continue to rise, adding so much operational efficiency and scalability.
Restraints
High Initial Costs
While warehouse automation yields certain gains in terms of productivity and cost efficiency for a long period, high initial capital costs of investment in these technologies keep the pace of the adoption of warehouse automation at a slow pace, particularly among SMEs in South Korea. Advanced automation installations involving robotics, conveyor belts, and AI-driven solutions are pretty capital-intensive which act as a major restraint.
Besides this, the cost of their maintenance opting for higher expenses probably creates certain financial burdens on businesses with restricted budgets. Due to this fact, several SMEs might not be able to go for full-scale warehouse automation solutions, which again acts as a hindrance to the overall growth of the market.
Technological Complexity and Integration Issues
This is an integration problem that could involve various automation technologies being combined into one within existing warehouse operations. Most companies in South Korea have to face the utmost challenging task of harmonizing such systems, WMS, and automated storage systems into one efficient workflow. Besides, the shortage of technical expertise and skilled labor required for the handling and operation of those systems presents an even greater difficulty.
Besides, the fact that many different automation technologies are incompatible with each other, let alone the inclusion of legacy systems, might make some automation processes more complex and delay the process or add more costs. These challenges might be holding many companies back from large-scale warehouse automation.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Component
Hardware is projected to dominate the components segment of the South Korean warehouse automation market as it holds 43.7% of the market share by the end of 2024.
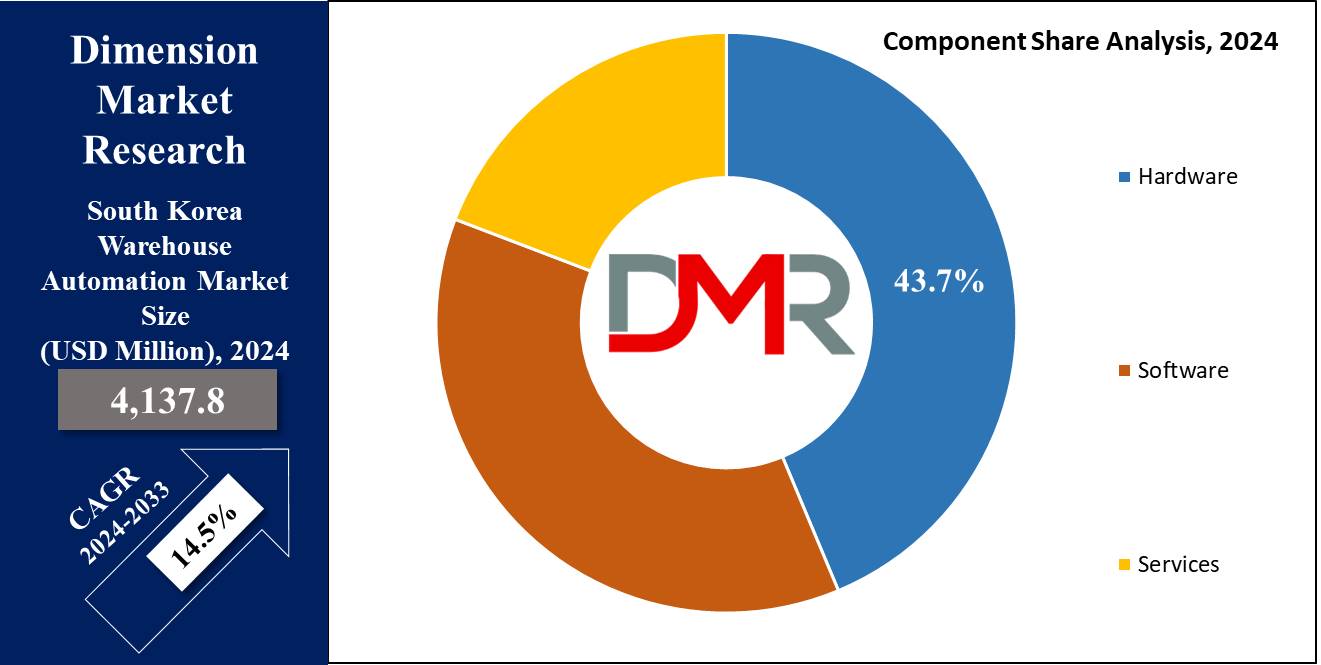
Hardware components dominate the South Korean warehouse automation market because they are the physical backbone of automated systems used in warehousing operations. Robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), conveyor belts, sorting systems, and mobile robots are some necessary hardware components of a warehouse automation system for automating processes related to picking, sorting, and transportation of goods within a warehouse.
While South Korea has to bear up against labor shortages and increasing labor costs for businesses, such automation systems contribute ever increasingly to minimizing human intervention and increasing efficiency in operations. The emphasis of the South Korean warehouse automation market on hardware solutions drives the need to focus on inefficiency in traditional warehouse operations. Robotics and other hardware technologies can perform repetitive tasks such as order picking, packing, and palletizing with greater speed and accuracy than human workers.
They minimize the risk of errors, and the variability in performance, and thus promote overall productivity. In this respect, commonplace warehouses in South Korea, especially those serving industries dealing in e-commerce and 3PL, have opted for huge investments to keep up with the increasing demand for faster and better logistics services.
Also, development in robotics and sensor technologies pushes innovation within the hardware segment by offering greater flexibility and functionality for better performance of warehouse automation systems. While becoming more intelligent, these are integrated with AI and machine learning to adapt to various operational requirements. For example, collaborative robots (cobots) can work together with human co-workers on complex tasks, offering a much more flexible and scalable automation alternative. As automation demands in warehouses continue to surge, the market size of hardware components in South Korea is likely to grow at a steady pace.
By Automation Level
The South Korean warehouse automation market is led by warehouse system automation in the automation level segment with the highest market share in 2024 since it offers a holistic and integrated solution to the whole spectrum of warehouse operations. This is because system automation embodies the integration of several technologies, such as robotics, WMS, AS/RS, and AI-driven decision-making tools, ensuring a well-integrated and efficient running of a warehouse.
It helps organizations master complex logistics processes more effortlessly, right from the receipting stages to order picking and shipment. The leading position of system automation in the warehouse automation market in South Korea may largely be explained by the country's rapidly changing logistics landscape, raising an increasing demand for higher speed, accuracy, and flexibility of operations. E-commerce giants, 3PL providers, and manufacturing companies require end-to-end automation solutions to handle increased complexity in their supply chains.
System automation provides capabilities for optimization in every stage of warehouse operations to reduce bottlenecks, improve productivity, and minimize human error. In addition, labor shortages and increases in labor costs are the significant issues that draw South Korean companies' keen interest in system automation. Fully automated warehouse processes can reduce human labor involvement, allowing a business to scale up its operations without dependence on large workforces.
That is of particular interest to industries such as e-commerce and retail, which strongly depend on the speed and effective processing of enormous volumes of orders. The integration of AI and machine learning into the automation of warehouse systems only adds to its attractiveness, since such technologies can make their mark in decision-making processes, enhancing efficiency at every level. It thus follows that system automation is gradually becoming the option of choice in companies that seek to futureproof their warehouse operations in South Korea.
By Application
Retail and e-commerce are projected to be the dominant application segments in the South Korean warehouse automation market as they hold 39.0% of market share in 2024. With the rapid growth of online shopping and the need for fast, accurate, and efficient logistics solutions, the retail and e-commerce industry dominate the warehouse automation market in South Korea.
South Korea has one of the highest rates of e-commerce penetration globally, with companies like Coupang, Naver Shopping, and Gmarket driving the market growth. With increasing demands from consumers for faster delivery times and smoother shopping experiences, a lot of investment is being eyed by retailers and e-commerce players in various warehouse automation technologies to meet such demands. These are being optimized by the usage of automated storage and retrieval systems, robotics, conveyor belts, and WMS, which together ensure faster and more accurate order picking, packing, and shipping.
It is not only that better operational efficiency can be obtained by automation of processes but also easier to manage these high volumes of SKUs (stock-keeping units) that retail and e-commerce companies must handle. This is particularly important with regard to e-commerce, as larger volumes of stock and regular ordering can give way to considerable logistical complications. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated this shift toward online shopping, hence increasing the demand for automation in warehouses serving the retail and e-commerce sectors.
Today, companies are emphasizing the adoption of progressive automation solutions for improved supply chain resiliency to reduce human interventions and allow timely delivery of products. As a result, the application segment for retail and e-commerce will most probably lead in the South Korean warehouse automation market, since companies will continue investing first in technologies that give them the best chance to outcompete their rivals and respond to shifting consumer demands.
The South Korea Warehouse Automation Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Component
- Hardware
- Autonomous Robots (AGV, AMR)
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
- Automated Sorting Systems
- De-Palletizing/Palletizing Systems
- Conveyor Systems
- Automatic Identification and Data Collection (AIDC)
- Software
- Warehouse Management System (WMS)
- Entry Function
- Location Function
- Stock Control Function
- Warehouse Execution Systems (WES)
- Labor Management Systems (LMS)
- Services
- Analytics and Reporting Tools
- Consulting, Training & Education
- Installation And Integration
- Maintenance And Support
By Automation Level
- Basic Warehouse Automation
- Warehouse System Automation
- Mechanized & Advanced Warehouse Automation
By Application
- Retail & E-commerce
- Healthcare
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Electronics & Semiconductors
- Other Application
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in the warehouse automation market of South Korea reflects both domestic and global players that are competing with one another in a bid to offer higher automation solutions as the demand for efficiency in warehouse operations gains momentum. Large companies such as Hyundai Movex, SFA Corporation, and Locus Robotics Korea stand ahead of the competition by offering a wide range of automation technologies, including robotics, warehouse management systems, and AI-driven inventory management tools.
International players such as Hik Robotics and AutoStore System Ltd also have a strong presence in the market, helping push the growth of the use of automation technologies at a high rate. The solutions proposed by these companies are innovative, thus helping South Korean businesses resolve labor shortages, achieve high accuracy in the processing of orders, and manage warehouse operations efficiently.
Apart from large organizations, several small firms like Mujin and Ocado Retail are also growing well in driving innovative transformations in automation. They focus on solutions for niche areas, including collaborative mobile robots and AI-driven decision-making tools, which will further enhance flexibility and efficiency in managing warehouses. The market is foreseen to be immensely competitive, with domestic and international players innovating and expanding their product portfolios.
The competitive landscape of the South Korean warehouse automation market will be driven by strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions.
Some of the prominent players in the South Korea Warehouse Automation Market are
- CJ Logistics
- Hanjin Transportation
- LG CNS
- Korea Express
- Hanjin Shipping
- STX Logistics
- Hyundai Glovis
- DB Schenker Korea
- Samsung SDS
- GS Global
- Kwangmyung Logistics
- DSV Panalpina
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- October 2024: Locus Robotics Expands Operations in South Korea
- Locus Robotics deployed collaborative mobile robots in a major South Korean 3PL warehouse, improving order picking, inventory management, and efficiency to meet the growing demand for warehouse automation, especially in e-commerce.
- September 2024: Hyundai Movex Launches Advanced AI-Powered Warehouse Management System (WMS)
- Hyundai Movex introduced an AI-powered WMS to optimize inventory management, automate decision-making, and reduce costs, primarily targeting the e-commerce sector's demand for accurate and fast order fulfillment.
- August 2024: SFA Corporation Partners with AutoStore System Ltd.
- SFA Corporation partnered with AutoStore to integrate compact, modular automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) in South Korean warehouses, enhancing storage capacity and operational efficiency in the retail and e-commerce sectors.
- July 2024: Hik Robotics Introduces AI-Driven Cold Storage Robotics
- Hik Robotics launched AI-powered robotic systems for cold storage, addressing the growing demand for temperature-controlled logistics, particularly in online grocery and food delivery, improving safety, inventory control, and energy efficiency.
- June 2024: Mujin Deploys AI-Based Collaborative Robots
- Mujin deployed AI-powered collaborative robots in South Korean warehouses, handling complex tasks like palletizing and picking, improving operational flexibility, and reducing human labor reliance, especially addressing labor shortages.
- May 2024: Ocado Retail Expands with New Fulfillment Center Technologies
- Ocado partnered with a South Korean e-commerce platform, introducing its robotic fulfillment systems to optimize order picking and packing processes, transforming the grocery delivery market with faster, more accurate deliveries.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2024) |
USD 4,137.8 Mn |
| Forecast Value (2033) |
USD 14,024.2 Mn |
| CAGR (2024-2033) |
14.5% |
| Historical Data |
2018 – 2023 |
| Forecast Data |
2024 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Estimate Year |
2024 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors and etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Component (Hardware, Software, and Services), By Automation Level (Basic Warehouse Automation, Warehouse System Automation, and Mechanized & Advanced Warehouse Automation), By Application (Retail & E-commerce, Healthcare, Automotive, Aerospace & Defense, Electronics & Semiconductors, and Other Application) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – The US and Canada; Europe – Germany, The UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Europe; Asia- Pacific– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, & Rest of MEA
|
| Prominent Players |
CJ Logistics, Hanjin Transportation, LG CNS, Korea Express, Hanjin Shipping, STX Logistics, Hyundai Glovis, DB Schenker Korea, Samsung SDS, GS Global, Kwangmyung Logistics, DSV Panalpina, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The South Korea Warehouse Automation Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 4,137.8 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 14,024.2 million by the end of 2033.
Some of the major key players in the South Korea Warehouse Automation Market are CJ Logistics, Hanjin Transportation, LG CNS, Korea Express, Hanjin Shipping, STX Logistics, Hyundai Glovis, and many others.
The market is growing at a CAGR of 14.5 percent over the forecasted period.