Market Overview
The Global
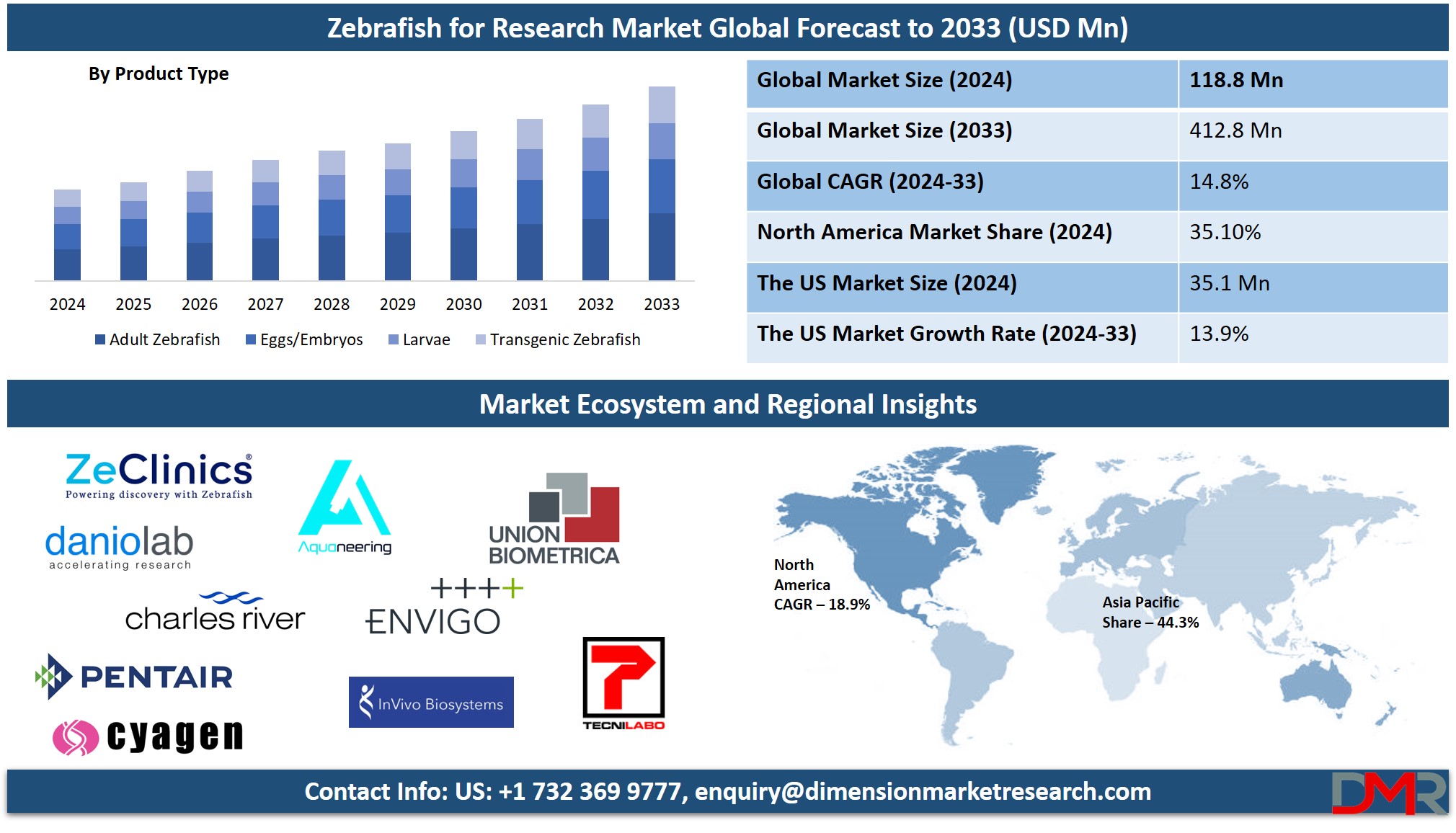
Zebrafish for Research Market size is expected to reach a
value of USD 118.8 million in 2024, and it is further anticipated to reach a market
value of USD 412.8 million by 2033 at a
CAGR of 14.8%.
The global market for zebrafish used in research is gaining phenomenal momentum, with increasing influences brought about by the emergence of the zebrafish as a model organism across a wide array of research fields. Zebrafish are particularly preferred in genetics studies, developmental biology studies, drug discovery studies, and toxicity testing studies, considering the animal's high genetic similarities to humans, its high reproductive rate, and transparent embryos that are advantageously conducive to observational studies.
Transgenic zebrafish lines have been somewhat common in recent years due to the advancement in genetic engineering for the understanding of disease mechanisms in humans and their ways of treatment. The major regional contributors are North America and Europe because of the high activities of research and development and the availability of advanced facilities in laboratories. Much as emerging biotechnological advancements are considered, expanding research activities and investments will make the Asia-Pacific region emerge as dominant in the forecast period.
Major players like Shanghai Model Organisms Center, ZeClinics, and InVivo Biosystems are focused on product innovation and market development activities that are crucial to the zebrafish for research market report of 2024. This report segments the market, based on product type and application, into minute fragments to give every possible detailed understanding of the growth levers and market dynamics. With research investments on the increase along with the growing diversification of biotechnological applications, the market size of zebrafish for research is expected to surge and offer new opportunities in disease modeling, genetic studies, and drug efficacy testing.
The zebrafish research market has a host of potential opportunities, with steady governmental funding, regulations, and investment in biomedical research that mounts specifically in the Asia Pacific region, which is expected to propel this market. In addition, zebrafish are increasingly becoming useful models in environmental monitoring, particularly in the area of water pollution, an avenue for extension beyond the traditional biomedical research avenues. Zebrafish demand is anticipated to rise in the coming years in different disciplines concerning toxicity and pollutants as stringent environmental laws are enforced worldwide, thereby presenting new channels of opportunity within academia, government, and industries.
Key trends that shape the landscape of the zebrafish research market include the adoption of CRISPR and the increased use of high-throughput screening techniques. Gene-editing tools allow the scientific modeling of human disease genes in zebrafish, making them highly useful in
drug discovery and disease modeling. Aided by automation, high-throughput screening has greatly increased the rapid screening of drug candidates, facilitating accelerated preclinical testing processes. These trends are expected to make the models of zebrafish increasingly relevant for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, as their focus shifts toward resource-efficient and innovative research.
Besides the host of advantages, the zebrafish market is also facing numerous challenges brought about by technical limitations and competition from alternative models. Human physiology with extreme complexities can't be fully emulated by zebrafish, and this greatly limits the advanced use of this animal in therapeutic studies. Examples of emerging models include 3D organoids and computational simulations, each bearing high specificities in the modeling of human diseases. Moreover, the standardization of protocols among different laboratories is still a problem; this further influences the reproducibility of large-scale studies and hence limits, in general, zebrafish applications in specific regulatory settings.
Some of the strengths of using zebrafish as models include that they are cost-effective, reproducing prolifically, have high genetic homology to humans, are largely considerate in preclinical and toxicological studies; are easy to breed, require small spaces, while their embryos provide transparency, thus permitting observation of biochemical events in real-time. Moreover, ethical restrictions are lesser with zebrafish compared to mammals, and that goes with the growing trend globally for more ethical consideration in research. This makes them a preferred choice in many regulatory environments since early-stage research is easy to conduct.
The global zebrafish for research market report offers a comprehensive scope of the report, providing an in-depth analysis of the market size and development potential as well as future growth rate projections through the forecast period. This 2024 report includes a detailed analysis of market segments, including service type breakdowns and market competitive landscape insights featuring key players such as Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services, Ikan Biotech, Biobide, Pentagrit, and Evotec. Additionally, the report examines quantitative and qualitative factors, gross margin data, and regional-level and country-level analysis to help readers find the blue ocean market opportunities.
Coverage of mergers and acquisitions and acquisition information offers insights into strategic moves by players in the zebrafish research market. This report provides essential analysis of various market segments, guiding market entry decisions and helping readers make informed choices through in-depth assessments of opportunities and challenges across the zebrafish for research market space.
The US Zebrafish for Research Market
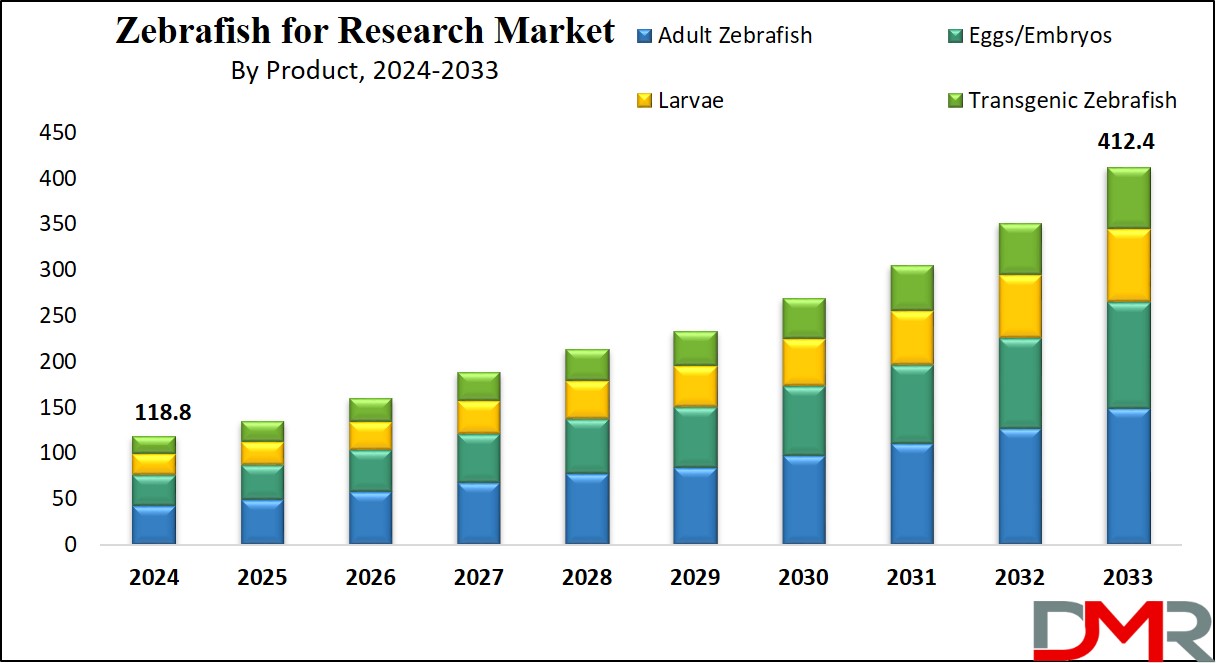
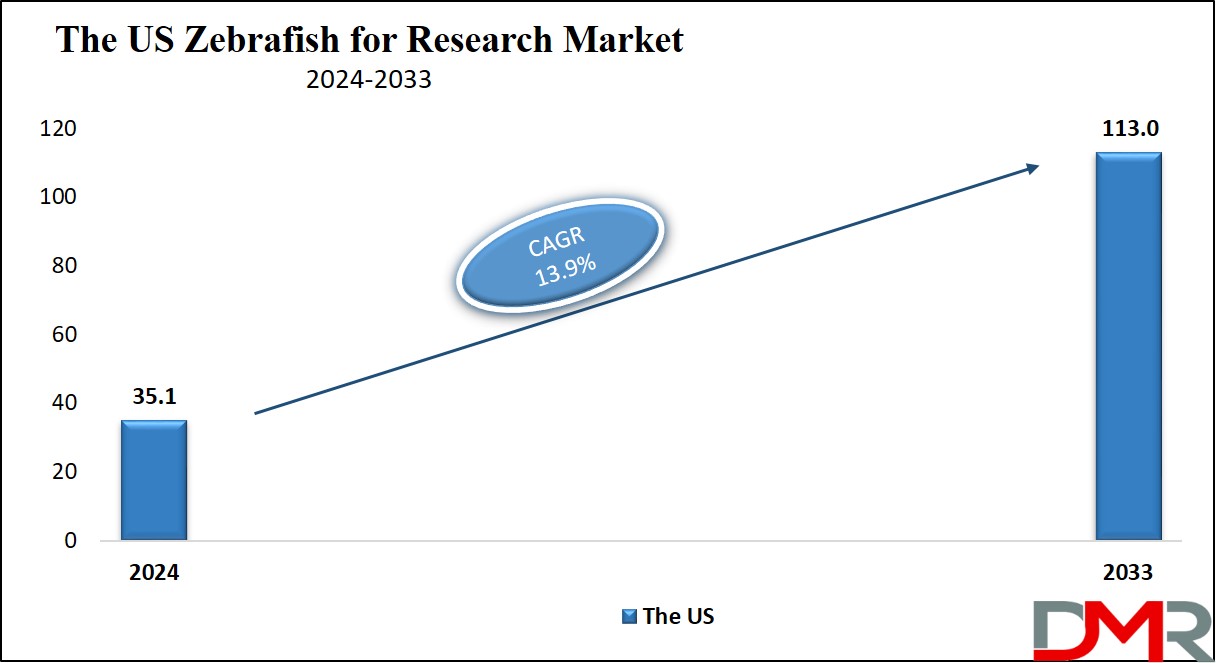
The US Zebrafish for Research Market is projected to be valued at USD 35.1 million in 2024. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 113.0 million in 2033 at a CAGR of 13.9%.
It is attributed to the increasing demand for strong research infrastructure, high pharmaceutical applications, and increased governmental and private funding in biomedical research. Zebrafish makes high utility in trials of a preclinical nature for testing the efficacy and toxicity of drugs, thus representing much more economical models compared to rodents. The technological advancements that allow precise gene editing and transgenesis, therefore extending the scope of involvement of zebrafish in personalized medicine and genetic studies, strengthen this trend.
One of the trends in the U.S. zebrafish research market would be an increasing focus on adopting toxicity testing for pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and cosmetics. In fact, with increasing regulatory scrutiny, it is expected that companies will increasingly adopt zebrafish as a reliable model organ for conducting safety assessments. Another key trend is the integration of high-throughput screening methodologies with testing methods using zebrafish, especially for large-scale screenings in drug development studies.
Innovation in the U.S. market by players such as Pentair, InVivo Biosystems, and Bioreperia is marked by significant investments in providing customized zebrafish services for various research needs. Competitive forces in the U.S. zebrafish market are intense; the highly enhanced research programs in the country will most likely continue to keep it on top throughout the forecast period in terms of market share and technological development.
Key Takeaways
- Global Market Share: The Global Zebrafish for Research Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 118.8 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 412.8 million by the end of 2033.
- The US Market Share: The US Zebrafish for Research Market is projected to be valued at USD 35.1 million in 2024. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 113.0 million in 2033 at a CAGR of 13.9%.
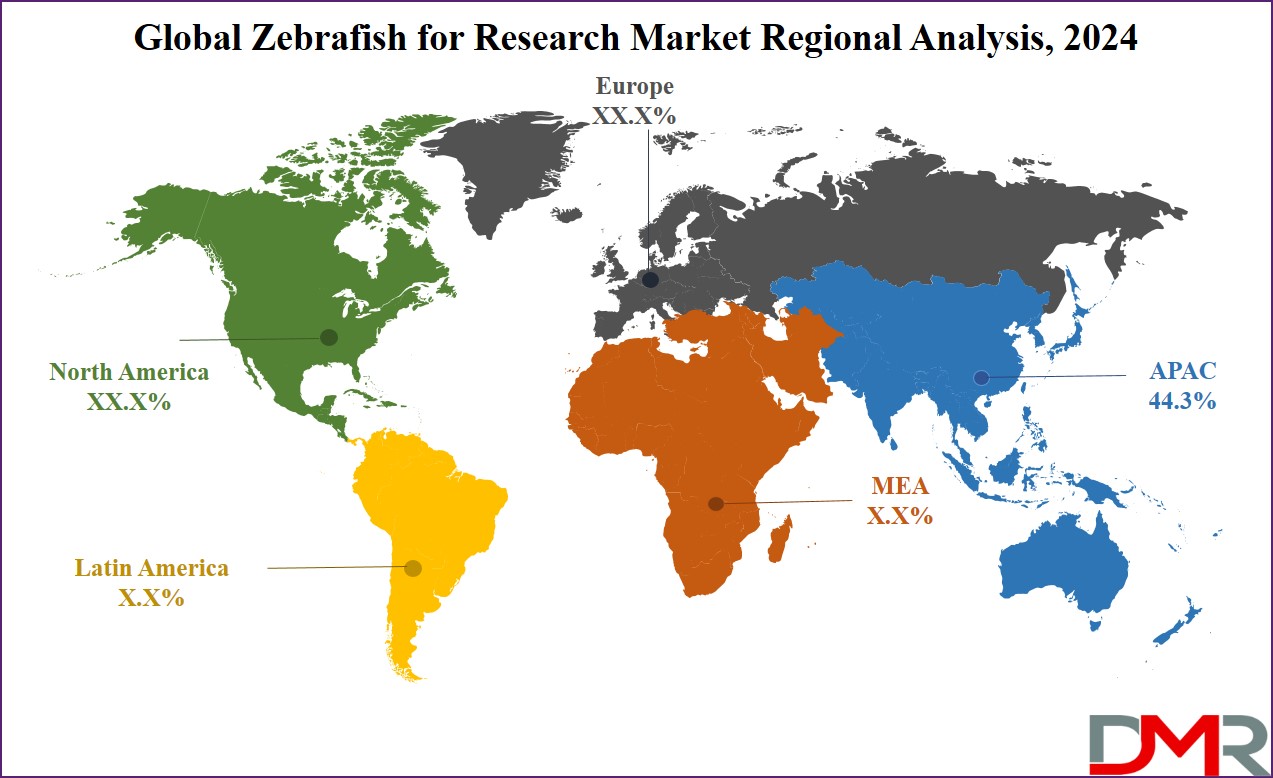
- Regional Analysis: Asia Pacific is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Zebrafish for Research Market with a share of about 44.3% in 2024.
- Key Players: Some of the major key players in the Global Zebrafish for Research Market are Aquaneering Inc., Pentair PLC, Envigo RMS LLC, Charles River Laboratories, Danio Lab, ZeClinics, Union Biometrica Inc., Techniplast, Cyagen Biosciences, and many others.
- Global Market Growth Rate: The market is growing at a CAGR of 14.8 percent over the forecasted period.
Use Cases
- Toxicity Testing: Zebrafish are highly utilized in toxicity testing in both pharmaceuticals and environmental sciences, hence serving early warnings of chemical toxicity in various compounds of drugs and chemicals.
- Disease Modeling: Zebrafish modeling designs in the study of human diseases, such as tumors and cardiovascular disorders, further enable the researchers to study the mechanisms of the disease and possible treatments.
- Genetic Studies: Zebrafish are used to study disorders related to genetic issues, functions of genes, and editing outcomes due to their genetic similarities with humans.
- Drug Discovery: Zebrafish are used in screens to identify potential drug candidates; most of these target neurological and cardiovascular diseases and help study the efficacy and side effects of drugs.
Market Dynamic
Trends
Adoption of Genetic Toolszebrafish have evolved into one of the primary tools in genetic research; with the assimilation of CRISPR and other gene-editing techniques, new dimensions of understanding a variety of diseases have been created. Allowing specific modifications to genomes, researchers can produce transgenic zebrafish lines with particular mutations or gene knockouts seen in human cancers, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.
They are essential models that further therapeutic research in the way they allow scholars to witness a disease's progress and drug responses very close to human biological responses. The use of genetic tools such as CRISPR in research on zebrafish is therefore gaining momentum in the world because they provide insight into undertreated disease areas that bridge the gap between traditional animal models and clinical outcomes.
Rise of High-Throughput Screening
High-throughput screening (HTS) has become an integral component of modern drug discovery, and increasingly, zebrafish have played an important role therein. Pharmaceutical firms are exploiting the advantages of using zebrafish for HTS: their small size and rapid development, coupled with genetic similarity to man, afford testing of thousands of compounds simultaneously for efficacy and toxicity.
Automated systems in zebrafish handling, imaging, and data analysis further enhance the efficiency of HTS, enabling large-scale drug screening at a fraction of the time and cost associated with mammalian models. In addition, the embryos are transparent, enabling researchers to directly observe physiological and biochemical responses in real-time, thereby affording great value for the identification of early-stage therapeutic candidates.
Growth Drivers
Cost-Effectiveness
Zebrafish are a less expensive and more convenient model than traditionally used mammals because they can survive in very little space, are cheaper to maintain, and are comparatively easy to breed compared to other vertebrates. This economic advantage will also attract several pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies that look for affordable ways of performing preclinical tests and high-throughput screening.
Unlike rodent models, zebrafish can be maintained in small aquaria, thus lowering the overhead costs related to space, feed, and care. Because of their rapid reproductive cycle, large numbers of specimens can be produced in an extremely short period, further decreasing the expenses associated with longitudinal studies and affording the ability to study multigenerational effects in relatively short time frames.
Ethical and Regulatory Support
Ethical concerns about animal testing are the driving forces towards finding alternative models, and among them, zebrafish come out to be widely accepted. Regulatory bodies such as the OECD have also recognized and accepted zebrafish for certain testing protocols, especially in toxicity studies. Other justifications for this regulatory acceptance include that zebrafish are suited for ethical testing methods and are less controversial than mammalian models.
The benefits of using zebrafish in toxicity testing and preclinical research include that the embryonic stage of development is responsive to environmental changes and chemicals, hence providing early signs of toxicity without necessarily involving damage to mammals. This ethical advantage comes with recent increased legislative moves around the world against traditional animal testing, thereby further increasing the appeal of zebrafish both in academic and industrial circles.
Growth Opportunities
Expansion in Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region, driven by countries such as China, Japan, and India, brings with it a huge potential for growth in the area of zebrafish research. All these factors are supported by the initiatives taken by the governments of these countries in providing funds for research and development in biotechnology and biomedical research. Growing funding and policies will also help in the growth of the market.
For example, the Chinese government's focus on developing the country's biotechnology industry is manifested in the setting up of high-tech research centers, which will increase demand for zebrafish in drug development and genetic studies. Additionally, competitive costs of research studies make the Asia-Pacific region attractive for international collaborations to bring global research to local institutions. With emerging countries continuing to invest in research and development infrastructure, pharmaceutical, academic, and environmental applications of the model organism are expected to see a substantial rise in demand for the zebrafish.
Emerging Applications in Environmental Monitoring
Zebrafish are gaining their right to recognition in the field of environmental research, especially in water quality monitoring and the assessment of pollution levels. Zebrafish embryos are extremely sensitive to toxins and usually serve as a good model in the detection of waterborne pollutants, heavy metals, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals.
This application is highly relevant in these modern times, as environmental regulations in most parts of the world continue to get more stringent, adversely making governments and organizations comply by finding better ways to monitor ecosystem health. Zebrafish models allow rapid assessment of toxicology, hence leading researchers to the main understanding of the consequences of industrial wastes and contaminants on the environment.
Restraints
Technical Limitations
While zebrafish are a versatile model system applicable to many types of studies, there are technical limitations to modeling complex human physiological systems with this animal. For example, some of the recognized disease mechanisms in mammals do not translate robustly in zebrafish, and hence, there is limited coverage across some therapeutic areas.
As such, while the zebrafish model cardiac and neurological conditions, there is a structural and functional difference between the organs in lower animals and in humans, due to which sometimes incomplete or non-replicative derivation of results occurs. These shortfalls are thus mandating the use of extra models such as rodents or organoids in the later stages of studies.
Competition from Alternative Models
The rise of alternative models involving organoids, 3D cell culture, and computational simulations also keeps on arising for particular applications and, with more specialized insights, they are in some competition with the zebrafish. For instance, organoids can model human-specific tissue architecture and provide valuable information on complex human diseases and drug responses that could fall out of the scope of the zebrafish model.
These models are especially favored when researching disease pathology in human-relevant contexts, and as such, they do limit the use of zebrafish in areas where specific human insight is required. Greater availability, coupled with development in these alternative models, many of which carry more specificity in human biology, develops competition in specific areas of research. This, in turn, will limit the inclusion of the growth of the zebrafish for the research market in certain segments.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Product Type
Within the global zebrafish market for research purposes, the product type of adult zebrafish has emerged as the most dominant segment with 36.0% of the market share in 2024. The reason behind this preference lies in their developed physiological systems, which allow them to mimic several aspects of human biology. Adult zebrafish exhibit more complex behavioral and metabolic capabilities, making them ideal models for research studies requiring mature physiology, such as behavioral studies, pharmacology, and chronic toxicity studies.
Their applications in long-term toxicology and drug efficacy studies have increased since adults tend to provide more reliable data on chronic exposure effects compared to embryos or larvae. Moreover, adult zebrafish have made behavioral studies possible in such fields as neurobiology, with a developed central nervous system and feasible social behavior that allows the examination of neurological disorders, mechanisms of addiction, and cognition.
Adult zebrafish are also contributing to drug discovery since they are more tolerant of compounds and hence more accurately reflect human metabolisms compared to earlier life stages. This resemblance provides more predictive data on drug safety and efficacy for human
clinical trials. Coupled with the increased emphasis of regulatory agencies on the use of non-mammalian models in preclinical testing, demand for adult zebrafish will rise, further strengthening their leading position in this segment. All in all, the wide range of applications of adult zebrafish across the different research areas makes them a mainstay in the market of zebrafish research, wherein sustained growth is expected in the forecast period.
By Type
Toxicity testing is the leading segment in research that involves the zebrafish model, with advantages over other models in assessing the safety of chemicals and drugs. Zebrafish provide a low-cost and sufficient alternative to mammalian models for conducting early-stage toxicity screening. Likewise, their transparent embryos, along with fast development, enable researchers to observe biological responses to toxicants in real-time and give rapid views about possible hazards that new compounds could cause.
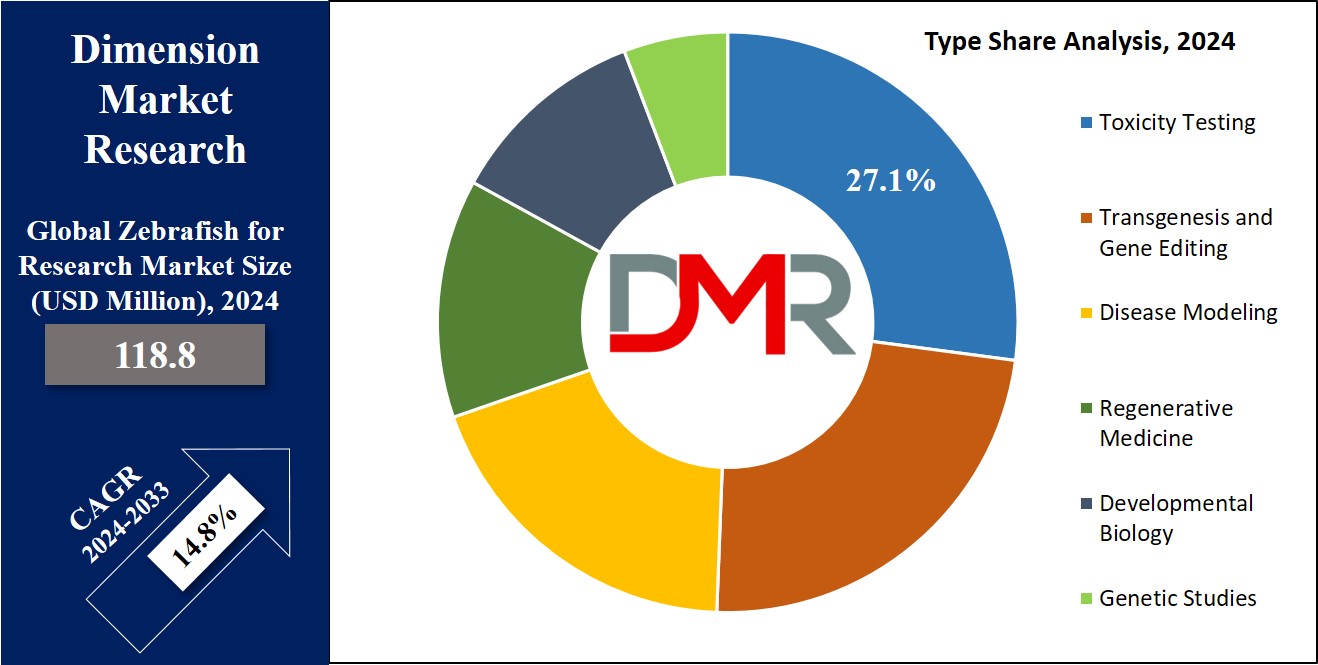
This has been further propelled by regulatory pressures across the industries, mainly in pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and cosmetics. Generally, this model of zebrafish is compliant with the OECD guidelines, thus supporting its validity for regulatory toxicology. Using zebrafish, firms can meet regulatory needs instead of increasing animal testing-a prime advantage since the ethics bar in laboratory research keeps going up.
Toxicity testing with zebrafish can be done using high-throughput screening; moreover, it is very efficient for the rapid evaluation of a huge number of compounds. That has special importance in the early stages of drug discovery, where enormous chemical libraries must be pre-screened for their toxicity before the selection of only safe and potent candidates for further testing. Zebrafish are particularly capable of predicting cardiotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and neurotoxicity incidences important in preclinical research.
This segment of toxicity testing is expected to further exhibit growth with a high CAGR influenced by the demands from industries such as pharmaceuticals and chemicals. The broad applicability of toxicity testing, and that the method is in alignment with the requirements set by government regulatory bodies, strongly establishes its leading position in the zebrafish research market.
By Application
The pharmaceutical segment leads the application segment of the zebrafish research market, owing to the increasing employment of zebrafish in drug discovery and preclinical testing. This is because zebrafish offer a really good model system that gives human-like physiological reactions to drugs, enabling pharmaceutical organizations to conduct mass screening for potential therapeutic agents. With the genetic similarities with
humans at about 70%, it allows researchers to study the efficacy and safety of various drugs regarding a wide scope of therapeutic areas like neurology,
oncology, and cardiology.
Zebrafish have many advantages in early-stage drug screenings due to their transparent embryos and short life cycles, which allow for quicker observations of the acting drugs. High-throughput screening methodologies can function well with zebrafish models to enable the screening of large chemical libraries necessary in the preliminary stages of pharmaceutical studies. This is not only cost-saving but also hastens the process of identifying viable drug candidates.
The utility of zebrafish in toxicity testing adds to their wide applications in the pharmaceutical industry, where drug safety is a concern. Many regulatory agencies are increasingly requiring comprehensive toxicity data, and the use of zebrafish replaces traditional animal models not only for ethical reasons but also for scalable reasons.
The pharmaceutical applications, with a growing market size of the required zebrafish for research, are poised to lead the growth as the industry continues its quest for reliable high-throughput models for the testing of new drugs. Overall, the pharmaceutical industry's need for zebrafish is being reinforced by the increasing demand for affordable, ethical, and quick ways to develop new drugs, further strengthening its dominance in the global zebrafish research market.
The Zebrafish for Research Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Product Type
- Adult Zebrafish
- Eggs/Embryos
- Larvae
- Transgenic Zebrafish
By Type
- Toxicity Testing
- Transgenesis and Gene Editing
- Disease Modeling
- Regenerative Medicine
- Developmental Biology
- Genetic Studies
By Application
- Pharmaceuticals
- Biotechnology
- Chemicals
- Cosmetics
- Environmental Monitoring
- Academic Research
- Others
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific is projected to dominate the global zebrafish research market as
it will hold 44.3% of the market share in 2024. The main share in the global zebrafish market for research comes from the Asia-Pacific region, driven by heavy investments in biotechnology, rapidly growing research infrastructure, and supportive policies by governments in the region. Key players in China, Japan, and South Korea are encouraging research in the field related to zebrafish by either establishing special facilities or setting up a research center for model development using zebrafish in drug discovery, toxicity testing, and genetic research.
For instance, in countries like China alone, large strides have been made; institutions such as the Shanghai Model Organisms Center and Hangzhou Hunter Biotechnology Co. are at the leading edge of large-scale research into zebrafish for pharmaceutical and environmental use. On the one hand, Japan and South Korea foster growth with growing annual research budgets, while their institute/industry collaborations will add another needed boost. The cost structure of the Asia-Pacific region is relatively more competitive, as research and development expenditures against Western countries remain comparably low.
This cost efficiency is also reinforced by access to highly trained scientific personnel, drawing international research collaborations and further strengthening the region's position. Besides, the large population and associated healthcare demands of the Asia-Pacific fuel local needs for pharmaceutical and biomedical research. Zebrafish regularly serve in toxicity testing, drug efficiency testing, and genetics; hence, they support everything from basic scientific research to various uses in applied biomedical fields.
The market outlook is promising, with government initiatives in China, India, and other countries in the Asia-Pacific region to promote innovation and create a strong ecosystem for the development of biopharmaceuticals. For example, the five-year programs of China orient their priorities toward biotechnological development and drug development to build a supportive environment for the expansion of research using zebrafish.
Keeping these factors in mind, the Asia-Pacific region would continue to rule the market for zebrafish employed in research applications and contribute significantly to several research developments across the world with an increase expected in the number of publications and patents dealing with zebrafish.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Competitive Landscape
The global zebrafish research market is pretty competitive, with well-established players and companies in the race to develop further uses of zebrafish for various research areas. Major players in this industry include Aquaneering Inc., Pentair PLC, and ZeClinics, prominent in the sector of zebrafish systems and services. Companies are investing intensely in improving product quality and offering advanced solutions for maintaining, breeding, and handling zebrafish to further facilitate research.
Companies like Shanghai Model Organisms Center and Invivo Biosystem are prominent in genetic research with specific lines of zebrafish contributing to answering some disease-related questions. Strategic collaborations are not lagging, as companies strive to expand their market share and leverage synergies. Mergers and partnerships with various academic and pharmaceutical institutions are common; from here, access to more developed genetic models and data can be assured.
The report on the zebrafish for research market underlines the fact that the competition is based on innovation, wherein players are increasingly focusing on automation in high-throughput screening and development of new CRISPR technologies. Besides this, the competitive matrix of the market is yet dynamic, considering that there has been the entry of new players such as BioReperia and YSY Biotech into the market with offerings addressed toward environmental toxicology testing applications.
Therefore, the competitive landscape in this market would continue to remain so dynamic, especially with continuous advancements, which would further encourage product development and market reach.
Some of the prominent players in the Global Zebrafish for Research Market are
- Aquaneering Inc.
- Pentair PLC
- Envigo RMS LLC
- Charles River Laboratories
- Danio Lab
- ZeClinics
- Union Biometrica, Inc.
- Techniplast
- Cyagen Biosciences
- InVivo Biosystems
- ZFBioLabs
- Sinnhuber Aquatic Research Laboratory
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- October 2024: Shanghai Model Organisms Center launched transgenic zebrafish models specifically designed for neurodegenerative disease research, advancing zebrafish's role in studying complex human neurological disorders.
- August 2024: ZeClinics collaborated with a major pharmaceutical company to implement high-throughput zebrafish-based toxicity testing, facilitating faster and more efficient novel drug candidate screening.
- June 2024: InVivo Biosystems expanded its service line to include CRISPR gene-editing services, allowing for the creation of highly customized zebrafish models tailored to specific research needs.
- December 2023: BioReperia introduced automated zebrafish screening solutions to accelerate toxicity testing processes, enhancing the efficiency of preclinical drug development studies.
- September 2023: Pentair PLC acquired a prominent zebrafish system manufacturer to strengthen its research portfolio, enhancing support for zebrafish-based research applications.
- July 2023: Aquaneering Inc. launched a next-generation zebrafish housing system featuring improved water quality monitoring, promoting healthier research environments for zebrafish models.
- April 2023: Techniplast partnered with European universities to use zebrafish in environmental research, focusing on innovative water quality monitoring techniques.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2024) |
USD 118.8 Mn |
| Forecast Value (2033) |
USD 412.8 Mn |
| CAGR (2024-2033) |
14.8% |
| Historical Data |
2018 – 2023 |
| The US Market Size (2024) |
USD 35.1 Mn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Estimate Year |
2024 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors and etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Product Type (Adult Zebrafish, Eggs/Embryos, Larvae, and Transgenic Zebrafish), By Type (Toxicity Testing, Transgenesis and Gene Editing, Disease Modeling, Regenerative Medicine, Developmental Biology, and Genetic Studies), By Application (Pharmaceuticals, Biotechnology, Chemicals, Cosmetics, Environmental Monitoring, Academic Research, and Others) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – The US and Canada; Europe – Germany, The UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Europe; Asia- Pacific– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, & Rest of MEA
|
| Prominent Players |
Aquaneering Inc., Pentair PLC, Envigo RMS LLC, Charles River Laboratories, Danio Lab, ZeClinics, Union Biometrica Inc., Techniplast, Cyagen Biosciences, InVivo Biosystems, ZFBioLabs, Sinnhuber Aquatic Research Laboratory, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users) and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The Global Zebrafish for Research Market size is estimated to have a value of USD 118.8 million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 412.8 million by the end of 2033.
The US Zebrafish for Research Market is projected to be valued at USD 35.1 million in 2024. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 113.0 million in 2033 at a CAGR of 13.9%.
Asia Pacific is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Zebrafish for Research Market with a share of about 44.3% in 2024.
Some of the major key players in the Global Zebrafish for Research Market are Aquaneering Inc., Pentair PLC, Envigo RMS LLC, Charles River Laboratories, Danio Lab, ZeClinics, Union Biometrica Inc., Techniplast, Cyagen Biosciences, and many others.
The market is growing at a CAGR of 14.8 percent over the forecasted period.