Market Overview
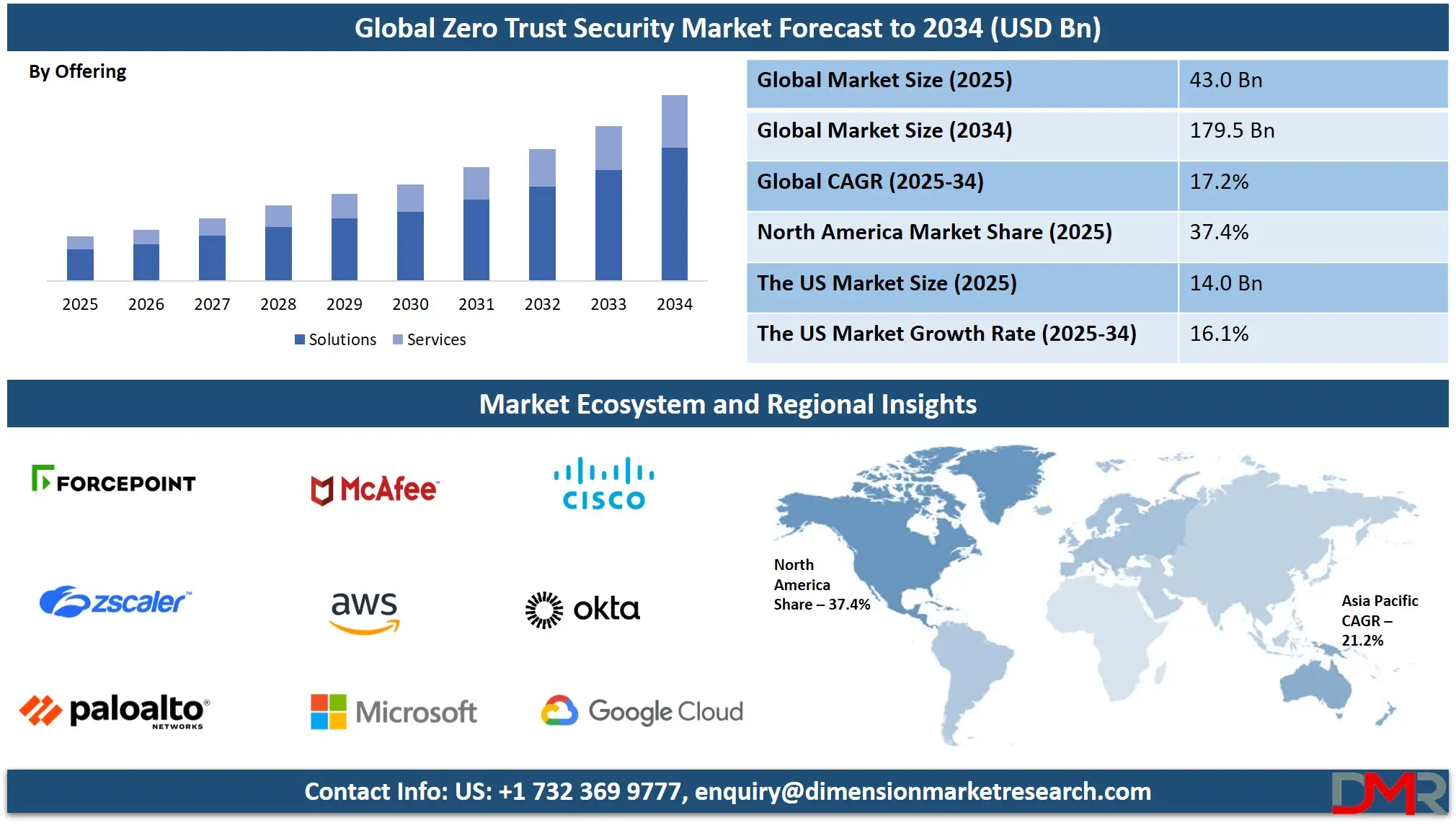
The Global Zero Trust Security Market size is projected to reach USD 43.0 billion in 2025 and grow at a compound annual growth rate of 17.2% from there until 2034 to reach a value of USD 179.5 billion.
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity approach based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that assume everything inside the network is safe, Zero Trust treats every user, device, and system as untrusted by default. It requires continuous verification of identity, strict access controls, and constant monitoring of network activities, regardless of where the request originates—inside or outside the organization. This framework helps reduce the risk of data breaches by limiting the chances of attackers moving freely within a network after gaining access.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
The rise in cloud computing, remote work, and growing cyberattacks has pushed organizations to adopt Zero Trust. As businesses shift to hybrid and multi-cloud environments, the traditional security perimeter has disappeared. Employees now access sensitive data from various locations and devices, making it harder to rely on perimeter-based security. High-profile breaches involving compromised credentials, insider threats, and ransomware have highlighted the need for a model that secures data at every point, not just at the entry gate.
Over the past few years, governments and regulators have also pushed for stronger cybersecurity standards, further boosting interest in Zero Trust. Public sector agencies, especially in the United States, have introduced Zero Trust mandates for federal institutions. Meanwhile, businesses in sectors like finance, healthcare, and energy have begun treating Zero Trust as a strategic investment to protect customer data and critical infrastructure. This shift has also sparked increased collaboration between cybersecurity vendors, cloud providers, and enterprises to build solutions that align with Zero Trust principles.
Several trends have shaped the Zero Trust landscape recently. One major trend is the integration of identity and access management with machine learning to detect suspicious behavior. Another is the adoption of micro-segmentation, which divides networks into smaller sections to control movement more tightly. Also, Zero Trust is no longer limited to large enterprises. Small and mid-sized companies are exploring simplified Zero Trust solutions offered as part of cloud security packages, making the model more accessible.
In recent events, major technology companies have launched Zero Trust frameworks, platforms, and services, promoting interoperability between tools such as endpoint detection, identity verification, and secure application access. At the same time, cybersecurity conferences and industry reports have focused on Zero Trust as a central theme, underlining its growing importance. Industry partnerships have also emerged to develop common standards and certifications to guide Zero Trust implementation.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Zero Trust is not a single product but an ongoing strategy. Organizations must plan for gradual adoption, starting with their most critical assets and user groups. A clear understanding of data flows, user behavior, and access needs is essential. With consistent policy enforcement, visibility, and adaptation, Zero Trust helps build a strong cybersecurity foundation in a world where threats constantly evolve. It marks a shift from reactive security to proactive and intelligent defense, helping businesses stay resilient in the face of modern cyber risks.
The US Zero Trust Security Market
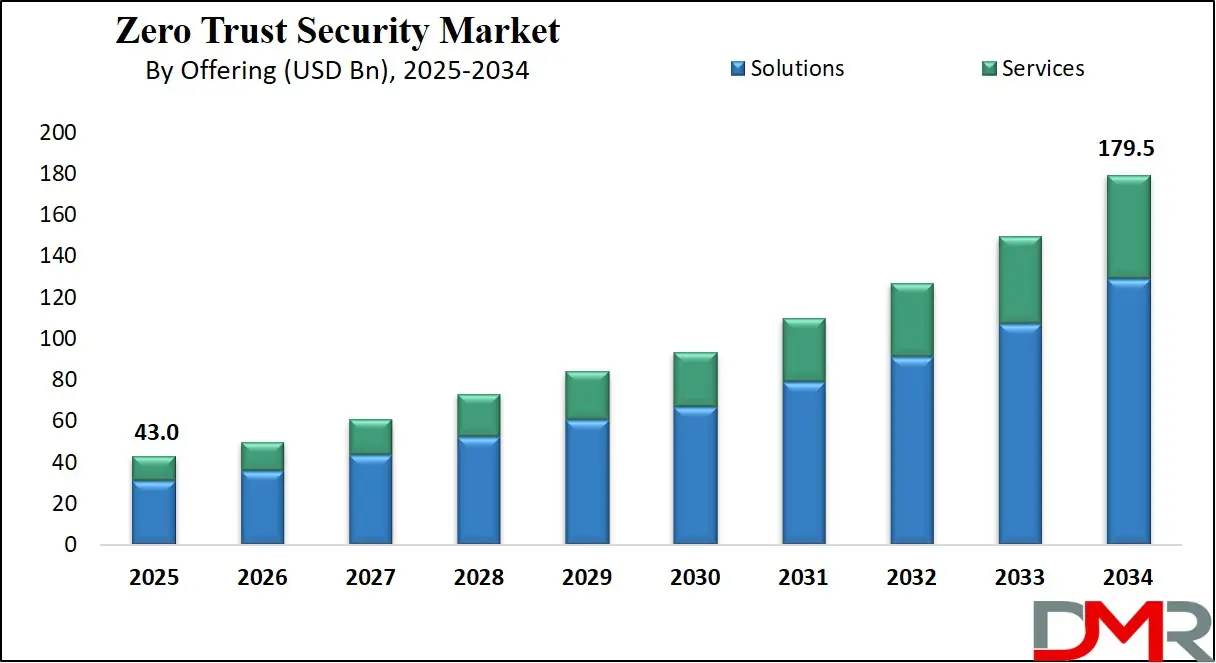
The US Zero Trust Security Market size is projected to reach USD 14.0 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 16.1% over its forecast period.
The US plays a leading role in the Zero Trust Security market, driving both innovation and adoption across industries. With its strong cybersecurity ecosystem, the US is home to many technology providers developing Zero Trust platforms, tools, and frameworks. The government has also been a major force, mandating Zero Trust implementation across federal agencies to strengthen national cyber defense.
This has encouraged private sector adoption as well, especially in critical sectors like finance, healthcare, and energy. The US is also a hub for cybersecurity research, policy development, and talent, which supports ongoing advancements in Zero Trust solutions. Through regulations, investments, and global partnerships, the US continues to influence the direction and growth of the Zero Trust Security market worldwide.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Europe Zero Trust Security Market
Europe Zero Trust Security Market size is projected to reach USD 11.2 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 16.7% over its forecast period.
Europe plays an important and growing role in the Zero Trust Security market, driven by strict data protection laws and rising cyber threats. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has pushed organizations across Europe to strengthen data access and security, aligning well with Zero Trust principles. Governments and industries in sectors like finance, manufacturing, and healthcare are increasingly exploring Zero Trust to improve compliance and reduce risk.
European businesses are also modernizing IT infrastructures, adopting cloud services and remote work models, which increases the need for strong security frameworks. While adoption has been slower than in the US, awareness is rising rapidly. Local cybersecurity vendors and global players are expanding their Zero Trust offerings in Europe, helping drive regional market growth.
Japan Zero Trust Security Market
Japan Zero Trust Security Market size is projected to reach USD 2.0 billion in 2025 at a compound annual growth rate of 17.3% over its forecast period.
Japan is gradually becoming an important player in the Zero Trust Security market, driven by digital transformation, rising cyber threats, and the need to protect critical infrastructure. As companies adopt cloud services, remote work, and connected devices, the demand for secure and adaptable cybersecurity models is growing. Sectors like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing are exploring Zero Trust to safeguard sensitive data and maintain business continuity.
The Japanese government is also promoting cybersecurity reforms and encouraging the use of Zero Trust principles through policy discussions and security guidelines. While challenges such as legacy systems and a shortage of cybersecurity professionals exist, increased awareness and modernization efforts are creating new opportunities. Japan’s focus on resilience and regulatory readiness supports its growing role in this market.
Zero Trust Security Market: Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Zero Trust Security Market size is expected to grow by USD 129.9 billion, at a CAGR of 17.2%, during the forecasted period of 2026 to 2034.
- By Offering: The solution segment is anticipated to get the majority share of the Zero Trust Security Market in 2025.
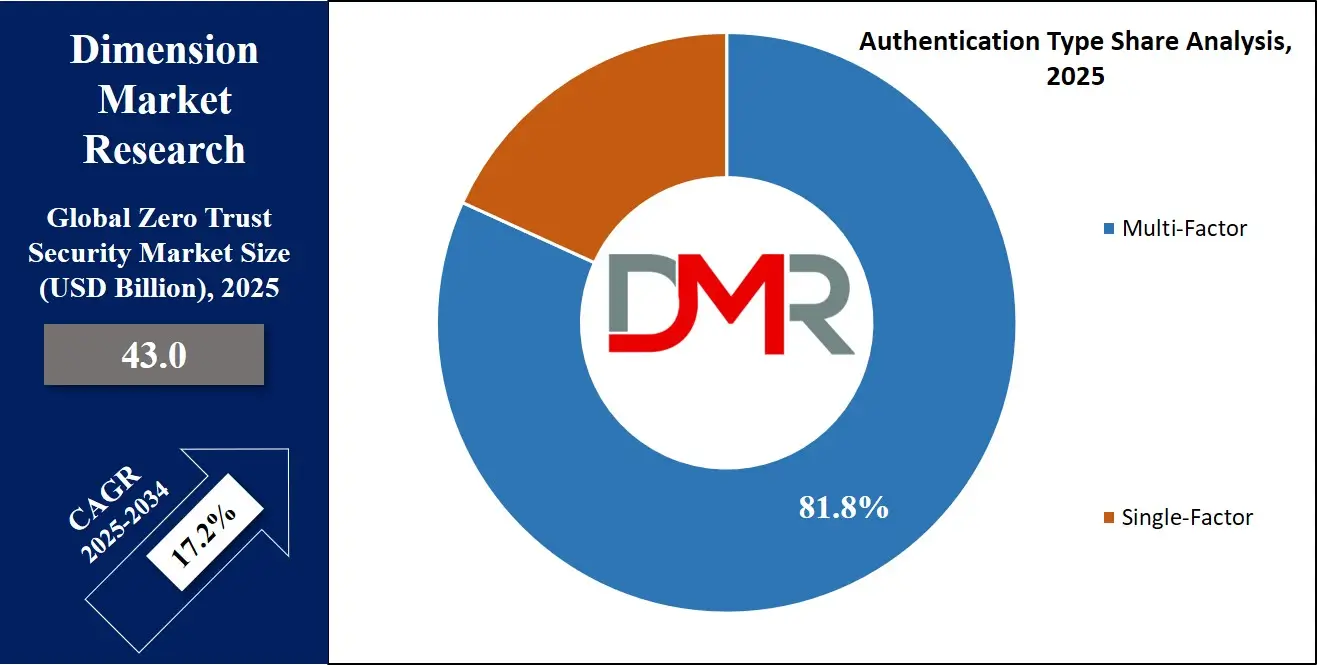
- By Authentication Type: The multi-factor segment is expected to get the largest revenue share in 2025 in the Zero Trust Security Market.
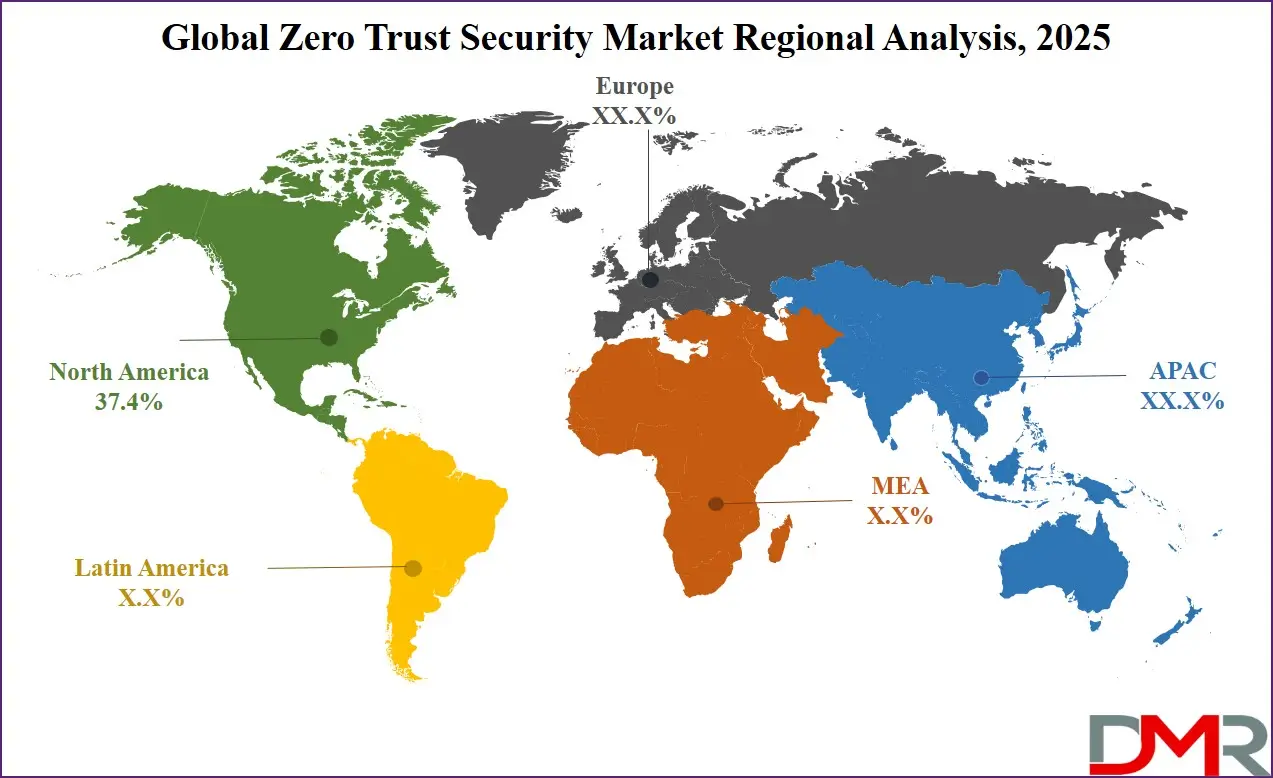
- Regional Insight: North America is expected to hold a 37.4% share of revenue in the Global Zero Trust Security Market in 2025.
- Use Cases: Some of the use cases of Zero Trust Security include third-party access control, data loss prevention, and more.
Zero Trust Security Market: Use Cases
- Remote Workforce Security: Zero Trust helps secure access for remote employees by verifying identity and device health before granting entry to applications. It prevents unauthorized access even if login details are stolen. This ensures secure work-from-anywhere setups without relying on traditional VPNs.
- Cloud Application Protection: Zero Trust controls who can access cloud apps and what they can do once inside. It monitors behavior continuously to detect threats and reduce lateral movement. This approach strengthens security across multiple cloud environments.
- Third-Party Access Control: Businesses often work with vendors or contractors who need limited access to internal systems. Zero Trust restricts their access to only necessary data and tracks all activity. This reduces the risk of breaches from external partners.
- Data Loss Prevention: Zero Trust enforces strict rules on who can view, share, or move sensitive data. It flags unusual data transfers or downloads instantly. This helps prevent accidental leaks or intentional theft of valuable information.
Stats & Facts
- CrowdStrike highlights that 80% of all cyberattacks use identity-based techniques, such as credential theft and privilege escalation, to infiltrate systems, indicating that identity is now the primary target for threat actors across most sectors.
- CrowdStrike again notes that identity-based attacks account for 80% of cyber threats, underlining the critical need for robust identity security solutions to guard against widespread credential misuse and lateral movement.
- According to CyberArk, 99% of security decision makers believe their organizations will experience an identity-related compromise within the next year, driven by the expanding number of identities and the increasing complexity of IT environments. Further, it reveals that the number of identities—both human and machine—is expected to grow by 240% in just 12 months, significantly widening the attack surface.
- According to Microsoft, password-based attacks surged to ten times their previous levels over the past year, signaling a growing reliance by attackers on stolen or weak credentials as a gateway into enterprise systems.
- One Identity reports that 80% of organizations believe improved identity and access management could have prevented some or all of the cyberattacks they experienced. This emphasizes how central IAM has become to building effective cybersecurity defenses.
- IBM reports that 40% of data breaches involve data stored across multiple environments, with public cloud-stored data breaches resulting in the highest average cost of USD 5.17 million. The use of generative AI and IoT further complicates cloud security, requiring organizations to implement better governance and monitoring practices across hybrid infrastructures.
- Mimecast research finds that 3 out of 4 CISOs believe collaboration tools bring significant new risks, and 94% say the native security features in Microsoft 365 are not sufficient. This shows a growing need for enhanced email and collaboration tool security in enterprise environments.
- Mimecast reports that 97% of 1,700 IT professionals reported being targeted by phishing emails within the past year, and 75% noted a rise in email-based threats. Additionally, 59% say attacks have grown more sophisticated, suggesting phishing remains a leading entry point for attackers.
- Microsoft observed an average of 156,000 daily attempts of business email compromise over the course of a year, illustrating the persistent and large-scale nature of phishing and impersonation attacks targeting enterprise users.
- Arctic Wolf reports that 48% of organizations now see ransomware as their top concern, with 42% having already experienced a ransomware attack in the past year. In another CyberArk survey, 89% of organizations stated they were targeted by ransomware, highlighting the scale of this threat.
- IBM states that breaches stemming from compromised credentials or insider threats take the longest to contain, with an average time to identify and resolve at 328 and 308 days, respectively. These prolonged breach durations increase exposure and potential financial losses.
- IBM found that organizations implementing AI and automation in their cybersecurity strategies saved an average of USD 2.22 million in breach costs compared to those that did not. These technologies enhance threat detection, reduce response times, and support prevention strategies such as red-teaming and posture management.
Market Dynamic
Driving Factors in the Zero Trust Security Market
Rise in Cyber Threats and Insider Attacks
One of the major forces driving the Zero Trust Security market is the growing frequency and complexity of cyber threats. Traditional perimeter-based defenses are no longer enough, as attackers increasingly use stolen credentials, phishing, and insider tactics to gain access. Organizations are recognizing that once a hacker gets inside the network, they can move freely and cause major damage.
Zero Trust prevents this by not trusting any request without verification, even from within the network. It also ensures that users have only the minimum level of access they need, reducing exposure. With data breaches becoming costlier and more damaging to brand reputation, companies are prioritizing Zero Trust as a proactive defense. The need for continuous verification makes it a must-have.
Expansion of Cloud and Hybrid Work Environments
The rapid shift to cloud-based systems and hybrid work models has created a distributed IT environment where users, apps, and data are no longer confined to one physical location. This change has made traditional security models outdated, as the network perimeter is now fluid and hard to define.
Zero Trust Security fits this new structure perfectly, offering protection at every level whether it's a remote worker accessing company apps or a cloud service interacting with internal systems. It ensures that every device, identity, and network flow is verified and controlled in real-time. As more businesses adopt digital transformation strategies, the demand for a scalable and adaptable security model like Zero Trust continues to grow, making it a central part of modern cybersecurity planning.
Restraints in the Zero Trust Security Market
Complexity of Implementation and Integration
One of the biggest challenges holding back the widespread adoption of Zero Trust Security is the complexity involved in its implementation. Moving from a traditional security model to a Zero Trust architecture requires a complete shift in mindset, tools, and workflows. Organizations often struggle with mapping user access, segmenting networks, and integrating new tools with legacy systems.
The process demands thorough planning, technical expertise, and often a phased rollout, which can be time-consuming. For businesses with limited IT resources, this can delay adoption or result in partial, ineffective deployment. Moreover, aligning multiple teams and ensuring consistent enforcement across departments adds to the complexity. This high level of difficulty can slow down or discourage investment in Zero Trust frameworks.
Lack of Awareness and Skilled Workforce
Another major restraint is the lack of awareness and expertise related to Zero Trust principles and technology. Many organizations still rely on outdated security beliefs and are unfamiliar with how Zero Trust differs from traditional models. Even when there is interest, the shortage of skilled professionals who can design, implement, and manage Zero Trust systems becomes a barrier.
Small and mid-sized businesses, in particular, may not have access to cybersecurity talent or proper training programs. This gap makes it difficult to adopt and maintain Zero Trust solutions effectively. Without a clear understanding of the value and process, some companies hesitate to move forward, viewing it as an unnecessary or overly complex investment. As a result, education and training remain key issues in market growth.
Opportunities in the Zero Trust Security Market
Growing Demand from Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
As cybersecurity threats increasingly target organizations of all sizes, small and medium enterprises are beginning to see the importance of advanced security models like Zero Trust. Previously seen as a solution mainly for large corporations, Zero Trust is now being offered in simplified, cloud-based versions that are more affordable and easier to manage for SMEs.
These businesses are actively adopting cloud services and remote work, which makes them vulnerable to the same risks faced by larger firms. Vendors offering scalable and flexible Zero Trust solutions tailored for smaller IT teams can tap into this growing segment. As awareness rises and more user-friendly platforms become available, the SME market presents a strong growth opportunity for Zero Trust providers.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Zero Trust Security has the potential to grow further by integrating with other emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and edge computing. AI-driven analytics can enhance Zero Trust by identifying suspicious behavior patterns and automating response actions. Similarly, with the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) and edge devices, Zero Trust can play a key role in managing identity and access control in a highly distributed environment.
As more companies adopt smart devices and real-time data processing, the need for strict verification at every level will increase. Vendors that can merge Zero Trust principles with next-generation tech will be well-positioned to serve future-ready digital infrastructures across industries.
Trends in the Zero Trust Security Market
Rise of Zero Trust as a Managed Service
A growing trend in the Zero Trust Security market is the rise of Zero Trust as a managed service. Many organizations, especially small and mid-sized businesses, lack the in-house expertise and resources to fully implement and maintain a Zero Trust framework. As a result, they are turning to managed service providers (MSPs) that offer end-to-end Zero Trust solutions, including identity verification, access control, monitoring, and compliance support.
These services are often delivered through cloud-based platforms, allowing for quicker deployment and easier management. The managed approach also helps companies stay updated with the latest security protocols without heavy investment. This shift is making Zero Trust more accessible to a broader range of industries and organizations, accelerating market growth.
Integration of Zero Trust with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
The convergence of Zero Trust Security with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is becoming a key trend across the cybersecurity landscape. SASE combines network security functions with wide-area networking capabilities, delivered as a cloud service. Integrating Zero Trust principles into SASE frameworks strengthens security by ensuring that every access request is continuously verified and that least-privilege policies are enforced.
This combination provides a unified solution for secure remote access, data protection, and network optimization. Organizations are adopting this approach to manage growing cloud workloads, distributed users, and hybrid workforces. The seamless integration of identity-based access control and secure connectivity improves overall cybersecurity posture. As cloud adoption continues to rise, the fusion of SASE and Zero Trust is reshaping how businesses build secure, flexible IT environments.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Zero Trust Security Market
- Enhanced Threat Detection and Response: AI helps Zero Trust systems identify unusual behavior by learning user patterns over time. It detects anomalies more quickly than manual systems, enabling faster responses to threats before they cause harm.
- Automated Access Decisions: AI enables real-time, automated decisions about whether to allow or block access based on behavior, location, device health, and risk level. This reduces dependency on static rules and improves dynamic security enforcement.
- Improved Identity Verification: AI strengthens identity and access management by analyzing biometrics, login habits, and device usage. This ensures only legitimate users are granted access, even in complex environments.
- Reduced Human Error: By automating routine security checks and responses, AI lowers the risk of mistakes made by IT teams. This makes Zero Trust systems more consistent and reliable.
- Scalable Protection for Large Environments: AI supports Zero Trust adoption across large and complex networks by continuously analyzing huge volumes of data and adapting to new threats without manual updates.
Research Scope and Analysis
By Offering Analysis
Solutions will be dominating in 2025 with a major share of 71.7%, playing a major role in driving the Zero Trust Security market forward. These solutions include key tools like identity and access management, data security, endpoint protection, and network segmentation. Businesses are turning to these technologies to build secure environments that don’t rely on traditional perimeters. The rising use of cloud computing, mobile devices, and remote work makes real-time access control and threat detection more important than ever.
Organizations prefer comprehensive Zero Trust solutions that are easy to integrate and scale. With growing demand for advanced security systems that verify every request, solutions are expected to remain the top choice. They offer flexibility, layered protection, and automation—important factors for businesses looking to stay ahead of modern cyber risks. Their role in creating a safer, more adaptive security structure is central to the market’s ongoing expansion.
Services are seeing significant growth over the forecast period due to their essential role in planning, implementing, and managing Zero Trust frameworks. Companies rely on professional and managed services to design tailored security strategies, especially when lacking in-house expertise. These services support organizations in risk assessment, identity verification setup, and continuous policy enforcement.
As Zero Trust Security adoption increases across various sectors, the need for expert guidance and ongoing system support becomes more important. Services also help businesses keep up with compliance, optimize security operations, and adapt to changing threats. The rising demand for consulting, integration, and monitoring is pushing service providers to expand their offerings. This steady support from services ensures long-term success in Zero Trust deployment, especially for enterprises managing complex or hybrid environments.
By Security Type Analysis
Network security will lead in 2025 with a share of 25.6%, making it a vital part of the Zero Trust Security market growth. As cyber threats become more advanced, businesses are focusing on securing their internal networks with strict access rules, segmentation, and continuous monitoring. Network security in Zero Trust models helps limit lateral movement of threats by allowing only verified traffic between devices, users, and applications. With the growing use of remote work, mobile access, and distributed IT environments, organizations need strong network-level controls to enforce real-time visibility and protection.
Companies are adopting firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and software-defined perimeters to create secure pathways for communication. Network security plays a key role in enforcing Zero Trust principles by verifying every request and reducing risk across both cloud and on-premises environments, making it a central layer in overall security architecture.
Cloud services are gaining strong momentum and are expected to see significant growth over the forecast period within the Zero Trust Security market. As more organizations move their operations to cloud platforms, securing cloud-based applications, storage, and infrastructure becomes critical. Zero Trust frameworks support cloud environments by enforcing strict identity verification, encrypted access, and real-time monitoring of user activities.
Businesses across sectors are increasingly relying on cloud-native security tools to manage remote access, data sharing, and workload protection. The flexible, scalable nature of cloud services allows for faster deployment of Zero Trust principles without the need for large physical infrastructure changes. This makes cloud security an ideal choice for both growing companies and large enterprises aiming to secure dynamic, hybrid work environments. The rising need for secure cloud access and policy-based controls positions this segment as a key driver of market expansion.
By Deployment Mode Analysis
Cloud deployment is set to lead in 2025 with a share of 62.7%, playing a key role in the rise of the Zero Trust Security market. As businesses increasingly shift to cloud environments, there is a growing need for security solutions that protect data, users, and applications across distributed networks. Cloud-based Zero Trust platforms offer fast deployment, scalability, and easier integration with existing systems, making them highly attractive for organizations of all sizes. These solutions enable real-time access control, identity verification, and threat detection without the need for heavy infrastructure.
Companies prefer cloud deployment for its cost-effectiveness and flexibility, especially in hybrid and remote work settings. The ability to manage and enforce security policies from anywhere also makes cloud a preferred choice. As demand grows for secure, adaptive, and centralized cybersecurity solutions, cloud deployment is expected to remain the dominant approach in supporting modern Zero Trust strategies across industries.
On-premise deployment is set to experience significant growth over the forecast period as certain industries continue to prioritize full control over their data and systems. Organizations with strict regulatory requirements or highly sensitive information, such as in government, defense, or healthcare, often choose on-premise models for enhanced privacy and compliance.
These deployments allow for tighter control over network access, identity management, and system updates within internal infrastructure. While cloud options are gaining ground, some enterprises prefer on-premise for its ability to align with specific internal protocols and security policies. On-premise Zero Trust setups also offer integration with legacy systems, which remain in use across many established organizations. The continued investment in building secure and private environments supports the steady growth of this deployment mode, especially where data sovereignty and in-house management are critical to operations.
By Authentication Type Analysis
Multi-factor authentication will be leading in 2025 with a share of 81.8%, making it a vital part of the Zero Trust Security market’s growth. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, relying on just passwords is no longer safe. Multi-factor authentication adds extra layers of protection by requiring users to confirm their identity using two or more methods, such as a code sent to a mobile device, a fingerprint scan, or a secure app. This approach helps prevent unauthorized access even if login credentials are stolen.
Businesses across sectors are adopting multi-factor solutions to meet compliance standards, protect sensitive data, and reduce the risk of breaches. Its ease of integration with existing systems and support for remote access make it a preferred choice. As organizations continue to embrace Zero Trust principles, multi-factor authentication remains a core element in strengthening identity verification and ensuring secure access control.
Single-factor authentication is expected to witness significant growth over the forecast period as it continues to serve specific needs in less sensitive environments. Some organizations and internal systems still use single-factor methods, like usernames and passwords, for quick and simple access. While not as secure as multi-factor options, single-factor authentication can be suitable for low-risk operations or non-critical data.
It is easy to deploy, user-friendly, and requires minimal resources, making it a practical choice for small businesses or legacy applications. In the broader Zero Trust model, it can serve as a starting point for organizations beginning their security journey. Though multi-factor remains the preferred option for high-level protection, the ongoing use of single-factor authentication in basic access scenarios contributes to its steady presence in the market, especially where convenience and speed are key considerations.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
By Industry Vertical Analysis
BFSI will be dominating in 2025 with a share of 27.1%, making it the top industry vertical contributing to the growth of the Zero Trust Security market. With rising cases of financial fraud, data breaches, and digital banking risks, banks and financial institutions are prioritizing strong identity verification, secure data access, and continuous threat monitoring. The Zero Trust model fits well into the sector’s need for strict compliance, privacy protection, and fraud prevention.
Financial firms are adopting multi-factor authentication, secure cloud access, and endpoint protection to reduce cyber risks while enabling digital transactions and online services. As digital banking expands and customer data grows in volume, Zero Trust offers a proactive and adaptive security layer. The sector’s need for real-time monitoring and policy enforcement keeps driving its reliance on Zero Trust architecture, making BFSI a major force in the market’s expansion.
Further, IT & Telecom is expected to see significant growth over the forecast period as the industry faces growing pressure to secure vast networks, remote users, and digital platforms. With rising data traffic, cloud adoption, and connected devices, companies in this sector require strong, flexible security frameworks. Zero Trust Security supports these needs by providing real-time access control, user verification, and network segmentation.
IT service providers also play a key role in delivering secure services to other industries, making their own systems high-value targets for cyberattacks. The push for 5G, edge computing, and hybrid work further increases security demands. Zero Trust helps telecom and tech companies reduce vulnerabilities and maintain service integrity, making it an essential part of their digital infrastructure strategy.
The Zero Trust Security Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Offering
- Solutions
- Identity and Access Management
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW)
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
- Services
- Professional Services
- Managed Services
By Security Type
- Network Security
- Endpoint Security
- Cloud Security
- Application Security
- Data Security
- Identity Security
By Deployment Mode
- On-Premise
- Cloud-Based
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
By Authentication Type
- Single-Factor Authentication
- Multi-Factor Authentication
- Biometric Authentication
- Token-Based Authentication
- Smart Card Authentication
By Industry Vertical
- BFSI
- Healthcare
- IT & Telecom
- Retail & E-commerce
- Government & Defense
- Energy & Utilities
- Manufacturing
- Education
- Others
Regional Analysis
Leading Region in the Zero Trust Security Market
North America, leading in 2025 with a share of 37.4%, plays a dominant role in the growth of the Zero Trust Security market. The region’s strong position is supported by widespread cloud adoption, a highly digital business environment, and rising incidents of cyberattacks that push both public and private organizations to strengthen their defenses. Regulatory efforts, such as government mandates promoting Zero Trust models for federal networks, further boost adoption.
Companies across sectors, including finance, healthcare, and critical infrastructure, are actively investing in Zero Trust frameworks to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance. The presence of major cybersecurity vendors, continuous innovation, and a mature IT ecosystem contribute to North America’s leadership in this space. Growing awareness, advanced threat landscapes, and the need for remote and hybrid work security are also key drivers. With the year still ongoing, the region is estimated to maintain its lead in Zero Trust Security through continued investment, policy support, and early technology adoption.
ℹ
To learn more about this report –
Download Your Free Sample Report Here
Fastest Growing Region in the Zero Trust Security Market
Asia Pacific is showing significant growth in the Zero Trust Security market over the forecast period, driven by rapid digital transformation, increased cyber threats, and the expansion of cloud computing. Businesses across countries like China, India, Japan, and Australia are adopting Zero Trust architecture to secure remote workforces, manage access controls, and protect sensitive data.
Growing investment in cybersecurity infrastructure, rising awareness, and government initiatives focused on digital security are further supporting market expansion. The region also benefits from the increasing demand for secure authentication, identity verification, and real-time threat detection. With ongoing developments, Asia Pacific is estimated to become one of the fastest-growing regions in the Zero Trust Security landscape.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Competitive Landscape
The Zero Trust Security market is becoming highly competitive as more technology providers enter the space to meet rising global demand. Companies are developing advanced solutions that combine identity management, access control, cloud security, and threat detection into a single, unified approach. The market includes both large players with broad cybersecurity offerings and smaller firms focused on specific Zero Trust features. With growing attention from governments, sectors like healthcare, finance, and energy are also driving more innovation. Partnerships, mergers, and collaborations are common as vendors try to expand their capabilities and reach. The focus is shifting from standalone tools to integrated platforms that are easy to use, scalable, and adaptable for businesses of all sizes and industries.
Some of the prominent players in the global . are:
- Microsoft
- Google (Cloud)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Cisco Systems
- Palo Alto Networks
- IBM Corporation
- Zscaler
- Okta
- Fortinet
- Broadcom (Symantec)
- CrowdStrike
- McAfee
- Check Point Software Technologies
- VMware (a Broadcom company)
- Akamai Technologies
- Ping Identity
- Forcepoint
- Trend Micro
- RSA Security
- F5 Networks
- Other Key Players
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, Zscaler, Inc. launched a new suite of solutions to help businesses adopt Zero Trust Everywhere. These enhancements to the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange™ platform enable secure, end-to-end segmentation across branches, users, devices, applications, and multi-cloud environments. As organizations face growing complexity from IoT, OT, and cloud adoption, Zscaler’s innovations make networks invisible to attackers and block lateral threat movement. The updates strengthen cybersecurity, simplify infrastructure, and support secure, scalable growth in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
- In February 2025, ThreatLocker introduced new solutions aimed at boosting its platform’s security and efficiency, announced at Zero Trust World 2025 in Orlando. Addressing the growing complexity of cyber threats, the updates focus on delivering effective, affordable, and user-friendly security. As the company highlighted, the innovations reflect its ongoing commitment to usability and simplifying Zero Trust for broader adoption.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 43.0 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 179.5 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
17.2% |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 14.0 Bn |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2023 |
| Forecast Data |
2026 – 2034 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Offering (Solutions and Services), By Security Type (Network Security, Endpoint Security, Cloud Security, Application Security, Data Security, and Identity Security), By Deployment Mode (On-Premise and Cloud-Based), By Authentication Type (Single-Factor Authentication and Multi-Factor Authentication), By Industry Vertical (BFSI, Healthcare, IT & Telecom, Retail & E-commerce, Government & Defense, Energy & Utilities, Manufacturing, Education, and Others) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, Rest of Europe; Asia-Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
Microsoft, Google (Cloud), Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cisco Systems, Palo Alto Networks, IBM Corporation, Zscaler, Okta, Fortinet, Broadcom (Symantec), CrowdStrike, McAfee, Check Point Software Technologies, VMware (a Broadcom company, Akamai Technologies, Ping Identity, Forcepoint, Trend Micro, RSA Security, F5 Networks, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the Global Zero Trust Security Market?
▾ The Global Zero Trust Security Market size is expected to reach a value of USD 43.0 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 179.5 billion by the end of 2034.
Which region accounted for the largest Global Zero Trust Security Market?
▾ North America is expected to have the largest market share in the Global Zero Trust Security Market, with a share of about 37.4% in 2025.
How big is the Zero Trust Security Market in the US?
▾ The Zero Trust Security Market in the US is expected to reach USD 14.0 billion in 2025.
Who are the key Zero Trust Security Market?
▾ Some of the major key players in the Global Zero Trust Security Microsoft, Google (Cloud), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and others
What is the growth rate in the Global Zero Trust Security Market?
▾ The market is growing at a CAGR of 17.2 percent over the forecasted period.