Market Overview
The Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market is expected to be valued at USD 18.9 billion in 2025, and is further anticipated to reach USD 141.4 billion by 2034 at a CAGR of 25.1%.
The global Edge AI for smart grid market refers to the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) at the edge of power grid infrastructure to enhance energy distribution, management, and efficiency. Edge AI enables real-time data processing within grid systems, allowing utilities and energy providers to make intelligent, automated decisions without relying solely on centralized cloud computing. This market is driven by the growing need for decentralized energy systems, grid modernization, and the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources.
Edge AI for Smart Grid market growth is driven by rising consumer demand for real-time data processing, efficient energy management strategies, and enhanced grid reliability. Edge AI refers to deploying artificial intelligence algorithms at the edge of a network, closer to data sources for faster decision-making, and reduced dependency on centralized cloud systems.
Edge AI provides smart grids with enhanced efficiency in power distribution, demand response, and predictive maintenance by providing localized intelligence at substations, transformers, and smart meters. This reduces latency, optimizes grid performance, and enhances resilience against outages or cyber threats. Integrating Edge AI with smart grids is rapidly transforming the energy landscape, promoting sustainability and operational efficiency.
One of the advantages of Edge AI in smart grids is its ability to process vast amounts of data locally, eliminating delays, and increasing transmission costs associated with cloud-based analytics. Traditional smart grids rely on cloud-based analytics, which can result in delays and increased transmission costs. Edge AI, on the other hand, allows critical computations to be performed closer to the source, minimizing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making. For instance, AI-powered edge devices can instantly detect fluctuations in energy demand, voltage irregularities, or equipment failures, enabling swift corrective measures. This is particularly beneficial for renewable energy integration, where solar or wind power generation fluctuations require immediate adjustments to maintain grid stability.
Another significant aspect of Edge AI in smart grids is its role in predictive maintenance and fault detection. Conventional grid maintenance often follows a reactive or time-based approach, leading to inefficiencies and unexpected failures. By leveraging machine learning algorithms on edge devices, smart grids can continuously monitor the health of grid components and predict potential failures before they occur, which reduces downtime, lowers maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of critical infrastructure.
Additionally, by detecting and isolating faults in real-time, Edge AI enhances grid resilience, preventing cascading failures and large-scale blackouts. Cybersecurity is another crucial factor driving the adoption of Edge AI in smart grids. As smart grids become increasingly interconnected with IoT devices and cloud systems, they are vulnerable to cyber threats that can disrupt operations.
Edge AI helps reduce these risks by reducing data transmission to centralized servers, limiting exposure to potential cyberattacks. Furthermore, AI-driven anomaly detection at the edge can identify and respond to security breaches in real-time, enhancing the overall security posture of the grid. The ability to decentralize data processing also ensures that grid operations can continue even in the event of network disruptions or cyber incidents. Edge AI facilitates dynamic load balancing, grid optimization, and demand-side management by analyzing consumption patterns and adjusting power distribution accordingly. It also supports the implementation of smart energy pricing models, allowing consumers to make informed decisions about their energy consumption.
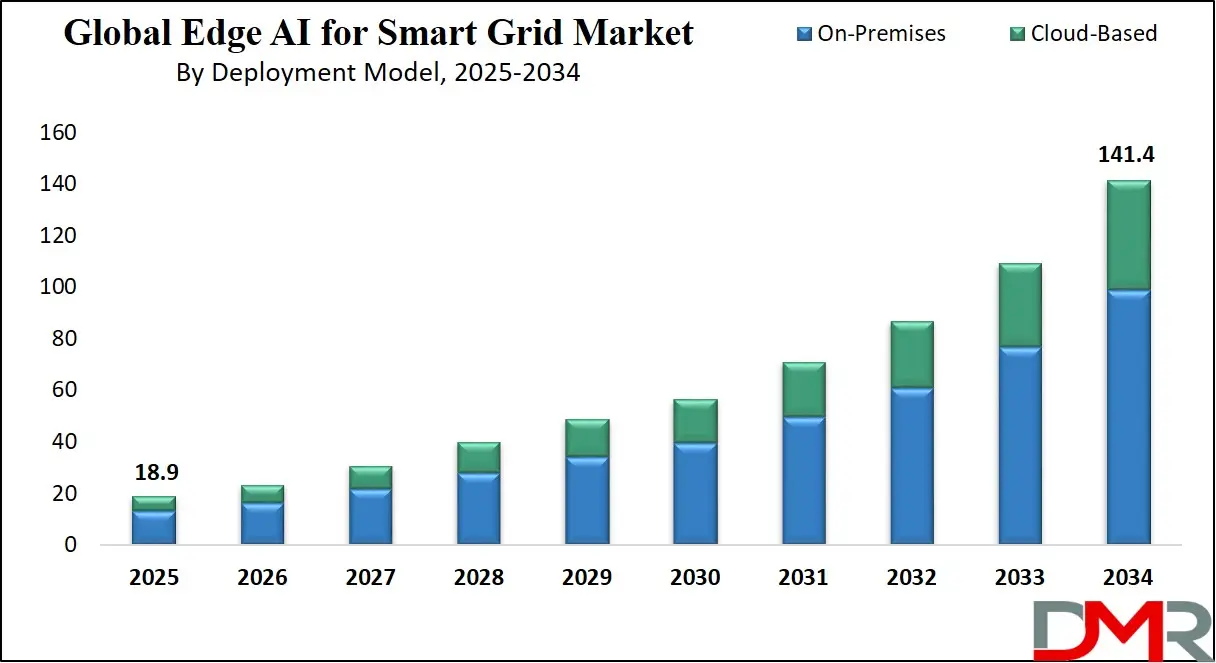
The US Edge AI for Smart Grid Market
The US Edge AI for Smart Grid Market is projected to be valued at
USD 5.2 billion in 2025. It is further expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period, holding
USD 35.1 billion in 2034 at a
CAGR of 23.5%.
The adoption of Edge AI for smart grids in the US is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing investments in grid modernization, the rising penetration of renewable energy, and the need for enhanced grid resilience. The US power grid is one of the world’s largest and most complex electricity networks, requiring cutting-edge technological solutions to enhance efficiency, reliability, and security. Edge AI plays a crucial role in transforming the nation’s grid infrastructure by enabling real-time decision-making at the edge, reducing dependency on centralized data centers, and optimizing power distribution. With initiatives such as the US Department of Energy’s Grid Modernization Initiative and federal investments in AI and
machine learning, the country is poised to lead in the integration of Edge AI into smart grid systems.
One of the key drivers for Edge AI adoption in the U.S. smart grid market is shifting reliance on renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Renewable power generation presents challenges to maintaining grid stability, necessitating real-time data analytics, and rapid response mechanisms to maintain grid equilibrium. Edge AI provides solutions by facilitating distributed energy resource (DER) management, and ensuring efficient integration of solar panels, wind farms, and battery storage systems.
AI-enabled edge devices installed at substations and transformer stations analyze fluctuations in power generation and consumption, making immediate adjustments to balance supply and demand. This is especially crucial in states like California and Texas, which lead in renewable energy adoption while simultaneously experiencing grid stability issues.
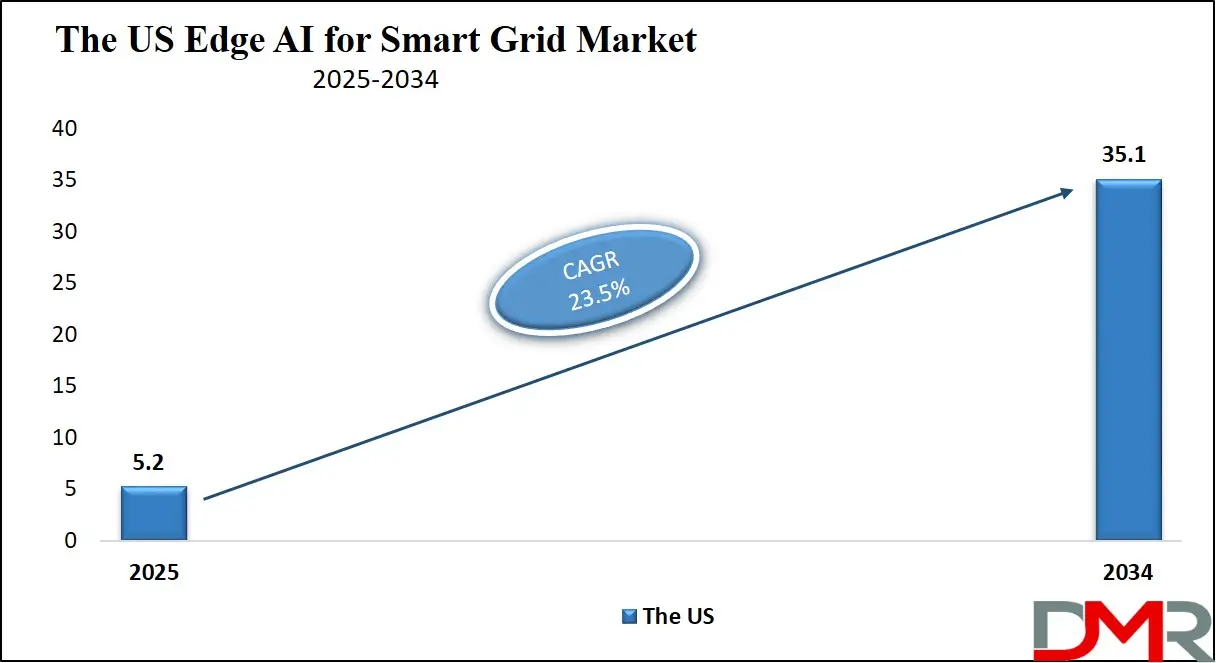
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Key Takeaways
- Market Value: The global edge AI for smart grid market size is expected to reach a value of USD 141.4 billion by 2034 from a base value of USD 18.9 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of 25.1%.
- By Component Type Segment Analysis: Hardware components are anticipated to lead in the component type segment, capturing 44.0% of the market share in 2025.
- By Deployment Model Type Segment Analysis: On Premises deployment model is poised to consolidate its market position in the deployment model type segment capturing 70.0% of the total market share in 2025.
- By Application Type Segment Analysis: Grid Management applications are expected to maintain their dominance in the application type segment capturing 34.0% of the total market share in 2025.
- Regional Analysis: North America is anticipated to lead the global edge AI for smart grid market landscape with 33.0% of total global market revenue in 2025.
- Key Players: Some key players in the global edge AI for smart grid market are NVIDIA Corporation, Intel Corporation, IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Siemens AG, General Electric (GE Grid Solutions), Cisco Systems, Inc., Schneider Electric SE, ABB Ltd., Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Itron, Inc., Oracle Corporation, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., and Other Key Players.
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Use Cases
- Real-Time Energy Demand Response and Load Balancing: In smart grids, managing fluctuating energy demand is a critical challenge, especially with the integration of variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Edge AI enables real-time energy demand response by analyzing consumption patterns at the edge of the network, such as smart meters, substations, and transformers. AI-driven edge devices process vast amounts of local data without relying on centralized cloud systems, allowing instant adjustments in energy distribution.
- Predictive Maintenance and Fault Detection in Grid Infrastructure: Aging power infrastructure and unexpected equipment failures pose significant risks to grid reliability. Traditional maintenance practices are either reactive (fixing issues after failures occur) or scheduled-based, leading to inefficiencies and increased operational costs. Edge AI revolutionizes this process by enabling predictive maintenance through real-time monitoring of transformers, substations, circuit breakers, and power lines.
- Cybersecurity and Anomaly Detection in Smart Grids: With the increasing digitalization of power grids, cybersecurity threats are becoming a major concern for utilities and energy providers. Traditional cybersecurity solutions rely on centralized monitoring, which can delay response times and leave the grid vulnerable to cyberattacks. Edge AI enhances cybersecurity by enabling real-time anomaly detection at the local level, reducing the risk of widespread attacks. AI-powered edge devices continuously monitor network traffic, identify irregular patterns, and autonomously respond to potential threats before they escalate.
- Renewable Energy Integration and Microgrid Optimization: The transition to renewable energy sources requires advanced grid management solutions to handle the intermittent nature of solar and wind power. Edge AI plays a key role in optimizing microgrids, which are localized energy networks that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. By deploying AI-powered edge devices at renewable energy plants, storage facilities, and distribution points, smart grids can efficiently manage energy flows, predict fluctuations in power generation, and enhance grid stability.
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Stats & Facts
- According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global electricity consumption rose by an estimated 4.3% year-on-year in 2024, up from 2.5% in 2023. This growth is expected to continue at a robust 3.9% in the outlook period.
- In addition, IEA reports that the electricity demand in emerging markets and developing economies is projected to increase by over 2,600 TWh by 2030, equivalent to five times Germany's current electricity demand. To meet this rising demand and facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, the widespread deployment of smart grids is critical for a secure, cost-effective, and clean energy future.
- Additionally, the IEA also emphasizes that delays in grid investment and reform could substantially increase global carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions, hindering energy transitions and jeopardizing the 1.5 °C climate goal.
- As per the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy sources are expected to meet nearly half of global electricity demand by 2030, with an addition of over 5,500 gigawatts (GW) of renewable energy capacity from now until 2030.
- A Stanford University index indicates that the United States leads the world in AI innovation, with private AI investment totaling USD 67.2 billion in 2024, substantially higher than China's USD 7.8 billion.
- In 2023, the United Nations launched an advisory body to provide recommendations on AI governance, comprising technology company executives, government officials, and academics, highlighting international efforts to address AI's societal impacts.
- At the AI Seoul Summit in 2024, 16 global AI technology companies agreed to safety commitments on the development of AI, reflecting a collective move towards responsible AI innovation.
- The IEA's Clean Energy Transitions Programme focuses on accelerating clean energy transitions in major emerging economies, including Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Mexico, and South Africa, emphasizing the role of AI in these regions.
- Additionally, the IEA has developed Energy Efficiency Indicators based on over ten years of data to track energy efficiency across major sectors such as residential services, industry, and transport, aiding in policy development. The IEA provides assessments of climate impacts on energy systems and offers guidance on measures to improve their resilience, including reports focused on hydropower under different climate scenarios.
- Also, the IEA supports over 6,000 experts involved in Technology Collaboration Programs across approximately 300 organizations in 55 countries, facilitating international cooperation in energy technology research and development.
- In November 2023, the first global AI Safety Summit was held in the UK, where 28 countries, including the United States, China, and the European Union, issued a declaration calling for international cooperation to manage AI challenges and risks.
- Microsoft is expanding its AI efforts in the Middle East and Africa in partnership with G42, aiming to compete with China in developing AI technology in developing countries and promote responsible AI use.
- A study by International Data Corporation (IDC) projects that artificial intelligence will augment the global economy by USD 19.9 trillion by 2030, including direct revenues from AI companies and indirect and induced spending.
- The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) highlights that artificial intelligence is the current technological innovation sparking hopes of rapid productivity gains and stirring fears of job loss.
- The IEA's "Electricity Grids and Secure Energy Transitions" report highlights the increasing integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, necessitating advancements in grid infrastructure to maintain stability and reliability.
- A survey by SAS and Coleman Parkes Research revealed that 83% of Chinese respondents were using generative AI, surpassing the global average of 54% and the U.S. rate of 65%.
- Further, in 2024, almost 10% of Britain's planned wind output and nearly 30% of Northern Ireland's were curtailed due to insufficient capacity to transport or store electricity when demand was low.
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Market Dynamic
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Driving Factors
Rising Demand for Real-Time Grid Intelligence and Automation
Traditional power grids rely on centralized data processing, in which information from various grid components such as substations, transformers, and smart meters is transmitted to cloud-based control centers for analysis and decision-making purposes. However, this approach creates significant latency, bandwidth limitations, and inefficiency when handling dynamic energy fluctuations and emergency responses. As energy demand grows and grid complexity increases due to the integration of distributed energy resources (DERs), there is a pressing need for decentralized, real-time processing capabilities, which Edge AI effectively addresses.
Edge AI allows power grids to function with localized intelligence, enabling key decisions to be made at the point of data collection. AI-powered edge devices enable instantaneous responses to fluctuations in electricity demand, voltage irregularities, and equipment failures by processing information directly on-site rather than sending large volumes to distant servers.
Integration of Renewable Energy and Decentralized Power Generation
As nations work toward sustainability goals and carbon neutrality, solar, wind, and other forms of renewable energy sources have seen tremendous success in becoming mainstream energy solutions. However, these energy sources bring inherent variation and intermittency that makes it more challenging for traditional power grids to maintain stability and reliability. Unlike conventional fossil-fuel-based power plants, which provide a consistent and controllable power supply, renewables depend on environmental conditions, such as sunlight and wind speed, which fluctuate unpredictably.
To effectively manage these dynamic energy flows, utilities and grid operators are increasingly turning to Edge AI-powered solutions. Edge AI helps improve renewable energy integration efficiency by providing localized real-time monitoring and optimization of distributed energy resources (DERs). AI-enabled edge devices installed at solar farms, wind turbines, battery storage units, and substations immediately assess energy generation and consumption patterns.
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Restraints
High Initial Deployment Costs and Infrastructure Complexity
Edge AI provides many benefits, such as real-time decision making, improved grid stability, and stronger cybersecurity. However, its implementation involves significant investments in hardware, software, and network infrastructure. Utilities and grid operators must deploy AI-powered edge devices like smart sensors, intelligent controllers, and distributed computing units throughout substations, transformers, and other crucial grid components. Additionally, integrating these AI-driven systems with existing grid management platforms often involves upgrading legacy infrastructure, which can be both time-consuming and expensive. The cost of deploying Edge AI is further compounded by the need for robust communication networks to support seamless data exchange between edge devices and central control systems.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
As smart grids become more digitalized and connected, they generate and process vast amounts of sensitive data generated from power generation units, substations, smart meters, and consumer devices. Edge AI, which operates by processing data locally at the edge of the network, helps reduce reliance on centralized cloud systems, but it also introduces new cybersecurity challenges. The decentralized nature of Edge AI increases the number of access points within the grid, making it more susceptible to cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
AI-powered edge devices continuously collect real-time energy consumption data that provides valuable insight into consumer behaviors, industrial operations, and critical infrastructure performance. If compromised, this data can be exploited for malicious purposes, including cyberattacks, fraud, or surveillance. For example, hackers could target edge computing nodes at substations or smart meters to manipulate power distribution, disrupt grid operations, or gain control over connected devices.
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market : Opportunities
Expansion of Smart Cities and IoT-Enabled Energy Infrastructure
As urbanization accelerates globally, governments and municipalities are investing in smart city initiatives that integrate advanced technologies to improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and enhance urban resilience. Smart grids, powered by Edge AI, play a crucial role in enabling these developments by ensuring real-time energy management, optimizing power distribution, and enhancing grid stability to meet the increasing electricity demands of modern cities.
The proliferation of IoT-connected devices in urban infrastructure such as smart meters, intelligent street lighting, EV charging stations, and distributed energy resources (DERs) is generating vast amounts of real-time data. Edge AI is essential for processing this data at the source, enabling faster decision-making, and reducing the burden on centralized cloud systems. By leveraging AI-powered edge computing, smart grids can dynamically adjust energy distribution based on real-time demand, detect faults instantly, and enhance energy efficiency in high-density urban areas.
Growing Investments in Renewable Energy and Grid Modernization
As countries globally transition toward clean energy to meet sustainability goals and reduce carbon emissions, governments and energy providers are allocating significant resources to upgrade aging power infrastructure and integrate renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. This shift creates a strong demand for advanced technologies like Edge AI, which can enhance the efficiency, reliability, and intelligence of modern power grids.
Renewable energy sources are inherently variable, as their output depends on environmental conditions like sunlight availability or wind speed. Traditional grid systems, which were designed for centralized, steady power generation, struggle to handle these fluctuations efficiently. Edge AI offers a solution by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and autonomous energy management at the grid’s edge. AI-powered edge devices can optimize energy flow, predict renewable energy generation patterns, and dynamically balance power distribution across the grid.
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Trends
Adoption of AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance for Smart Grids
Traditional grid maintenance approaches rely on scheduled inspections or reactive repairs after failure occurs, which leads to inefficiencies, high operational costs, and potential power outages. Edge AI allows utilities to shift towards predictive and preventive maintenance strategies using real-time data analysis that detect potential faults before they cause disruptions.
Edge AI-enabled sensors and monitoring devices are being utilized across critical grid infrastructure such as transformers, circuit breakers, substations, and power lines to collect operational data such as voltage fluctuations, temperature variations, and equipment vibrations. By applying machine learning algorithms at the edge, the system can identify early warning signs of wear and tear, enabling utilities to take proactive measures before a failure occurs. This not only minimizes downtime but also reduces maintenance costs by preventing unnecessary servicing of healthy components.
Integration of Edge AI with 5G for Real-Time Smart Grid Operations
As power grids become increasingly complex due to the integration of renewable energy, electric vehicles (EVs), and decentralized power generation, the need for high-speed, reliable, and low-latency communication networks is more critical than ever. The rollout of 5G networks provides a transformative opportunity for smart grids by significantly enhancing data transmission speeds and connectivity between edge devices, grid control centers, and distributed energy resources (DERs).
Edge AI-powered sensors and controllers deployed across substations, power lines, and consumer energy devices can instantly communicate with each other over 5G networks, enabling seamless coordination between different parts of the grid. This real-time connectivity is crucial for balancing power loads, detecting faults, and optimizing energy distribution, particularly in dynamic grid environments where renewable energy sources fluctuate unpredictably.
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Component Analysis
The hardware components segment is projected to dominate the component type category, accounting for 44.0% of the market share in 2025. As smart grids become more sophisticated, there is a growing need for high-performance computing hardware, including AI processors, edge servers, and intelligent controllers, to enable real-time data processing and decision-making. These devices allow utilities to analyze power consumption patterns, detect anomalies, and optimize grid performance with minimal latency.
One major reason behind the hardware segment's dominance is the incorporation of AI chipsets and accelerators into grid infrastructure, facilitating on-device machine learning to reduce reliance on cloud-based systems while speeding response times in critical grid operations. Additionally, advancements in semiconductor technology are making AI-powered edge hardware more efficient and cost-effective, encouraging widespread adoption among power utilities. The deployment of microcontrollers, GPUs, and dedicated AI chips in substations and smart meters further strengthens this segment’s position in the market.
The software segment is a crucial component of the Edge AI for smart grid market, enabling the seamless operation, optimization, and automation of AI-driven grid management systems. While hardware forms the foundation of
edge computing, software provides the intelligence required to process real-time data, make predictive decisions, and optimize power distribution. As utilities globally shift toward digital transformation, the demand for AI-powered software solutions is increasing, driving significant growth in this segment. One major driver for software innovation is
artificial intelligence -powered predictive analytics platforms that help utilities monitor grid conditions, forecast demand, and detect potential failures before they happen. These solutions utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze massive datasets collected from sensors, smart meters, and distributed energy resources (DERs).
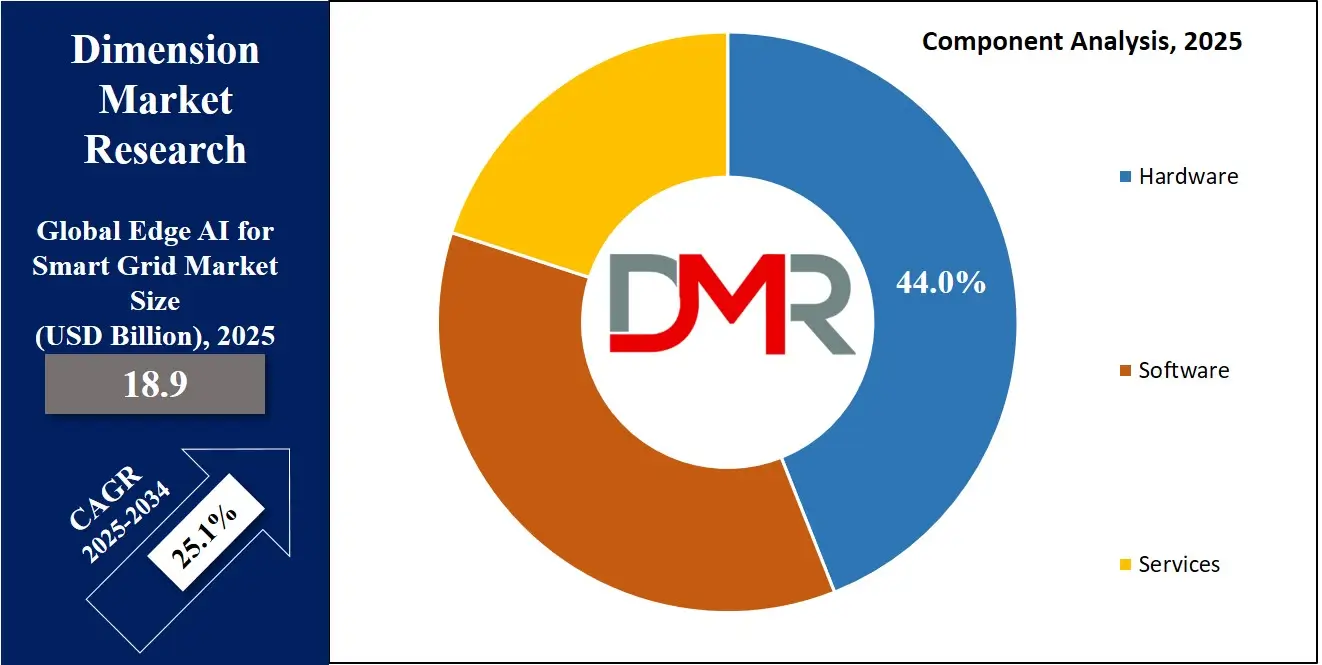
By Deployment Mode Analysis
The on-premises deployment model is set to strengthen its market position within the deployment model type segment, capturing
70.0% of the total market share in 2025. This dominance is largely driven by the critical need for real-time data processing, enhanced security, and operational control in the energy sector. On-premises deployment ensures that AI-powered grid management systems operate within a controlled environment, reducing latency, and speeding decision making processes.
Given the complexity of modern power grids, where split-second adjustments are essential for load balancing, fault detection, and energy optimization, on-premises solutions provide an advantage by allowing direct data processing at the edge without reliance on external servers. Another factor contributing to the dominance of this model is the stringent regulatory compliance and data privacy requirements imposed upon power utilities and grid operators by governments and regulatory bodies.
Governments require that critical grid data is processed and stored within national infrastructure to prevent cybersecurity threats and unauthorized access. On-premises AI deployment helps utilities comply with these requirements by keeping sensitive operational data within secure local environments.
The cloud-based deployment model is also gaining traction, particularly among utilities seeking scalability, remote accessibility, and cost flexibility. Cloud-based AI allows grid operators to leverage advanced machine learning models from central processing for massive datasets collected from smart meters, IoT devices, and distributed energy systems.
By taking advantage of cloud AI's continuous updates, advanced analytics, and central grid monitoring services, they can benefit from optimizing large-scale smart grid operations. One key advantage of cloud deployment lies in its capacity for predictive analytics and long-term data storage. Unlike on-premises systems that process data locally for immediate decision making, cloud solutions store historical data, allowing energy providers to conduct trend analyses, forecast demand, optimize grid performance over time, and conduct trend analyses.
By Application Analysis
Grid management applications are expected to retain their leading position in the Edge AI for smart grid market, accounting for 34.0% of the total market share in 2025. This growth is driven by the rising demand for real-time monitoring, automation, and optimization of power grids, fueled by increasing electricity consumption and the accelerated integration of renewable energy sources. Traditional grid management systems often rely on slow centralized control mechanisms that are exposed to fluctuations and inefficiencies.
However, with the advent of Edge AI, power utilities can now analyze, predict, and act on grid conditions in real time, ensuring improved stability, efficiency, and resilience. One key reason behind the popularity of grid management applications is their growing complexity. Renewable sources, electric vehicles (EVs), and battery storage technologies have combined to create dynamic grid environments which require instantaneous decision-making processes. AI-powered grid management apps deployed at the edge enable utilities to effectively manage this complexity by optimizing energy distribution, balancing loads, and preventing congestion within their networks.
The asset management segment plays a critical role in the Edge AI for smart grid market by enhancing the monitoring, maintenance, and optimization of grid infrastructure. As modern power grids become more complex, utilities must ensure the reliability and longevity of key assets such as transformers, substations, power lines, and distributed energy resources (DERs).
Traditionally, asset management relied on scheduled inspections and reactive maintenance, often leading to costly downtimes and unplanned outages. However, with the integration of AI-driven edge computing, asset management has evolved into a more predictive and proactive approach, ensuring maximum operational efficiency.
One of the primary drivers behind AI-powered asset management systems is their ability to reduce equipment failures and extend asset lifespan. Edge AI enables real-time condition monitoring by processing data from smart sensors, IoT devices, and intelligent meters deployed across the grid. These sensors collect information on parameters such as temperature, vibration, voltage fluctuations, and load stress, helping AI models detect early signs of wear, degradation, or potential faults.
The Edge AI for Smart Grid Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following
By Component
- Hardware
- Processors
- Sensors
- Memory Devices
- Edge Nodes/Gateways
- Others
- Software
- Edge AI Platforms
- Analytics Software
- Machine Learning Models
- Data Management Tools
- Others
- Services
- Deployment and Integration
- Maintenance and Support
- Training and Consulting
By Deployment Model
By Application
- Grid Management
- Load Forecasting
- Demand Response
- Outage Management
- Voltage/VAR Optimization
- Others
- Asset Management
- Predictive Maintenance
- Asset Health Monitoring
- Fault Detection and Diagnosis
- Others
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Smart Meter Data Analytics
- Energy Theft Detection
- Billing and Customer Insights
- Others
- Distributed Energy Resource Management
- Renewable Integration
- Microgrid Control
- Energy Storage Optimization
- Others
- Others
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Regional Analysis
Region with the Largest Revenue Share
North America is expected to dominate the global Edge AI for smart grid market,
capturing 33.0% of total market revenue in 2025. The region's success can be attributed to technological advancements, wide-scale smart grid deployments, and robust government initiatives aimed at modernizing energy infrastructure. Furthermore, North America has been at the forefront of integrating artificial intelligence with power grid operations by using edge computing techniques for increased efficiency, reliability, and resilience. Utilities across North America and Canada have actively invested in AI-powered solutions to optimize energy distribution, minimize outages, and support transition towards more sustainable and decentralized energy ecosystem.
North America's market growth is being propelled by rapid adoption of smart meters, IoT-enabled sensors, and AI-driven automation technologies. North America boasts one of the highest penetration rates of smart grid technologies, utilities are using Edge AI systems at local substations, transformers, and distributed energy resource (DER) nodes to process real-time data locally in real time, enabling instantaneous grid adjustments, autonomous fault detection, and optimization energy flow without depending on centralized data centers.
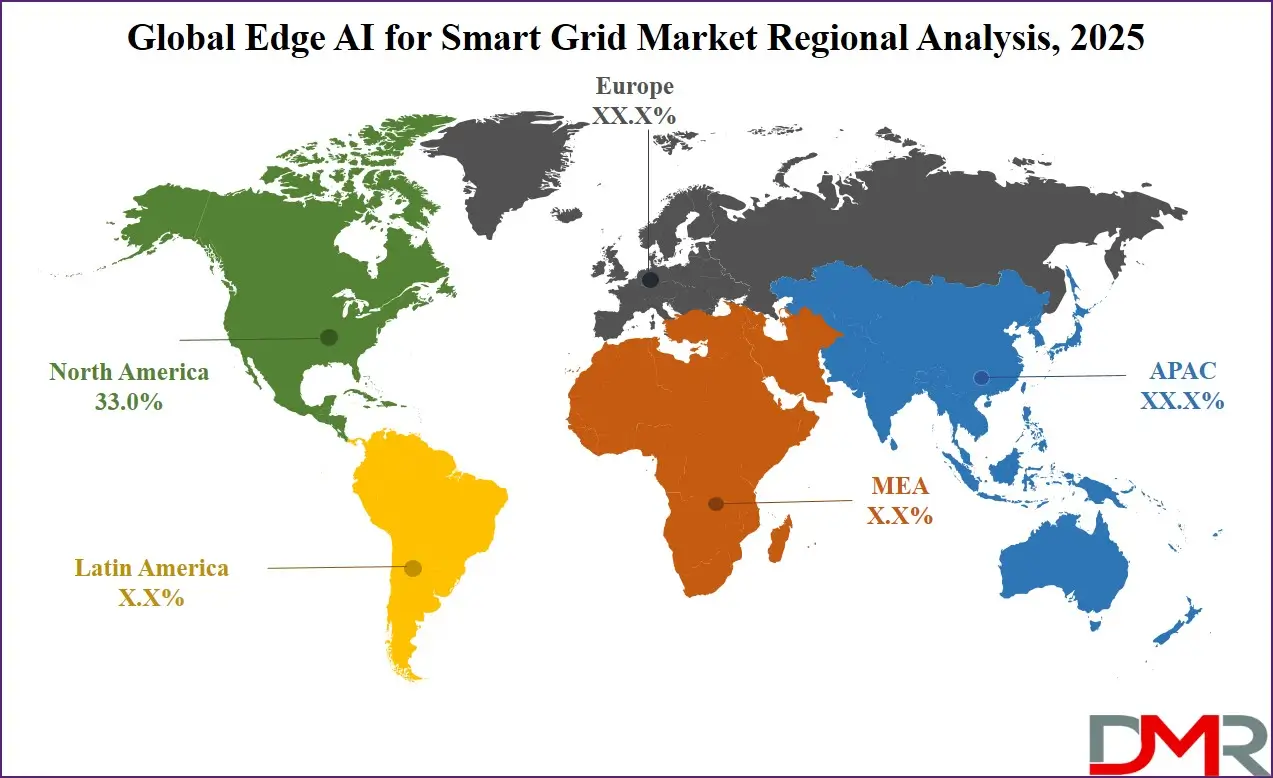
Region with the Highest CAGR
Asia Pacific is projected to experience the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the Edge AI for smart grid market, driven by rapid urbanization, expanding energy demand, and large-scale investments in smart grid infrastructure. The region is undergoing a significant transformation in its power sector, shifting towards AI-powered automation, renewable energy integration, and digitalized grid management. Countries like China, Japan, India, and South Korea are at the forefront of adopting Edge AI solutions to enhance energy efficiency, improve grid reliability, and support carbon neutrality goals.
One of the primary reasons for Asia Pacific's rapid growth is the rising electricity consumption fueled by industrialization and population expansion. With urban centers growing at an unprecedented pace, power grids face immense pressure to handle increasing loads, prevent energy losses, and reduce transmission inefficiencies. Edge AI plays a crucial role in addressing these challenges by automating grid operations, optimizing energy distribution in real time, and enabling predictive maintenance to minimize outages and ensure uninterrupted power supply.
By Region
North America
Europe
- Germany
- The U.K.
- France
- Italy
- Russia
- Spain
- Benelux
- Nordic
- Rest of Europe
Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- ANZ
- ASEAN
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Colombia
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- South Africa
- Israel
- Egypt
- Rest of MEA
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Competitive Landscape
The global Edge AI for smart grid market is marked by intense competition among established industry leaders, technology firms, and innovative startups. Companies are competing to develop AI-powered solutions that improve grid automation, optimize energy distribution, and increase reliability. Major players have made substantial investments in edge computing, predictive analytics, and decentralized energy management to meet growing demands for intelligent power infrastructure.
The developing need for efficient and self-sustaining grid systems has led to a surge in technological advancements, with firms leveraging AI to enable real-time decision-making and fault detection within the grid network. Leading companies such as General Electric, Siemens, Schneider Electric, ABB, and Hitachi Energy are at the forefront of the market, offering advanced AI-driven grid management solutions.
These firms leverage their expertise in automation and energy optimization to deploy intelligent grid analytics, predictive maintenance, and AI-powered control systems. Alongside them, technology giants including IBM, Nvidia, Microsoft, and others are integrating AI capabilities with edge computing to enhance the performance and scalability of smart grid infrastructure.
Some of the prominent players in the global Edge AI for Smart Grid market are:
- NVIDIA Corporation
- Intel Corporation
- IBM Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- Siemens AG
- General Electric (GE Grid Solutions)
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Schneider Electric SE
- ABB Ltd.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Itron, Inc.
- Oracle Corporation
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- SAP SE
- Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Fujitsu Limited
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Nokia Corporation
- Other Key Players
Global Edge AI for Smart Grid Market: Recent Developments
- February 2025: TE Connectivity announced plans to acquire Richards Manufacturing for approximately USD 2.3 billion to strengthen its position in the electrical utilities sector. The deal aims to address increasing electricity demand driven by AI-powered infrastructure and the need for more resilient smart grids. The acquisition is expected to be finalized by June 2025.
- February 2025: NXP signed a definitive agreement to acquire Kinara, an AI chip manufacturer, for USD 307.0 million. This move is aimed at expanding NXP’s capabilities in edge AI computing by integrating Kinara’s advanced processors into its portfolio, further enhancing smart grid automation and AI-driven energy optimization.
- February 2025: NRG Energy partnered with GE Vernova and Kiewit Corp. to develop four natural-gas power plants that will generate approximately 5 gigawatts of electricity to support AI-driven data centers. The collaboration is part of a broader effort to modernize power infrastructure in Texas and other regions.
- February 2025: Constellation Energy acquired Calpine as part of its strategic move to meet the rising electricity demands of AI-driven industries and data centers. The deal is expected to strengthen Constellation’s ability to provide large-scale energy solutions for the growing smart grid sector.
- March 2024: Gcore acquired StackPath’s WAAP solution to enhance its cybersecurity and edge AI capabilities. This acquisition allows Gcore to strengthen its defense mechanisms for smart grid applications, improving network security and AI-driven grid management.
- January 2024: LightEdge expanded its footprint in the colocation and edge computing sector by acquiring a 76,000-square-foot, 3.6 MW data center in Minneapolis. This acquisition is aimed at bolstering LightEdge’s presence in the growing smart grid infrastructure market.
Report Details
|
Report Characteristics
|
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 18.9 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 141.4 Bn |
| CAGR (2025-2034) |
25.1% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| The US Market Size (2025) |
USD 5.2 Bn |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors and etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Component (Hardware, Software, and Services), By Deployment Model (On-Premises, and Cloud-Based), By Application (Grid Management, Asset Management, Advanced Metering Infrastructure, Distributed Energy Resource Management, and Others) |
| Regional Coverage |
North America – The US and Canada; Europe – Germany, The UK, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Europe; Asia- Pacific– China, Japan, South Korea, India, ANZ, ASEAN, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa, Turkey, Egypt, Israel, & Rest of MEA |
| Prominent Players |
NVIDIA Corporation, Intel Corporation, IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Siemens AG, General Electric (GE Grid Solutions), Cisco Systems, Inc., Schneider Electric SE, ABB Ltd., Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Itron, Inc., Oracle Corporation, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., SAP SE, Hitachi Energy Ltd., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Honeywell International Inc., Fujitsu Limited, Dell Technologies Inc., Rockwell Automation, Inc., Nokia Corporation, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user), Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users) and Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to 0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days and 5 analysts working days respectively. |
Frequently Asked Questions
The global edge AI for smart grid market size is estimated to have a value of USD 18.9 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 141.4 billion by the end of 2034.
The US edge AI for smart grid market is projected to be valued at USD 5.2 billion in 2025. It is expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period as it holds USD 35.1 billion in 2034 at a CAGR of 23.5%.
North America is expected to have the largest market share in the global edge AI for smart grid market with a share of about 33.0% in 2025.
Some of the major key players in the global edge AI for smart grid market are are NVIDIA Corporation, Intel Corporation, IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Siemens AG, General Electric (GE Grid Solutions), Cisco Systems, Inc., Schneider Electric SE, and many others.
The market is growing at a CAGR of 25.1 percent over the forecasted period.