The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market size is projected to be valued at
in 2025. It is further expected to witness subsequent growth in the upcoming period, holding
Key players such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the space, providing public cloud solutions that cater to a wide range of industries, including healthcare, finance, and retail. The growing adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud environments has also contributed to the rapid expansion, as companies look for the ability to manage workloads across various cloud platforms while optimizing performance and costs. The rise in data storage needs, along with the surge in remote work and digital transformation initiatives, has further bolstered the demand for cloud infrastructure services in the U.S.
Cloud service providers in the U.S. continue to innovate, delivering advanced solutions such as edge computing, container orchestration, and AI-driven cloud services. These innovations enable businesses to enhance their operational efficiency, reduce latency, and support the growing volume of data generated by IoT devices, applications, and real-time analytics. Public cloud services remain the dominant segment, with enterprise adoption expanding rapidly as organizations of all sizes recognize the benefits of leveraging Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions. Security and compliance remain top priorities, with providers focusing on delivering robust cloud security features, data encryption, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
The U.S. government’s investment in cloud computing has further accelerated the market’s expansion. With federal agencies adopting cloud-first strategies, there is a significant push for cloud modernization to enhance efficiency and drive innovation in public services. Furthermore, the U.S. is home to some of the world’s largest data centers and cloud infrastructure hubs, with companies investing in next-generation technologies to support the growing demand for storage and compute resources.
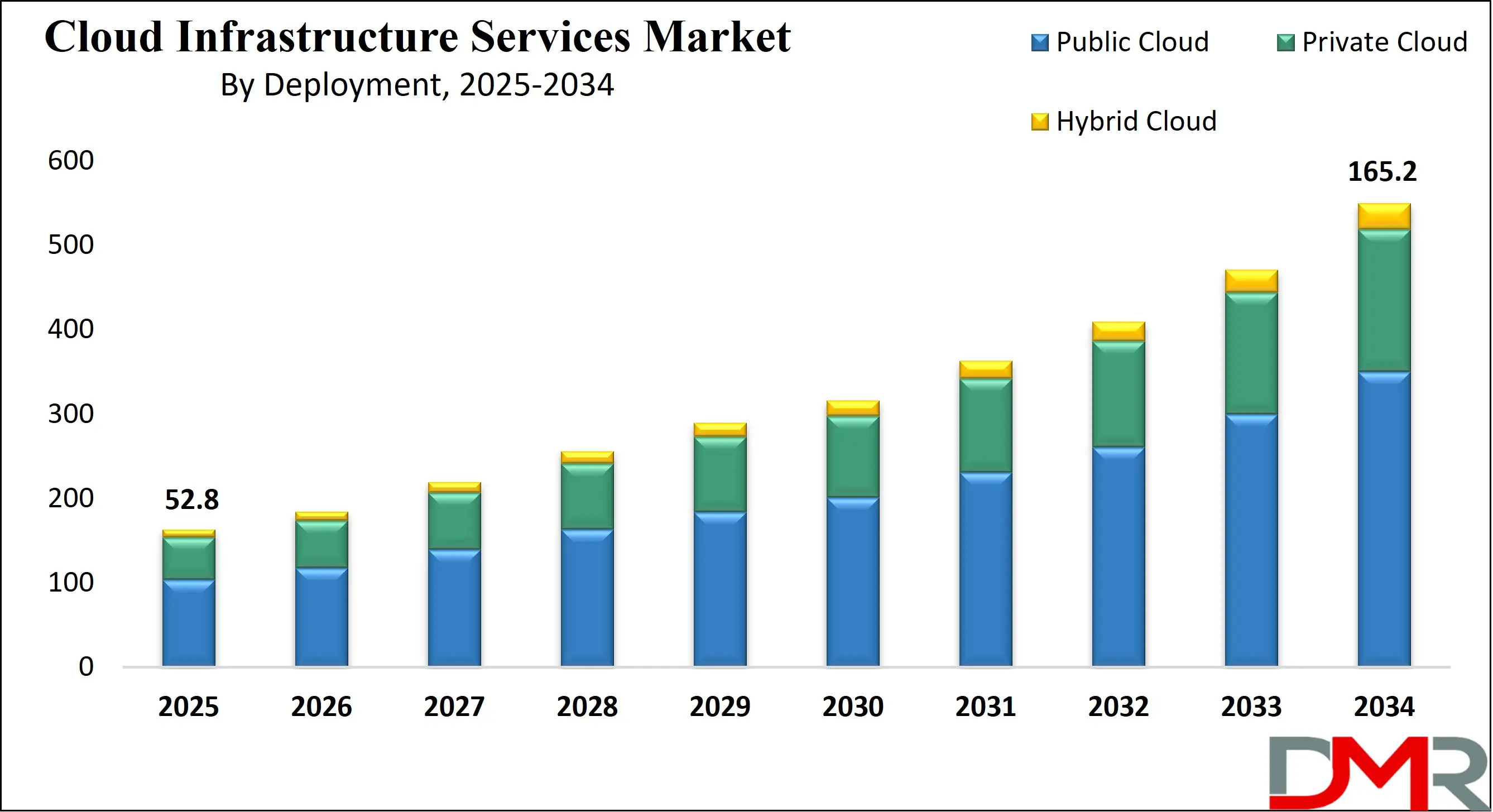
The market’s rapid growth has also led to a surge in the number of cloud infrastructure providers, including regional players, startups, and niche providers, which are expanding their footprint by offering specialized cloud solutions such as private cloud hosting, disaster recovery, and managed services. As the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market continues to evolve, it will play a critical role in shaping the global digital economy, fostering innovation across various sectors, and enabling businesses to thrive in an interconnected world.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Key Takeaways
- Market Value: The U.S. cloud infrastructure services size is expected to reach a value of USD 165.2 billion by 2034 from a base value of USD 52.8 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of 13.5%.
- By Service Type Segment Analysis: Storage as a Service type is poised to consolidate its dominance in the service type segment, capturing 51.2% of the total market share in 2025.
- By Deployment Segment Analysis: Public Cloud deployment model is expected to maintain its dominance in the deployment type segment, capturing 63.6% of the total market share in 2025.
- By Enterprise Size Segment Analysis: Large Enterprises are anticipated to maintain their dominance in the enterprise type segment, capturing 73.5% of the total market share in 2025.
- By Industry Vertical Segment Analysis: The IT & Telecom industry is anticipated to maintain its dominance in the industry vertical segment, capturing 46.9% of the total market share in 2025.
- Key Players: Some key players in the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Salesforce, VMware, Rackspace Technology, Equinix, SAP, Red Hat, DigitalOcean, ServiceNow, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Adobe Cloud, Cloudflare, Nutanix, Citrix Systems, Verisign, Joyent (now part of Samsung), CoreSite Realty Corporation, and Other Key Players.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Use Cases
Cloud-Driven Digital Transformation in Healthcare
The healthcare sector in the U.S. has adopted cloud infrastructure to enable digital transformation, improve patient care, and streamline operations. Cloud computing provides healthcare organizations with scalable, secure, and cost-efficient platforms for storing and processing vast amounts of sensitive patient data. By leveraging cloud-based electronic health records (EHR) systems, healthcare providers can seamlessly share patient information, ensure compliance with regulatory standards like HIPAA, and enhance collaboration among different healthcare providers.
Additionally, cloud platforms support advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, enabling healthcare professionals to offer personalized treatment options and improve patient outcomes. The cloud's flexibility allows healthcare providers to scale their IT infrastructure quickly in response to evolving needs, particularly during crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, when telemedicine and remote patient monitoring became crucial.
Cloud for Financial Services and Banking
Cloud infrastructure has become a cornerstone of innovation in the U.S. financial services sector. Traditional banks and fintech companies are leveraging the cloud to enhance their capabilities in data storage, financial transactions, and regulatory compliance. Cloud-based systems allow financial institutions to process transactions at scale, ensuring high availability and reducing downtime during peak transaction periods.
Moreover, cloud infrastructure enables real-time data analytics, which banks use to detect fraud, manage risks, and provide personalized services to customers. Financial institutions are adopting hybrid cloud models, which allow them to store sensitive customer data on private clouds while utilizing public clouds for non-sensitive operations like customer interactions and data analysis. The scalability and cost efficiency of cloud services are critical for financial institutions looking to modernize their legacy systems and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Cloud for E-Commerce and Retail
The U.S. retail industry has seen a rapid shift towards cloud adoption, particularly among e-commerce giants like Amazon, Walmart, and Shopify. Cloud infrastructure has become essential for managing large volumes of customer data, inventory, and order processing. By using cloud-based solutions, e-commerce platforms can scale their infrastructure dynamically to accommodate fluctuating customer demand, especially during peak shopping seasons like Black Friday and Cyber Monday.
Retailers benefit from the cloud’s ability to provide real-time insights into customer behavior, enabling personalized shopping experiences, targeted marketing campaigns, and efficient supply chain management. Cloud technologies also enable omnichannel strategies, where consumers can shop across multiple platforms (online, mobile, and in-store) seamlessly. With the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the cloud, retailers can optimize their pricing strategies, forecast demand, and enhance customer engagement through chatbots and personalized recommendations.
Cloud for Government and Public Sector Innovation
The U.S. government has been at the forefront of adopting cloud infrastructure to modernize public services and improve operational efficiency. The federal government’s Cloud-First policy has accelerated the adoption of cloud technologies across various departments, enabling faster deployment of applications and services to citizens. Cloud solutions allow government agencies to securely store vast amounts of data, ranging from public records to law enforcement and defense-related information, while ensuring compliance with strict regulations.
Furthermore, cloud computing enhances the government’s ability to scale services during times of crisis, such as during natural disasters or national emergencies. The cloud also plays a critical role in digital transformation initiatives such as smart city projects, where cloud infrastructure is used to manage data from IoT devices, optimize traffic systems, and monitor public health. Cloud-based platforms have also become essential for improving citizen engagement through digital portals and self-service options, enabling easier access to government services and improving overall public sector efficiency.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Stats & Facts
- Department of Defense (DOD)
- In fiscal year 2022, the DoD obligated approximately USD 3 billion for cloud computing contracts, part of a broader USD 7 billion spent by major federal agencies on cloud services.
- General Services Administration (GSA)
- The GSA's Technology Transformation Services (TTS) supports federal agencies in adopting cloud technologies through initiatives like cloud.gov, which provides secure cloud hosting services for federal agencies.
- U.S. Census Bureau
- The Census Bureau's OCIO Cloud Services utilizes FedRAMP-authorized cloud offerings under the shared-responsibility model, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) offerings.
- Government Accountability Office (GAO)
- The GAO has identified leading practices in the private sector for adopting cloud solutions, which can inform federal policymakers and program managers in their efforts to adopt cloud solutions.
- Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
- The DHS migrated its network for information sharing and collaboration to the cloud, ensuring it remains continuously available for law enforcement and emergency response.
- CIO Council
- The CIO Council's "Cloud Smart" strategy emphasizes the federal government's shift to cloud computing, aiming to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics (NCSES)
- The NCSES reports that 19.5% of all firms use data analysis cloud computing services, which is much higher than the adoption rates of other advanced technologies.
- Census Bureau
- The Census Bureau's OCIO Cloud Services utilizes cloud-based systems/components to support its statistical mission of serving as the Nation's leading provider of quality data about its people and economy.
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
- The BLS's Producer Price Index tracks price changes in cloud computing services, providing insights into the economic impact of cloud adoption.
- General Services Administration (GSA)
- The GSA's Office of Government-wide Policy provides resources for federal agencies to modernize their IT infrastructure and technology stacks, including cloud computing services.
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
- The FCC's broadband data collection efforts support the expansion of cloud infrastructure by providing data on broadband availability and adoption.
- Department of Commerce
- The Department of Commerce's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides guidelines and standards for cloud computing, including the definition of cloud service models and deployment models.
- Federal Reserve
- The Federal Reserve has adopted cloud computing solutions for various operations, enhancing efficiency and scalability.
- Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)
- The VA has implemented cloud-based solutions to improve healthcare delivery and data management for veterans.
- Social Security Administration (SSA)
- The SSA utilizes cloud computing to enhance service delivery and data management for beneficiaries.
- Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
- The IRS has adopted cloud-based solutions to improve tax processing and service delivery.
- Department of Education
- The Department of Education utilizes cloud computing to enhance data management and service delivery in education programs.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- The FDA has implemented cloud-based solutions to improve regulatory processes and data management.
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- The EPA uses cloud computing to enhance environmental data management and analysis.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
- NOAA utilizes cloud-based solutions for weather data analysis and forecasting.
- Department of Justice (DOJ)
- The DOJ has adopted cloud computing solutions to improve case management and data analysis.
- Department of Transportation (DOT)
- The DOT utilizes cloud computing for transportation data analysis and infrastructure management.
- Department of Energy (DOE)
- The DOE has implemented cloud-based solutions for energy data management and analysis.
- Department of Agriculture (USDA)
- The USDA uses cloud computing to enhance agricultural data management and analysis.
- Department of Homeland Security
- The DHS has adopted cloud computing solutions for cybersecurity and emergency response coordination.
- Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)
- The HHS utilizes cloud computing for healthcare data management and analysis.
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- NASA has implemented cloud-based solutions for space mission data analysis and management.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Market Dynamics
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Driving Factors
Growing Demand for Scalable and Cost-Efficient Solutions
One of the primary driving factors behind the growth of the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market is the growing demand for scalable and cost-efficient IT solutions. Cloud computing enables businesses of all sizes to scale their IT resources up or down according to their specific needs, which allows them to optimize costs.
As companies move away from traditional on-premises data centers, they are turning to cloud infrastructure for its flexibility, cost savings, and ability to handle fluctuating workloads. Cloud services provide enterprises with access to vast amounts of storage and computing power without the upfront capital expenditures associated with building and maintaining physical infrastructure, which makes it an attractive solution for organizations aiming to reduce operational costs while maintaining high levels of performance.
Rapid Adoption of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
Another significant factor driving the growth of the cloud infrastructure market in the U.S. is the rapid adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud environments. As businesses seek to enhance their agility and avoid vendor lock-in, many are choosing hybrid cloud solutions, which combine both private and public clouds. These solutions enable companies to store sensitive data on private clouds while leveraging public clouds for less critical operations.
Additionally, multi-cloud strategies are gaining traction as organizations use multiple cloud providers to optimize their infrastructure. This allows companies to ensure business continuity, avoid service disruptions, and gain access to best-in-class services across different platforms. The trend toward hybrid and multi-cloud adoption has fueled demand for advanced cloud management tools and platforms, further accelerating market growth.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Restraints
Concerns around Cloud Security and Data Privacy
Despite the benefits, cloud infrastructure services are often met with concerns around security and data privacy, especially for businesses handling sensitive information. Companies are worried about the potential risks of data breaches, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks. While cloud service providers implement robust security measures, such as data encryption, firewalls, and advanced authentication protocols, organizations still fear the potential exposure of sensitive customer and operational data.
This concern, especially in industries like finance, healthcare, and government, can serve as a significant restraint on the full adoption of cloud infrastructure services. Regulatory frameworks like the GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA have heightened the importance of ensuring compliance with data privacy laws, further complicating the decision for businesses to move to the cloud.
Integration and Compatibility Challenges
The complexity involved in integrating cloud infrastructure with legacy IT systems remains a significant restraint for many organizations. Many businesses in the U.S. still rely on legacy systems that were not designed for cloud environments, and the migration process can be complicated and time-consuming. These integration challenges can delay the adoption of cloud services, especially for enterprises with large, complex IT infrastructures.
Moreover, ensuring compatibility between different cloud providers and on-premises systems often requires significant investment in middleware, specialized cloud management tools, and custom development, which can hinder market expansion. These issues are particularly relevant for businesses in highly regulated industries, where seamless integration and full compliance with industry-specific standards are essential.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Opportunities
Cloud Services for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
One of the most promising opportunities in the U.S. cloud infrastructure market is the growing adoption of cloud services by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Traditionally, SMEs were hesitant to adopt cloud solutions due to concerns over costs and complexity. However, as cloud service providers offer more flexible pricing models and simplified solutions, SMEs can access enterprise-grade infrastructure without significant capital investment.
Cloud computing allows SMEs to compete with larger companies by providing access to advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics, which were previously only available to larger enterprises. As more SMEs migrate to the cloud, this segment presents a significant growth opportunity for cloud providers in the U.S.
Cloud-Based AI and Machine Learning Solutions
As AI and machine learning continue to shape industries, cloud infrastructure is being utilized to support these advanced technologies. The availability of powerful computing resources in the cloud has made it easier for businesses to implement AI-driven applications, such as predictive analytics, automated customer service, and data-driven decision-making.
Cloud platforms provide on-demand access to machine learning frameworks and large datasets, reducing the need for costly in-house computing resources. This presents a significant opportunity for cloud service providers to cater to the growing demand for AI and machine learning solutions across industries like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing. As businesses seek to unlock the potential of AI, the demand for cloud infrastructure will continue to rise.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Trends
Edge Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT)
A prominent trend in the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market is the rise of edge computing, driven by the growing adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT). As more devices become connected and generate massive amounts of data, there is a growing need for processing that data closer to its source rather than sending it all to centralized cloud data centers.
Edge computing allows for faster data processing, lower latency, and more efficient use of network resources, particularly in applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation. As IoT devices proliferate, cloud providers are investing in edge computing solutions that will enable businesses to handle real-time data processing and analytics at the edge, opening up new opportunities in industries that rely on low-latency applications.
Serverless Computing and Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)
Serverless computing is emerging as a key trend in the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market, driven by the need for developers to focus on building applications without worrying about managing servers or infrastructure. Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) allows developers to write code that is triggered by events or specific actions, and the cloud provider automatically handles the infrastructure, scaling, and execution.
This model offers businesses a more cost-effective and flexible approach to deploying applications, as they only pay for the computing resources used during execution. The growing popularity of serverless computing reflects a shift toward more agile, event-driven architectures in application development, making it an important trend for both cloud providers and end-users seeking increased efficiency and reduced operational complexity.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Research Scope and Analysis
By Service Type Analysis
The Storage as a Service (STaaS) segment is set to maintain its dominance within the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market, with projections indicating that it will capture 51.2% of the total market share in 2025. This growth can be attributed to the growing demand for scalable and flexible storage solutions, driven by the exponential rise in data generation from enterprises and consumers alike. Businesses are moving away from traditional on-premises storage systems, which often involve significant capital investment and maintenance costs. Instead, they are turning to cloud-based storage solutions that offer greater scalability, reliability, and cost-efficiency.
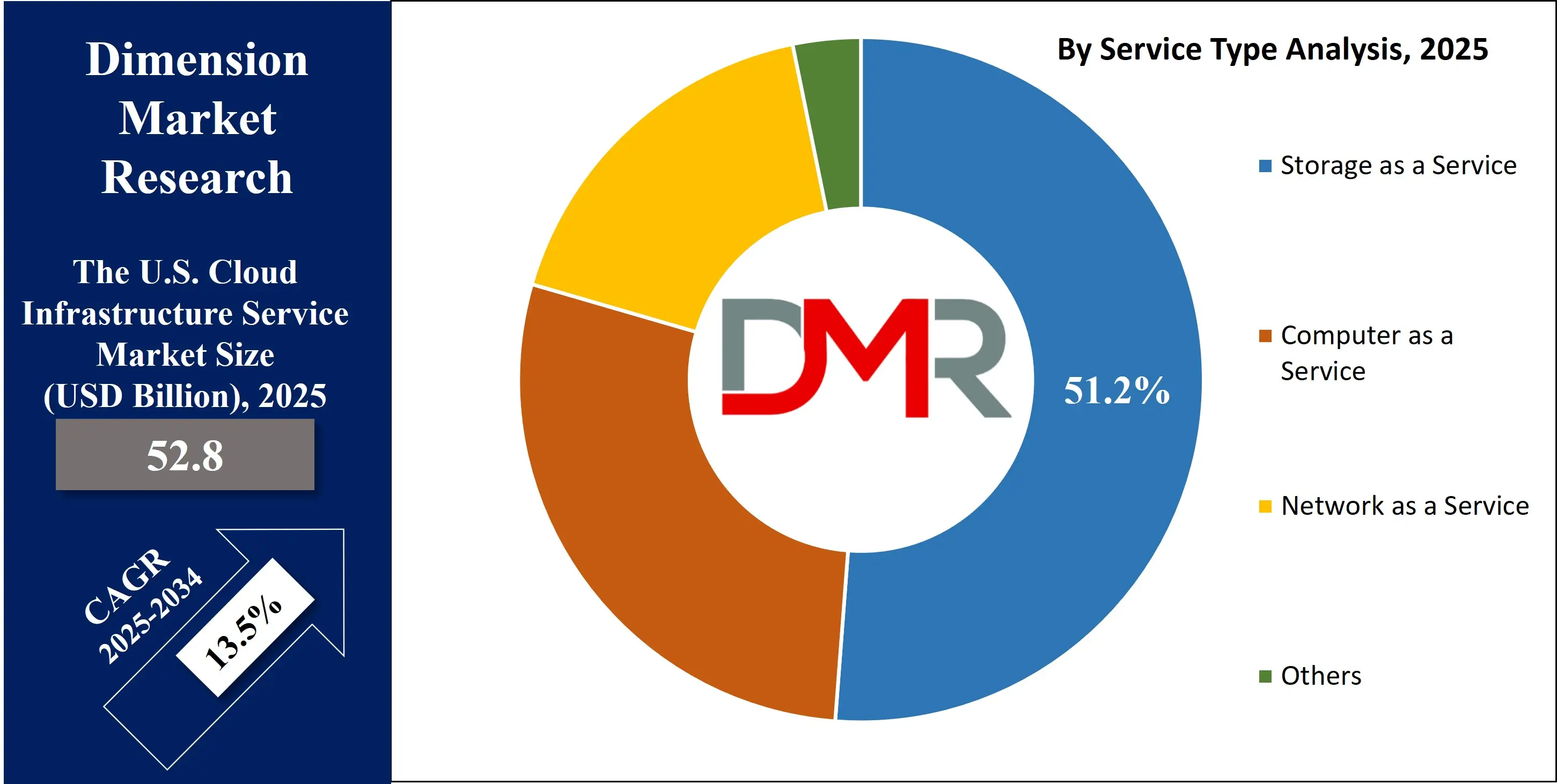
Cloud storage allows organizations to store large volumes of data securely, with the ability to access and manage it from anywhere, which is crucial in today's mobile and data-driven business environment. As data privacy concerns become more prominent, cloud providers are implementing advanced encryption and security features, which further enhance the appeal of storage as a service. The rapid growth of data across various sectors, including e-commerce, healthcare, finance, and media, is driving the demand for cloud storage solutions. With the advent of technologies like big data analytics, Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI), businesses require a robust and secure data storage infrastructure that can scale in real-time to accommodate dynamic workloads.
Another important aspect of the cloud infrastructure landscape in the U.S. is the growing prominence of Compute as a Service (CaaS). CaaS refers to the delivery of computing resources and processing power over the cloud, typically as part of Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) or Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offerings. This market is expanding rapidly as businesses seek to leverage powerful computing resources without the need for upfront hardware investments. CaaS solutions offer businesses the ability to scale compute capacity up or down based on their workload needs, enabling them to run applications more efficiently while optimizing costs. The flexibility and scalability of CaaS are particularly beneficial for industries with fluctuating workloads, such as gaming, media, and software development.
By Deployment Analysis
The public cloud deployment model is expected to maintain its dominance in the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market, with projections indicating that it will capture 63.6% of the total market share in 2025. This dominance is driven by several factors, including the public cloud's inherent scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility. Public cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, offer a wide range of services that enable businesses to rapidly scale their infrastructure without the need for significant upfront capital investments.
The public cloud allows companies to access a vast pool of computing resources on demand, meaning they can adjust their capacity based on workload fluctuations, which is particularly beneficial for industries with dynamic operational requirements. Moreover, the pay-as-you-go pricing model of public cloud services reduces the financial burden of maintaining on-premises infrastructure, making it an attractive choice for organizations of all sizes.
While the public cloud remains dominant, the private cloud model is also growing in the U.S. market as organizations seek greater control over their data and IT environments. Private cloud deployment refers to the use of cloud infrastructure dedicated solely to a single organization, either hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. This model offers several benefits, particularly for industries with stringent security, compliance, or regulatory requirements.
For example, in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government, the private cloud allows businesses to maintain full control over their data and ensure it is stored and processed by industry-specific regulations such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and FedRAMP. Unlike public cloud services, where resources are shared with other tenants, a private cloud provides enhanced security, control, and customization, as organizations can tailor their cloud environment to meet specific business and operational needs.
By Enterprise Size Analysis
Large enterprises are expected to maintain their dominance in the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market, with projections indicating that they will capture 73.5% of the total market share in 2025. This dominance can be attributed to the significant resources available to large organizations, which enable them to invest in comprehensive, enterprise-grade cloud solutions that offer a wide array of services. Large enterprises typically have complex and varied IT needs, ranging from advanced computing power and data storage to the deployment of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics.
Cloud infrastructure provides these organizations with the scalability, reliability, and flexibility necessary to meet their high demands. The adoption of cloud solutions allows large enterprises to modernize their infrastructure, support digital transformation efforts, and enhance operational efficiency by leveraging cloud-based tools that streamline collaboration, improve data accessibility, and reduce the time to market for new products and services.
On the other hand, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the U.S. market are adopting cloud infrastructure services, though they face different challenges compared to their larger counterparts. Traditionally, SMEs have been more cautious in adopting cloud solutions due to concerns over costs and complexity. However, with the availability of more flexible and affordable cloud offerings, SMEs are beginning to realize the numerous benefits of cloud adoption.
These businesses are turning to cloud infrastructure to reduce capital expenditures on IT hardware, as well as to access scalable, on-demand computing resources that allow them to compete more effectively in the marketplace. Cloud services provide SMEs with access to enterprise-grade tools and technologies, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software, analytics platforms, and collaboration tools, which were previously beyond their financial reach.
By Industry Vertical Analysis
The IT & Telecom industry is expected to maintain its dominance in the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market, with projections indicating that it will capture 46.9% of the total market share by 2025. This growth can be attributed to the critical role cloud infrastructure plays in supporting the rapidly evolving IT and telecom sectors. The IT & Telecom industry requires vast amounts of computing power, storage, and data processing capabilities to manage the huge volume of data generated by telecom networks, internet services, and IT applications. Cloud infrastructure enables organizations in this sector to offer scalable, on-demand services to customers while optimizing their internal operations.
The deployment of cloud-based services such as Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS) has revolutionized how telecom and IT providers deliver services to businesses and consumers alike. The adoption of cloud infrastructure in the IT & Telecom industry facilitates improved service delivery, enhanced network performance, and greater operational efficiency. Telecom companies, for instance, utilize cloud solutions to manage their networks, handle traffic routing, and streamline customer interactions through virtualized services and applications.
In contrast, the banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) sector is also experiencing significant growth in cloud adoption, driven by the growing need for digitalization, security, and agility in financial operations. Cloud infrastructure enables BFSI organizations to enhance their customer service offerings, manage vast amounts of financial data, and comply with stringent regulatory requirements.
The ability to store, process, and analyze large volumes of sensitive customer data in the cloud provides financial institutions with the flexibility to offer more personalized services, streamline transactions, and deploy innovative products. Additionally, cloud-based platforms allow banks to implement real-time analytics, fraud detection systems, and machine learning models to enhance decision-making and risk management.
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market Report is segmented on the basis of the following:
By Service Type
- Computer as a Service
- Storage as a Service
- Network as a Service
- Others
By Deployment
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
By Enterprise Size
- Large Enterprises
- Small And Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
By Industry Vertical
- BFSI
- IT & Telecom
- Retail
- Healthcare
- Government
- Others
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market is characterized by a dynamic and rapidly evolving environment, where both established tech giants and emerging players are vying for market share. The market is driven by the growing demand for scalable, cost-efficient, and secure cloud solutions, with businesses across various sectors seeking to modernize their IT infrastructure, enhance operational efficiency, and support digital transformation initiatives. The competition is primarily focused on offering comprehensive cloud solutions, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), with an emphasis on flexibility, reliability, security, and innovation.
The leading players in the U.S. cloud infrastructure services market include major cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and IBM Cloud. These companies have established themselves as industry leaders due to their vast global infrastructure, extensive service portfolios, and ongoing investments in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data analytics, and 5G integration.
Some of the prominent players in the U.S. cloud infrastructure services are
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Salesforce
- VMware
- Rackspace Technology
- Equinix
- Red Hat
- DigitalOcean
- ServiceNow
- Hewlett-Packard Enterprise (HPE)
- Adobe Cloud
- Cloudflare
- Nutanix
- Citrix Systems
- Verisign
- Joyent (now part of Samsung)
- CoreSite Realty Corporation
- Other Key Players
The U.S. Cloud Infrastructure Services Market: Recent Developments
- March 2025: Microsoft acquired Minit, a leader in process mining technology, to bolster its cloud capabilities, particularly around enhancing business process analytics. The acquisition will integrate Minit’s process mining into Microsoft’s Dynamics 365 and Power Platform to provide businesses with better operational visibility and efficiency in cloud environments.
- February 2025: AWS acquired the Australian e-commerce platform Selz, which specializes in empowering small businesses to create online stores and manage e-commerce operations. The acquisition will help AWS enhance its offerings for small to medium-sized businesses, expanding its reach into the e-commerce sector with integrated cloud services for online sales platforms.
- January 2025: Google Cloud acquired Mandiant, a leading cybersecurity company, to strengthen its security offerings across cloud infrastructure. This acquisition is expected to enhance Google Cloud's security capabilities, particularly in threat detection and response, and support its enterprise clients in securing their cloud environments.
- November 2024: Oracle completed its acquisition of Cerner, a major provider of healthcare IT services, to expand its cloud infrastructure solutions in the healthcare sector. Oracle plans to integrate Cerner’s healthcare systems into its Oracle Cloud platform, enhancing cloud-based electronic health records (EHR) management and cloud adoption in healthcare.
- October 2024: IBM acquired ReaQta, an artificial intelligence-based cybersecurity company, to integrate advanced threat detection into its hybrid cloud offerings. The deal strengthens IBM's position as a leading provider of cloud-based security solutions, catering to enterprises with complex hybrid environments.
- August 2024: Salesforce completed its acquisition of Slack Technologies, a collaboration software company, to enhance its cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platform. The integration of Slack enables Salesforce to provide more seamless communication and collaboration tools within its cloud infrastructure services, particularly for enterprises with remote workforces.
- June 2024: VMware acquired Carbon Black, a cloud-native endpoint protection provider, to further enhance its cloud security and virtualization capabilities. The acquisition strengthens VMware’s position in the cloud security space by integrating Carbon Black’s capabilities into VMware’s cloud infrastructure and virtualization solutions.
- April 2024: Cisco acquired Acacia Communications, a leader in high-performance optical interconnect technologies, to enhance its cloud and data center infrastructure offerings. This deal enables Cisco to offer more efficient, high-capacity networking solutions for cloud providers and enterprises transitioning to the cloud.
- March 2024: Equinix, a global data center and colocation services provider, acquired GPX Global Systems to expand its presence in the Middle East and enhance its cloud infrastructure services. This acquisition strengthens Equinix’s ability to deliver reliable, low-latency cloud infrastructure solutions across multiple regions.
- January 2024: HPE acquired Zerto, a disaster recovery and business continuity provider, to enhance its cloud-based backup and recovery solutions. The acquisition allows HPE to offer more resilient cloud infrastructure services, particularly in the areas of data protection and business continuity for hybrid cloud environments.
Report Details
| Report Characteristics |
| Market Size (2025) |
USD 52.8 Bn |
| Forecast Value (2034) |
USD 165.2 Bn |
| CAGR (2025–2034) |
13.5% |
| Historical Data |
2019 – 2024 |
| Forecast Data |
2025 – 2033 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Estimate Year |
2025 |
| Report Coverage |
Market Revenue Estimation, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, etc. |
| Segments Covered |
By Software Type (Procure-to-Pay (P2P) Software, Spend Analysis Software, E-Sourcing Software, E-Procurement Software, Supplier Management Software, Strategic Sourcing Software, Other Software Type), By Deployment Type (Cloud-Based, and On-Premises), By Organization Size (Large Enterprise, and Small and Medium Enterprise), By End-User Industry (Manufacturing, Retail & E-commerce, BFSI (Banking, Financial Services & Insurance), Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals, IT & Telecom, Government & Defense, Energy & Utilities, and Other End Users) |
| Regional Coverage |
The US |
| Prominent Players |
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Salesforce, VMware, Rackspace Technology, Equinix, Red Hat, DigitalOcean, ServiceNow, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Adobe Cloud, Cloudflare, Nutanix, Citrix Systems, Verisign, Joyent (now part of Samsung), CoreSite Realty Corporation, and Other Key Players |
| Purchase Options |
We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License (Limited to 1 user),
Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), and
Corporate Use License (Unlimited User) along with free report customization equivalent to
0 analyst working days, 3 analysts working days, and 5 analysts working days respectively.
|